Executive summary
Despite their medical ability, stem cells have become the subject of controversy. For example, the Catholic Church objects to the destruction of embryos for the sake of stem cell research. On the other hand, the Islamic perspective of the research on stem cells is flexible and friendlier.
In addition, Islamic law differentiates embryos based on the position where an egg is fertilized. Consequently, the Shari’ah posits that the embryo is not a human being at the beginning of pregnancy despite its high potential of becoming one Moreover, the Islamic law states that outside of the womb, an embryo does not have the environment to become a human being; it is not a viable fetus. Therefore, it is acceptable to use embryos outside of the womb in research to find cures for diseases. A majority of the scientists opine that stem cell research will open the door for the advancement of medical therapy, for understanding human development, and providing treatment for many diseases that are difficult to treat using current therapeutic procedures.
The Scope
The purpose of this report is to define stem cells and assess the research on stem cells by analyzing and summarizing six scholarly articles. In addition, the report explains the potential of stem cells and their ability to treat human diseases. This report also shows some of the controversies surrounding the research on stem cells relative to the Catholic and Islamic Faith.
Introduction
This report is an informative analysis of Stem cells, undifferentiated and unspecialized cells that regenerate themselves and increase in size resulting in one or more specific kinds of tissue and organs, which possess specific functions in the human body (McKay, 2000). Alarfaj’s report is an analysis of stem cells and the research on stem cells in the context of their definitions, types, importance, and controversies that would give the reader a general idea of the current research on stem cells.
According to Siddiqi (2008), there are three types of human stem cells, which are classified according to where they are found in the human body and the stage of development of the donor. Therefore, the human stem cells include adult, embryonic and cord blood stem cells. Moreover, it is interesting to note that researchers have shown the potency of all these three types of stem cells in treating human diseases such as diabetes, heart disease and blood complications in the future. However, the controversies surrounding the research on stem cells particularly from the Catholic and Islamic faith threaten to disorient the efforts made by many scientists in the world in discovering new remedies for the world’s dreaded diseases.
The purpose of Alarfaj’s report is to simplify the idea of stem cells to the reader and to make it understandable. Moreover, Alarfaj’s writing is directed towards undergraduate students studying medicine who probably need to be aware of current studies that are related to the medical field.
Methodology
Alarfaj’s research consists of well-known websites, scholarly articles and journals. Some of the articles were retrieved from the OSU library catalog while others were found through internet search engines such as “Google”. Using these sources Alarfaj presents a summary and analysis of the writings, which will then be supported by critical and personal commentaries of his own. In this report, Alarfaj’s previous knowledge on the research of stem cells that were obtained from reading several articles and following health news documentaries on the research of stem cells will enhance his personal interpretation of the materials used.
Background of the study
Brief history and timeline of the discovery of stem cells
The embryonic and benign beginning of stem cell research has its history in the mid-1880s, a time when discoveries revealed that it was quite possible for cells regeneration. At the moment, a controversy appears to surround research on stem cells over the decision to utilize human embryonic stem cells for purposes of research. Following the ruling on the Roe v. Wade case by the Supreme Court in the mid-1970s, discussions were started in earnest on how best to undertake research on the fetal tissue of humans in an ethical manner.
In the years that have followed, stem cell researchers have achieved significant milestones, the most outstanding one being the ability to isolate the embryonic stem cell of humans (All About Popular Issues, 2010). The discovery of the first “real stem cells” happened in the early 1990s, after discoveries that some cells had the potential to generate blood cells.
Progressive presidents and conservatives have been seen to have played a contributing role in restraining the funding of stem cell research by the federal government, citing ethical reasons. However, President Bush assumed to take a position that not only sought to ignore ethical guidelines, but also curtailed developments in regenerative medicine. For instance, according to a 2008 report, it emerged that only 16 of the 21 viable lines that qualified for federal funding in line with the guidelines of the Bush administration were ethically derived.
