Abstract
Realtech system PLC is in trouble to raise 3m for short term financing. If it wants to raise the fund form the banks it will have to pay LIBOR+2% which will be threat for liquidity position. So, the firm is thinking to use some derivatives for risk exposure. The forward rate agreement, options and futures are the major issues. The option is the way to hedge the risk exposure. It is not an obligation to buy or sell but forward contracts compel the buyer or seller to mitigate the transaction.
The LIBOR rates are a prime factor here. The firm wants to raise the fund form inter banking exchange but the rate is too high. So, the firm goes for forward contract and makes the fund available through hedging. The LIBOR rates go up on July 1. The risks of using derivatives are too high as the maintenance is more complex. On the other hand it depends on the market factors consideration. So it is required to study the past data.
Introduction
There is a need for great wisdom on the concept behind ideal credit – risk – reduction – tools for the investors domestic and world exposures in , Futures and Options, Consequently, the building interest in calculating credit default probabilities was by no means then limited to the highly industrialized countries like the United States, Europe, Thailand, Australia to name a few. However, it is now spreading all over the world at a rate that surprises even the third world countries. People have developed great enthusiasm in these tools to protect their interest in the form of investments.
Realtech System Plc. is a SME enterprise that provides technical equipment and services to the water industry. The business has been successfully growing over the last decade but has found trading difficult in the last two years due to supplying companies in a regulated industry. This has led to the business being reliant on short time borrowing at this time but the outturn as £35m. It addressed that they could not obtain as favourable terms as usual with the bank and they had to pay a rate of LIBOR +2%.
To hedge the risk exposure some derivatives can be used by the management. These are forward rate agreement, Swaps, Option, Future contracts and etc. These can reduce the risks but in sometimes have some risks to hedge. The risk of using of derivatives is given below in context with Realtech Systems PLC;
When the option is used the company may be faced with risk exposure, if there is zero value. As the firm needs short term financing, it should go for floor trading and of the stipulated price is less than anticipated the firm may incur with no loss if the stock is hold. But the requirement of short term financing is hampered. So, the liquidity position may get worse. It is same in put and call option
At the time of using forward rate agreement, if the market price of deliverable instruments is falling down below the stipulated rate, it may face with loss and the requirement of short term financing. It is same if the firm act as a seller except the price is increasing.
Brief explanation of FRAs, Futures and Options
Option
An option is a contract giving its owner the right to buy or sell and asset at a fixed price on or before a given date. This might be on any items that can be traded. Options are unique type of financial contract because they give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to do something. The buyer uses the option only if it is advantageous to do so; otherwise the option can be thrown away. The exercise price or striking price in option is used to indicate the value at which the buyer or seller is implementing the transaction at a specified price. The expiration date indicates the time of implementation.
It can be two types; American and European. An American option may be exercised anytime up to the expiration date. A European option can be exercised on the expiration date. The most common type of option is call option. A call option gives the owner the right to buy an asset at a fixed price during a particular time period. There is no restriction on the kind of asset, but the most common ones traded on exchanges are option on stocks and bonds.
If the buyer calls the option when the price is arisen above the base it is called valued than base and if the price of stock is lower than the stipulated price it is called zero valuation. So, the call option can not be negative. Here in the case of call option buyer may not loose if he wants to hold the stock when the price decline. The put option is reverse of call option. Here the seller can put or sell his stocks at a stipulated date. If the seller sees that the price is declining at the expiration date, he may be a gainer and if the price increases the seller can retain the stock and in this case it has zero valuation.
Forward rate agreement (FRA)
If any contract is made for the delivery of goods at a stipulated rate in near future, is called forward rate agreement. Under this method the buyer promised to sell his goods to a buyer at a stipulated rate when the goods arrived. The goods can be delivered at the time of arrival of goods or services. In this case the buyer or seller’s gain depends on the market value of goods at the time of arrival. If the price of goods increases the buyers are gainer and vice versa. Both the buyer and seller are obligated to implement the contract. The goods are called deliverable instrument. The act of turning the goods to the buyer is called making delivery.
Future contracts
Contracts are exchanged are called future contracts. Under this agreement seller can delivery the instrument at any date during the stipulated delivery month. This gives the seller leeway that he would not have a forward contact. Forward contracts are generally traded off an exchange. Because of this, there is generally a liquid market in future contracts. A buyer can net out of her futures position of sale. A seller can net out his futures position with purchase. The future contracts are marked to the market on a daily basis. It determined through up and low method. The open interest under future contracts is called the number of contacts outstanding.
