The current requirement is a clear indication that the library board has considered the proposed model for providing self-service to meet the demands of more young readers. The suggested attributes and procedures will support the functions of every kiosk, reduce operational costs, serve more customers, and eventually promote reading culture. This paper describes the most appropriate check-out process that will ensure that patrons have 10 or less items while those who owe 5 US dollars or more in fine do not check out materials.
Check-Out Process
The introduction and implementation of the simple check-out procedure is possible in every kiosk. The most appropriate solution is that of radio frequency identification (RFID) system or technology. This means that all books, Compact Discs (CDs), and Digital Versatile Discs (DVDs) will contain unique tags that will make them identifiable and easy to track. Such devices will contain specific antennas that can communicate with the installed RFID technology (Chelliah, Sood, and Scholfield, 1). The system will be designed in such a way that it can read Credit Cards, thereby making it possible for patrons to pay for their borrowed books.
Additionally, it will only allow individuals to borrow and be in possession of a maximum of 10 items at any given time. The system will not accept or clear any additional books or DVDs. The installed RFID technology patrons who have fines amounting to 5 US dollars or more will be unable to check-out new materials.
The presented diagram has been considered since it gives a detailed analysis of the entire process and how it will meet the demands of both library workers and patrons. This flowchart indicates that individuals will begin by getting items from the main shelves in the kiosk. They will then go to the system with three scanners for different roles. They will be connected to the primary RFID that communicates with the existing database (Yusof and Saman, 2).
The first scanner will allow patrons who have fines of less than 5 US dollars to go to the next stage. The system will be designed in such a way that patrons can pay at this point to be allowed to get new materials. The second one will ensure that those who do not have arrears can clear their items (Surname, 4). This technology will allow patrons to get not more than 10 materials from the kiosk. The final scanner is intended for those who want to pay for their books, DVDs, or CDs. However, this option can be bypassed by those who want to clear their areas when returning their items. The individuals can then leave the facility with their selected and cleared materials. A scanner installed at the exit door will alert members of staff when a patron has not cleared or stolen a given item.
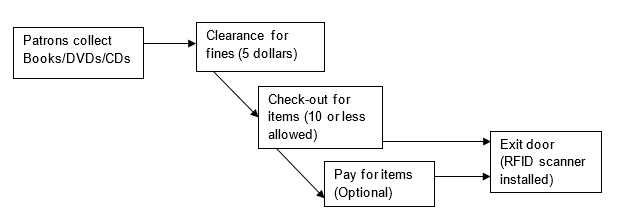
The identified attributes are simple to undertake and maximize the experiences of the targeted clients. This is the reason why it has been designed and presented for this proposal. Those involved in the acquisition and implementation of this technology will find the diagram capable of delivering positive results (Surname, 4). It can also be replicated elsewhere to deliver similar experiences to the targeted beneficiaries.
Options for Implementing the Best Software
The library’s IT department can create the best software for the kiosk or purchase and the existing off-the-shelf system to deliver the intended objectives. The first choice presents various benefits to this facility. The leading ones include the reduction in acquisition and implementation cost, effective monitoring, proper support and maintenance, and the delivery of positive results (Pal and Sharma, 3). However, the technology will present these drawbacks: ineffectiveness due to the absence of controlled standards, time consumption throughout the designing, testing, and launching stages, and the need for additional engineers and specialists to deliver positive results.
The decision to purchase an existing or off-the-shelf system will present these crucial benefits: timely implementation, low maintenance costs, continuous support from the selected vendor, step-by-step procedures for efficient use, and reduced operational expenses. However, this system is capable of resulting in various challenges or drawbacks. Firstly, it is expensive to purchase and install in all kiosks (Pal and Sharma, 3). Secondly, it might be hard to get a reliable software system that supports the intended model. Thirdly, the library will be forced to transform its operations in such a way that they are in accordance with the vendor’s specifications.
From these options, it agreeable that the kiosk needs to purchase an off-the-shelf system because e it presents numerous advantages. For instance, it can reduce the time taken to achieve positive results and minimize maintenance costs. The vendor will also be involved to solve emerging issues and improve the system continuously (Yusof and Saman, 2). The technology will be user-friendly since many vendors in the sector understand the major requirements that have the potential to improve effectiveness and the experiences of the targeted users.
Possible Issue
The introduction of the proposed technology or system will result in various ethical or cultural issues. The outstanding one is the issue of data privacy or security. As described above, the new model is expected to collect credit Card information from different users and patrons. This means that the collected data is sensitive and can become a primary target for hackers. The leakage of personal information or access by unauthorized persons will breach the established confidentiality principles (Pal and Sharma, 3). Additionally, some librarians and other employees might decide to use such data for their personal gains. These occurrences will definitely amount to an ethical dilemma.
It will be necessary for the library to implement powerful mechanisms for improving the level of data security. This will be achieved by ensuring that high-quality devices and anti-phishing software are put in place. Passwords for databases should only be accessible to a selected number of professionals (Yusof and Saman, 2). The IT department will have to monitor the effeciency and security of the established system continuously and report any malicious incident. The installation of firewalls and antivirus software will address this ethical issue and eventually improve the level of privacy.
Conclusion
The above discussion has described how the introduction of the proposed RFID technology will streamline the check-out process in various kiosks by ensuring that individuals with minimum fines are able to borrow 10 items or less. The institution can go further to acquire a functional system that is in accordance with the outlined procedures. Those in charge will have to monitor and maintain the technology continuously if positive results are to be recorded. These suggestions will, therefore, ensure that the greatest number of patrons receive high-quality and reliable services.
Sources
Chelliah John, Suresh Sood, and Sally Scholfield. 2015. Realizing the Strategic Value of RFID in Academic Libraries: A Case Study of the University of Technology Sydney. Web.
Mohd Kamir Yusof and Md Yazid Saman. 2016. The Adoption and Implementation of RFID: A Literature Survey. Web.
Nirmalendu Pal and Ajay Kumar Sharma. 2017. Implementation of RFID Technology in Library. Web.
Student Name. 2009. Chart 1. Own creation.