Definition of stem cells
The best definition for stem cells would be what Dr. McKay defined as the “ undifferentiated and unspecialized cells that can renew themselves and also give rise to one or more specific cell types with specific functions in the human body” (McKay, 2000). Therefore, studies indicate that stem cells differentiate into hepatocytes (liver cells), cells of the brain, and blood corpuscles (red blood cells, erythrocytes, and blood platelets). Additionally, most stem cells are generated by embryonic and fetal tissues because of their high potency for regeneration, differentiation, and growth. However, some scientists argue that the body of a mature person produces small amounts of stem cells, which possess the potential of differentiating and regenerating new cells, tissues, and organs (Bongso, 2008).
Origins and Categories of stem cells
From the preceding discussions, it is notable that the origins of stem cells are the embryonic and fetal tissues. Additionally, stem cells can also be generated from the tissues of mature human beings though at low levels and they have the same level of regeneration and differentiation as those derived from the fetus and embryos (Siddiqi, 2008). As a result of research by scientists on mice, it is realized that during a specific period of time, certain cells in body have a significant ability to change into a different variety of cells (McKay, 2000).
Because of their ability to differentiate into other highly specialized cells, the experimental cells were referred to as Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs). There are three types of human stem cells (ESCs), which are named according to where they are found and the stage of development of their donor. Thus, in human beings, there are adult, embryonic and cord blood stem cells. Each of these cells can be used in stem cell research, and all these cells can treat diseases in the future (Biotechnology Australia, 2008).
In addition, ESCs in humans are usually obtained from additional embryos that are produced in fertility clinics (Franklin, 2008). Most importantly, there are two reasons that motivate scientists to investigate early human cells. First, these cells can be used to research specific aspects of development in early human beings. Second, ESCs are the variety of cells that make up the human body. Therefore, the study of ESCs provides clear understanding of human growth by researchers (McKay, 2000). However, there are still barriers in place, which hinder the study of human ESCs. However, the study of human stem cells derived from mature human beings shows that the cells in most tissues are replaced during adulthood and that there are new sources of cells in adults (Biotechnology Australia, 2008).
The importance of the research on human stem cell
According to McKay (2000), stem cells can be used in most scientific studies aimed at examining the process of human development and the diseases that affect the process, which can be reversed by the introduction of new stem cells. Therefore, stem cells have the potency of treating certain human diseases particularly most blood complications. Stems cells can also be used in most clinical drug tests. According to Siddiqi (2008), most of the experimental drug tests that are carried out to determine the efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products should be performed on stem cells instead of human patients to avert unnecessary pain, violation of human rights, and possible lawsuits. The use of stem cells in such tests will also allow the pharmaceutical companies to consider the ethical issues involved in experiments done on living human beings (Bongso, 2008).
Moreover, because of the potential of stem cells to regenerate new tissues, they can be used to produce new liver tissues in the lab. These tissues can then be used to replace the damaged ones in patients suffering from liver complications. In this way, the lives of most patients who die because they are unable to get the right organ donors will be saved in addition to averting the problem of organ shortages in most hospitals. Furthermore, stem cells are effective in the future treatment of diabetes mellitus.
This is because stem cells with the potential to differentiate and regenerate pancreatic cells, which produce insulin, can be extracted and grown in the lab. These cells can then be transferred into diabetic patients to boost the insulin-producing capacity in their bodies. Overall, stems cells can be used to treat liver complications, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and heart disease among a host others (Siddiqi, 2008).
Most importantly, the research on stem cells has enabled scientists to help individuals who lack the capacity to develop pregnancies to bear children of their own. This occurs through the process known as invitro-fertilization. Here, the ovum of a woman who cannot develop a pregnancy due to some reasons, is extracted and fertilized externally in the lab using sperm cells from a male donor. After fertilization has occurred, the fertilized egg is transferred into the womb of a surrogate mother whereby the embryo divides and differentiates to form a fetus. Inside the surrogate mother’s womb, the normal stages of pregnancy occur and finally a baby is born at the end of the gestation period (Franklin, 2008).
Limitations of the research on stem cells
Developments made on tissues from cell lines could provide toxicology testing of potential new treatments and therapeutics for several diseases. However, some limitations will need to be eliminated before this technology can be used. First, there are barriers to organ construction using human stem cells. Here, organs derived from stem cells will be grown outside the human body and will therefore need some kind of scaffolding during their development. Secondly, unintended side effects like cancer could result from ESCs therapies. Thirdly, the body could reject the newly developed cells and tissues if there is an immune reaction between the cells of the embryo being used and those of the person who will receive the new cells during treatment (Biotechnology Australia, 2008).