Numerical illustration of the possible alterative strategies
To hedge for short term financing pricing if forward contracts, future contract, Swaps can be used. All of them are to be judged with interest rate. As the firm is frightened to collect the money from inter bank, it may pose for greater degree of risk as LIBIOR rate volatile. If the LIBOR rate goes down the firm will be gainer and vice versa. The historical date shows the following pattern:
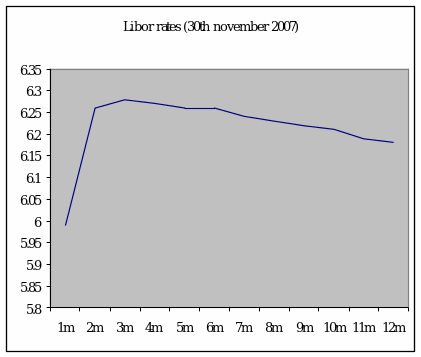
From the above pattern it is seen that after growing it too sharply, it is finally going down which may suffice for the firm. But several factors affect the rate. As credit market is in crunch, it may go up. So, the firm is in fear whether the rate will go up or down as the bank is charging additional 2 % interest rate with the existing Libor. So, the firm will have to consider several methods to propose the methods for collecting of loan.
If the firm wants to sell out commercial paper for collecting the fund of 30, 00,000, it will have to incur with the payment of fixed interest rate. On the other hand the firm can borrow from the other bank with additionally paying 2% extra premium. The cash on the loan on the loan borrowing begin exactly in six months earlier than do the cash flows on the forward contract. The loan is purchased with the cash form September 1 2007, the last coupon received occurs at the date of 40, along with the face value of $1000.The forward contract compels us to pay PFORW.CONT, the price of the forward contract.
The first coupon payment occurs on October 1. We receive a new loan at that time. The first coupon payment form the bond we receive occurs on March 1 of the following year (date2). The last coupon payment occurs at date 41, along with the face value of $1000.

Given the 40 spot rates, equation showed how to price an interest rate. The net present value analysis can show the flow pf cash flow in the long run. The equation can be contributed by:
PFORW.CONT= 40/(1+r2)+ 40/(1+r2)+ 40/(1+r2)+ 40/(1+r2)+ 40/(1+r2)+ 40/(1+r2)+ 3,0000000/(1+r2)+ 1+ri
So, the firm can hire with forward contract with 3, 0000000. Forward contract are similar to the underlying bonds themselves. If the entire team structure of interest rate unexpectedly shifts upward on October 15, the loan may become obsolete. With the use of the firm’s borrowing capacity, the firm can go for a forward contract with analyzing the historical rate of return.
Suppose the interest rate falls below 12% by October 15. The borrower can be sold at a premium under the scenario. If the insurance company buys the loan at 3.0m the buyer has the advantage of gaining unexpected profit of 5, 00000
Swaps are closed cousins to forward and futures contacts. Swaps are arrangement between two counterparties to exchange cash flows over time. There is enormous flexibility in the forms that swaps can take, but the two basic types are interest rate swaps are interest rate swaps or currency rate swaps. Often these are combined when interest received in one currency is swapped for interest on another currency. Like other derivatives, swaps are tools that firms can use to easily change their risk exposure and their balance sheet.
The firm’s reference point to for floating rate commitments is called LIBOR. Libor stands for the London inter bank offered rate and it is he rate that most international banks charge on e another for dollar-denominated loans in the London market. Libor is commonly used as the reference rate for a floating rate commitment. The rate can vary from LIBOR to LIBOR plus one point or more over LIBOR. The numerical presentation is given below:
Therefore, form the above discussion, we can conclude the following ways:
Forward contracts
The firm can stipulate a rate for borrowing 3, 0000000. The put will be given under the stipulated date. If the firm wants to borrow the amount of money, that will be paid with adjusting the borrowing rate with complying with LIBOR rates. There is likely a chance to gain as the delta is not changing over the time period.
Future contract
The firm can buy the bulk of loan and the loan supplier can provide the loan when it is available and the borrower will be taken the loan during the month at a stipulate rate. So, in this case the buyer and taker have the risk. But it is risky as the firm sees the volatility of the market.
Appraisal of tools
Though hedging may seem quite sensible to us, it should be mentioned that not everyone in business understands the hedging concept. The hedging has two risks for that it can be denied: First, we may simply be uniformed about hedging. We have found that not everyone in business understand the hedging concept. Many executives have told us that they do not want to use future markets to hedging their investors because the risks are too great.