Discussions
US laws and policy on stem cell
Although there are no federal laws in the US to ban research on stem cells, nevertheless, there are restrictions on the issues of use and funding, as provided for by the spending powers of Congress. President George W. Bush sought to have the NIH guidelines reviewed in February 2001 (Vestal, 2008). Below is a timeline of the laws and policies on embryonic stem cells in the United States.
Timeline
In 1993, for the first time, President Bill Clinton and Congress, in line with the National Institutes of Health Revitalization Act, allowed the funding of human embryo research by the NIH. In 1995, the Dickey Amendment was passed, seeking to prohibit the use of funds approved by the federal government for application in human embryonic research. In 1999, a legal opinion was released by the Health and Human Services Department to give shape to the policy on stem cell research by the Clinton Administration.
Between 2006 and 2006, an executive order was signed by President Bush, seeking to forbid stem cell research using funds from the federal government to those cell lines that had already been derived. In November 2004, the state of California voted in favor of Proposition 71, in effect allowing for the allocation of $ 3 billion in the form of state funds for a period of more than 10 years, which is dedicated to research on human embryonic stem cell. In May 2006, bill number S.2754 was introduced into the Senate by Senator Rick Santorum. On July 18th of the same year, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act H. R. 810 was voted by the U. S. Senate in favor of the S. 2754 Act as proposed by Senator Santorium.
On July 19th, 2006, President Bush voted in favor of the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act. On November 7th, 2006, the Amendment 2 was passed by the state of Missouri, effectively enabling the application of research or therapy on stem cells in line with the federal laws, although it still forbids the cloning of humans. On February 16th, 2007, a research grant to the tune of $ 45 million was awarded to the Regenerative Institute of Medicine in California. On November 4, 2008, the passing of Proposal 08-2 by the state of Michigan meant that researchers in the state could make cultures of embryonic stem cells out of the excess embryos emanating from the fertility treatments. On January 23rd, 2009, stem cell therapy clinical trials involving human embryos were approved by the FDA. On March 9th, 2009, President Obama appended his signature to a document that sought to reverse the opposition of the federal government to embryonic research on stem cells.
General bioethics on stem cell research
Research on embryonic stem cells has generated heated debates ever since they were discovered, in comparison with other forms of stem cells. The reason behind this could be that an IVF (in vitro fertilized) egg needs to be destroyed after 5 days of its development for purposes of facilitating its inner cell mass that often contains the embryonic stem cells. To a majority of the people, this process is usually regarded as a move that at best, results in the destruction of potential life. On the other hand, we have other proponents of stem cell research who harbor the belief that at that point, life is yet to begin. On the basis of moral context of an individual, and from the religious perspective of different believers, the debate on embryonic stem cell research is an attempt to assess if the fertilized egg ought to be subjected to similar rights as those awarded to a human being?
The ethical question of patents
There is a possibility for the refusal of patents on stem cell research on ethical grounds. Even as this issue has been seen to come up infrequently in the past, nonetheless, following recent development in stem cell research on human embryos, this has effectively elicited conflicting opinions regarding the best approach to utilize in addressing the issue of patents (Sharples, 2006).
Whereas we have had countries that have been seen to embrace a positive policy as regards the issue of human embryonic stem cells inventions (case in point, the UK Patent Office), on the other hand, others are still yet to grant patent applications on the same issue. There are a number of legal questions that have thus far been proposed as regards the ethical roles involved during the process of granting patents. When and if answers to such questions are found, this will greatly facilitate attempts to resolve the row on the issuance of patents on embryonic stem cell research.
Controversies and views

Religions
Catholic view
The Catholic Church objects to the destruction of embryos for the sake of stem cell research. The Catholic Church considers embryos as full human beings. Therefore, according to Pope John II, research involving stem cells derived from embryos is equated to abortion, destruction of human life, and euthanasia (Brien, 2008). With this view in mind, scientists find it hard to convince people about the long-term importance of using embryos in research. Therefore the research on human stem cells to develop new medications and for clinical tests may be hindered by such misinformed and one-sided views. Besides, studies show that the embryonic cells are present in the amniotic fluid, which can be extracted without injuring or killing the fetus (Weissman, 2007; Monroe et al., 2008).
Islamic view
The Islamic view of stem cell research is a little flexible and friendlier than the Catholic Church’s view. According to Islamic law (Shari’ah), a man and a woman who are lawfully married but are unable to bear children of their own are given the opportunity to carry out an invitro-fertilization procedure. Here, an ovum from the woman is extracted and its fertilization is carried out outside of the human body (Jones, 2005).
However, instead of the fertilized egg being given to a surrogate mother, Islamic law demands that the egg should be returned to its original donor (Siddiqi, 2008). Moreover, Islamic law demands that the sperm cells that will be used in the process of invitro-fertilization should be donated by the woman’s lawful husband (Siddiqi, 2008). Therefore, it is evident that most of these provisions in the Islamic law contradict the objectives of stem cell research. In addition, these laws may lead to the failure of the invitro-fertilization process.
Furthermore, Islamic law discriminates between an embryo that has a chance for life and one that does not. Here, the law differentiates embryos based on the exact location where an egg is fertilized. Therefore, Islamic law has it that an embryo is not a human being at the beginning of the pregnancy despite its high chances of becoming one. In addition, Islamic law posits that outside of the womb, an embryo does not have the environment to become a human being and therefore, it is not a viable fetus. Overall, according to the Islamic law, it is acceptable to use an embryo located outside of the womb in research to find cures for diseases (Siddiqi, 2008; Czarnecki, 2009).
Politics

America and Stem cells
At the beginning of 2009, Obama revived the research project on stem cells in the United States by signing an executive order that allows the research to be federally funded after eight and a half years of the ban (Childs & Stark, 2009; Meyer, 2009). These funds enable researchers in the United States to carry out their research on ESCs to produce effective medications, vaccines, and other surgical remedies that will see the treatment of millions of people with diabetes and heart disease in the United States. Moreover, these research studies will give many people the opportunity to live a better life in the absence of the deleterious symptoms of diabetes such as blindness and nerve damages (Childs & Stark, 2009).
Other viewpoints
Scientific viewpoints
Scientists believe that stem cell research will open the door for the advancement of medical therapy, for understanding human development, and providing treatment for many diseases that are difficult to treat by current therapeutic methods (Moore, 2008). Therefore, these scientists will not stop developing the stem cells in labs even if some countries do not support their activities. Moreover, some researchers are said to leave their countries of birth and live in foreign countries where research on stem cells is funded by the government (Monroe, 2008).
Patient viewpoint
Research on stem cells is often aired by most media stations and a lot of people have strong and divergent views on the origins and the use of embryo cells in research studies. For example, patients who was asked if she could donate her spare embryos said, “if the spare embryos are definitely not going to be suitable for use during the PGD cycle, then I have no objection to them being used for scientific research as opposed to being destroyed” (Franklin, 2008, 23).
While another patient who was unsure of whether or not to donate her embryo commented, “I am not always confident that research is being done for the ‘right’ reasons rather than because it is simply advancing medical science” (Franklin, 2008, p. 23). Apart from the individualized views, religious groups also have strong feelings about the moral justification of stem cell research.
Analysis
Stem cells have become an important issue because they can form different types of cells, which create complex organs and tissues capable of saving lives. Despite the controversies and objections on the research of stem cells, the research has spread widely and countries all over the world are competing to develop these research studies to serve humanity.
Recommendation
This report could help undergraduate students in understanding the research on stem cells and some of the controversies behind it. In addition, this report serves as a starting point for additional research on the same topic, and thus, it aims to motivate students in terms of reading widely and wildly besides developing their research skills.
Conclusion
This report presents the analysis of the research articles examining the research on stem cells. Alarfaj’s writing is relevant to medical students and anyone interested in learning about the idea of stem cells and the current status of the research. Using previous knowledge obtained from following the Health news on the research of stem cells and reading several scholarly articles and journals on the same topic, Alarfaj describes stem cells and shows their benefits and the controversies behind the research. Thus, the report illustrates the importance of stem cells and how they help scientists in understanding human development and how they are capable of treating some human diseases. Overall, this report intends to clear any misunderstanding about stem cells and to simplify the idea to whoever is interested.