However, we disagree. While there are large price fluctuations in these markets, hedging actually reduces the risk that an individual holding inventories bears. Secondly, we may have a special insight or some special information that commodity prices will rise. We would not lock at a price of 3.75, if we expect the cash price in October to be well above the price. The hedge of strategy 1 is called a short hedge, because we reduce the risks by selling the future contracts. The short hedge is very common in business.
The options can be used as put and call parity. The call option can be used when the stocks and bonds are purchased for short time. At the time if the firm wants to purchase 6, 00,000 and held the contract at a stipulated rate of 10, 00,000 the firm can make at least a fund of extra 4, 00000. This will helps the firm to raise the initial capital. But this tool is risky as the prices are volatile. If the price of the stock is goes down firm may incur with loss. The data of September shows the volatility. So, firm may expose to a great risk exposure.
The forward rate agreement can be purchased. The main problem will be as the prices are volatile; seller will not be inclined to negotiate with the buyers. Thigh it will be lucrative, it will be difficult to manage the firm’s risk exposure.
Recommendation
The firm can go for forward rate agreement. The firm could have attempted to acquire 3m for forward contract by means of any deliverable instruments for 3 months. The firm would have broken even. In theory this would have been a perfect hedge. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to find firms who will commit to buying or selling 3m in near future. There is no organized market for this type of transaction.
The firm could have tried to buy a future contract that would guarantee delivery of 3m in 3 months from now. But, as forward trading there is no organized market like this.
Because there no longer 3 months future contract existed, Realtech can employ a “rolling stack” strategy. That is first bought a short term, say, a three month, future contract. At the end of the year when the future contract matured, Realtech wrote another 3 months futures contract. The strategy called a series of 1 one year futures contract over the years.
The strategy can be best understood in 3 months example. At date 0 Realtech would sell equipments forward 1 year, at, say 2, 00,000, to its investors. Simultaneously, Realtech would buy a one year future contract also at 4000000. Now assuming that the spot price is, the price for immediate delivery rises to 2500000 at date 1. Also, at date 2 the price of the 1 year futures contract sells as 2, 50,000. Here Realtech would break even and date 1, would gain 50, 0000. That is its future contract issued at date 0 required it to pay 50,000 for the equipment at date 1.It could immediately sell this contract in the spot market at 2,500000.
Unfortunately there are two potential problems with this hedge. First, the entire term structure of the equipments would move together. For example if the spot price of equipment was only 1,80000 as date1 while one year future contract was quoted at 2,500000., the firm would lose 50000.. That the gain for the first contract of 50000(250000-50000) would be less than the loss 20,000 on the second market.
Evaluation of recommendation for July 1
Before July 1, the put option was started at 50 and after the date it reaches to 10%. The call option is on this stock with a one year expiration date and 50 exercise price. Investor can borrow at 10% LIBOR rate plus 2 % interest rate. The total number of stocks are 6000 are required to collect 3m for short term financing.
Before July 1, 2008, the firm had placed order for forward contract loan to take after 6 months was 4,00000. The firm stipulated the rate that if the interest rate goes over 10 % it will place the deal or the arrangement will be hold. So, the firms waited for 6 months and found it on July the interest rate rise to 10%. And Realtech places the deal. So, there is scope to raise 3m that avoid the burden of 5m/ But the deed might expose a risk as if the Libor rate was dropped. If the firm went for options, it may have to bear greater degree of risk. It will be the obligation to buy the loan at a stipulated or sell. So, the forward rate agreement was the perfect choice for short term financing.
Bibliography
Aczel, A. D., (1996), Complete Business Statistics, 3rd Ed., Irwin/ McGraw-Hill, Companies, New York, pp. 100 – 106, 549-553, and 470 – 479.
Altman, E (1968) Financial Ratio, Discriminate Analysis and the Prediction of Corporate Bankruptcy, Journal of Finance, Vol. 23, No. 4.
Brigham, E. & Houston, J. (2007), Derivatives: Concentrated on risk exposure, Thomson, 4 (P 117-156).
Crosbie, P. I. and Bohn, J. R.(2002), Modeling Default Risk, KMV LLC, Mimeo.
Fraser, L. & Ormiston, A. (2001), Derivatives, Prentice Hall of India private ltd., 5 (P 154-213).
Pandey, I. (2005), Financial management, Vikash publication house Pvt. Ltd, 23 (P 843-883).
London stock of exchange.
Sobehart, J. R., and Keenan, S. C. (2001), A Practical Review and Test of Default Prediction Model, The RMA Journal.
Sobehart, J. R. and Keenan, S. C., (2001) Understanding hybrid model of default risk, Citigroup Risk Architecture, Mimeo.
Vlieghe, G. (2001) Corporate Liquidations in the United Kingdom, Bank of England Financial Stability Review.