Summaries of resources
Childs, D. & Stark, L. (2009). Obama Reverses Course, Lifts Stem Cell Ban. ABC News/Health. Web.
This web article is from ABC news in March 2009 and it talks about the historic order that Obama signed to support stem cell research in the United States. At the beginning of Obama’s presidency, he revived the research on stem cells in the United States by signing an executive order that allows the research to be federally funded after eight years and half years of ban.
These funds enable researchers in the United States to carry out their research on ESCs to produce effective medications, vaccines, and other surgical remedies that will see the treatment of millions of people with diabetes and heart disease in the United States. Moreover, these research studies will give many people the opportunity to live a better life in the absence of the deleterious symptoms of diabetes such as blindness and nerve damages. During the Bush administration, the research was purely not funded and some researchers in America moved overseas where they could find the necessary funding and resources for their activities.
Biotechnology Australia. (2008). Support for use of embryonic stem cells remains high, but therapeutic cloning not well understood. Media Release, Public Awareness Research 2005. Web.
This article is from an Australian Biotechnology website. I found this article useful for my paper because it has clear definitions and explanations of stem cells and their usefulness. Besides, the article notes that the stem cell research in Australia is a relatively new area of science. Thus, this article contains basic information on stem cells that might help beginners in the medical field. However, additional research studies on the development and growth dynamics of stem cells are needed particularly in Australia to allow scientists to develop cures for certain killer diseases. These studies will act as a useful literature resource base for the Australian stem cell research, which is currently under the custodianship of the Australian Stem Cell Centre. The center was established in 2003 by the Australian government with the aim of providing biotechnological tools for most scientists in Australia who are involved in the study of embryonic and adult stem cells.
Siddiqi, M. (2008). An Islamic perspective on stem cells research. IslamiCity. Web.
This research article is written by Dr. Muzammil Siddiqi, a professor in the field of Genetics. The article presents the Islamic view on the research of stem cells and the provisions in Islamic law, which may interfere with the research. The research article also elaborates on the definition of stem cells and the embryo from the perspective of Islamic law. Furthermore, the research article provides a wide range of information on the origin and development of stem cells. Additionally, the author explains in detail the importance of stem cells in the human body and to better health. Therefore, this article is significant to the current research study in terms of providing the meaning of stem cells from the Islamic perspective, the importance of stem cells, and the controversies created by the Islamic law relative to the research on stem cells.
Bongso, A. (2008). Human embryonic stem cells: Science and ethics. NUS. Web.
This is a research paper written by a professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in NUS. The article presents useful information on the definition of stem cells, the sources and derivation of stem cells, the benefits of stem cells to mankind, current state of stem cells research, and the ethical issues surrounding the research on stem cells. To make the article easier to read, the author divided it into several parts. The first part provides a detailed explanation of what stem cells are and the second part talks about the appropriate use of stem cells in the production of liver cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells, and blood cells. The third part of the article provides the sources of stem cells. Lastly, the fourth part shows the current research and the developments made on the research and how various scientists are extracting stem cells from mature tissues of adult human beings and the process of differentiating them into various cell types.
Brien, N. (2008). Stem- cell Research and the Catholic Church. American Catholic Organization. Web.
This research is from the American Catholic website. It explains the position of the Catholic faith on the study of stem cells, which objects to the destruction of embryos for the sake of scientific research. The Catholic Church considers embryos to be full human beings. Besides, Pope John Paul II argues that extraction of embryos for the sake of research is equitable to murder, abortion, euthanasia, and unnecessary destruction of the human life. In addition, the article also provides a description of the origins of stem cells and the ethical issues surrounding the study of stem cells. In addition, the Catholic Church feels that some of the ethical issues concerning the research on stem cells have been ignored by most scientists and governments around the world.
The significance of this article to the current study is that it provides useful ideas on the origins of stem cells and the ethical issues that should be considered by scientists as they go about their studies on stem cells. In addition, the article presents a clear view of the controversies of the Catholic Church relative to stem cell research, which may interfere with the success of the scientific studies.
McKay, R. (2000). Stem cells-hype and hope.” Nature, 406, 361-364. Web.
This scholarly article was very useful for my paper since it contains useful materials about stem cells research. Besides, the article gives a lot of information on the sources and development of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Additionally, the author provides a clear definition of stem cells, which guided most of the definitions provided in this report. Furthermore, the author presents an elaborate discussion on Germ cells and Cancer cells in which he shows how research studies done on mice enable researchers to understand the nature of stem cells and how they develop and differentiate into different cells.
Czarnecki, S. (2009). The importance of stem cell research. Quality Health, Medical Advisory Board. Web.
This scholarly article was very resourceful to my paper because it presents useful facts about the importance of the research on stem cells and its relevance to quality health. In this article, the author starts off with discussions on the historical developments made in the research on stem cells and their impact on the medical field. Additionally, the article describes the major health complications that are treatable through the scientific technologies utilizing stem cells. Subsequently, the article presents a description of the various categories of stem cells that are in use and the ones under development. Overall, the article is significant to the current study in terms of informing and reinforcing my discussions on the importance of the research on stem cells.
Dialogica. (2007). Stem cells. Web.
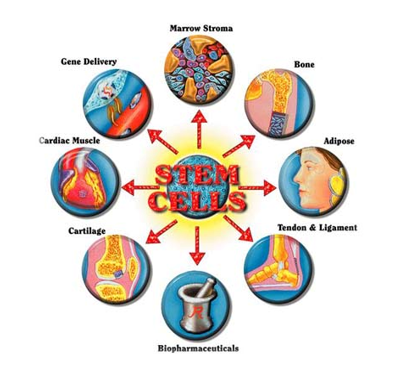
This is a scholarly site that presents useful discussions on the division, differentiation, and regeneration of stem cells. Most importantly, the site contains several pictures illustrating the different categories of stem cells and their respective sources. Subsequently, the site offers a great deal of useful data concerning the different categories and origins of stem cells. Relative to the current study, the site was significant because it is the source of the picture provided on the first page of this research paper. In addition, the site informed the discussions provided in this paper on the different types and sources of stem cells.
Franklin, S. (2008). Human fertilization and embryology authority. Web.
This article reviews the process of human fertilization and the laws that govern the use of embryonic stem cells in different countries. In this article, the author describes the process of fertilization, the division of the ovum, the development of the embryo, and the differentiation of the embryonic stem cells. Furthermore, the different stages in the development of the embryo are provided relative to different stages where scientists can extract stem cells without disturbing the normal process of embryonic development. Thus, the article was useful to the current research study because of its resourceful data on the stem cell research and the fundamental authorities influencing the research activities in different countries.
Meyer, B. (2009). Obama’s lifting of stem cell ban will benefit local National Center for Regenerative Medicine. Health news, Los Angeles Times. Web.
This article was retrieved from the Los Angeles Times, Health news and it talks about President Obama’s move to lift the ban on the research of stem cells in the United States. In addition, the article discusses the importance of stem cell research in the United States relative to the critics’ views on the whole process. Subsequently, the author highlights the beneficiaries of the President’s move such as the National Center for Regenerative Medicine (NCRM). In this case, the author argues that the NCRM will benefit in terms of receiving the funds necessary for developing new remedies for several human diseases and complications affecting millions of Americans and the world population. Thus, this article was useful to this paper in terms of providing the information used in the discussions on the importance of the research on stem cells in the United States.
Sharples, C. D. (2006). Ethical questions to ponder in the European stem cell patent debate. J Biolaw Bus, 9(3): 12-16.
This particular journal, published in Pub Med, examines how the issuance of patents on stem cell research could be denied to those undertaking this form of research in Europe. The article further argues that in the past, this kind of issue only occurred very infrequently. However, following the recent developments that have occurred in the field of stem cell research on human embryonic cells, this has acted to elicit the emergence of conflicting opinions in Europe regarding the kind of approach that ought to be embraced in as far as the issue of patents is concerned.
Monroe, K., Miller, R., & Tobis, J. (2008). Fundamentals of the stem cell debate. Berkeley: University of California Press. Web.
“Fundamentals of the stem cell debate” is an article that reviews the different controversies surrounding the research on stem cells in different parts of the world relative to the Christian and the Islamic faiths. In this article, the author discusses the scientific, the Christian, the Islamic, and the Patients’ views on the research of stem cells. Subsequently, the author takes a stand on the issue of stem cell research based on the information gathered from the opponents and proponents of the research on stem cells. Therefore, the article was important to the current research paper because it informs the discussions on the controversies surrounding the research of stem cells.
Moore, H. (2008). Embryonic stem cell therapy ‘best route’. University of Sheffield: Center for Stem Cell Biology. Web.
This article was retrieved from the Center for Stem Cell Biology at the University of Sheffield. In this article, the author describes the medical procedures utilizing stem cells to treat different human complications such as the Embryonic Stem Cell Therapy. Subsequently, the article describes the importance of using these therapies to treat diseases that are perceived to have no immediate cure. Therefore, the article is significant to the current research paper because it supports the discussions provided on the importance of the research on stem cells and the future applications of therapies utilizing stem cells to treat emerging human complications.
Weissman, I. (2007). The Politics and Promise of Stem Cell Research. Lecture, Standford Medical School. Web.
This is a scholarly article that presents useful information on the political controversies surrounding the research on stem cells and the importance of the research in eliminating some of the human complications affecting millions of people in the world. In this article, the author describes the political views that are hindering the progress of the research on stem cells relative to the scientific views on the whole research process. Additionally, the article offers a great deal of information on the human complications, which can be treated using stem cell technology and the future uses of the same therapy in eliminating some of the current human complications. Thus, this article was useful in providing ideas on the importance of stem cell research provided in the current research paper.
Young, W. (2007). Stem cell controversy: The science of growing parts. Tonya Winchester. Web.
While discussing the controversies surrounding the research on stem cells, the author presents several arguments given by politicians, church leaders, Islamic leaders, and physicians concerning the research on stem cells. According to the author, the views of different people interviewed have a bearing in the future direction of the research on stem cells and thus, it is important to consider and address them to allow for the smooth development of the research process. On the other hand, the author identifies other arguments that do not hold any significant impact on the progress of the research on stem cells. Thus, this research article was important in terms of informing the discussions and illustrations provided in this paper concerning the controversies surrounding the research on stem cells.
Reference List
All About Popular Issues. (2010). What is the history of stem cell research? Web.
Biotechnology Australia. (2008). Support for use of embryonic stem cells remains high, but therapeutic cloning not well understood. Media Release, Public Awareness Research 2005. Web.
Bongso, A. (2008). Human embryonic stem cells: Science and ethics. NUS. Web.
Brien, N. (2008). Stem- cell Research and the Catholic Church. American Catholic Organization. Web.
Childs, D. & Stark, L. (2009). Obama reverses course, lifts stem cell ban. ABC News/Health. Web.
Czarnecki, S. (2009). The importance of stem cell research. Quality Health, Medical Advisory Board. Web.
Dialogica. (2007). Stem cells. Web.
Franklin, S. (2008). Human fertilization and embryology authority. Web.
Franklin, S. (2008). Human fertilization and embryology authority. Web.
McKay, R. (2000). Stem cells-hype and hope.” Nature, 406, 361-364. Web.
Meyer, B. (2009). Obama’s lifting of stem cell ban will benefit local National Center for Regenerative Medicine. Health news, Los Angeles Times. Web.
Monroe, K., Miller, R., & Tobis, J. (2008). Fundamentals of the stem cell debate. Berkeley: University of California Press. Web.
Moore, H. (2008). Embryonic stem cell therapy ‘best route’. University of Sheffield: Center for Stem Cell Biology. Web.
Sharples, C. D. (2006). Ethical questions to ponder in the European stem cell patent debate. J Biolaw Bus, 9(3): 12-16.
Siddiqi, M. (2008). An Islamic perspective on stem cells research. IslamiCity. Web.
Weissman, I. (2007). The Politics and Promise of Stem Cell Research. Lecture, Standford Medical School. Web.
Young, W. (2007). Stem cell controversy: The science of growing parts. Tonya Winchester. Web.