Introduction
Owing to the various aspects associated with professional identity formation, the nursing profession must comprehend how nursing students construct a professional identity and connect with universities and institutions that offer nursing education. Education has been deemed essential for nursing students to develop their professional identities. Creating a professional identity is inextricably linked to a socialisation process in which a person feels and recognises a sense of belonging. Exposure and awareness to academics and practising nurses must establish a blend of knowledge and real-world experiences while creating a professional identity.
Definition of Key Terms
- Professional Identity – Professional identity refers to a person’s social, educational, and professional values; it is widely considered to define a professional and set one field apart from another (Maginnis, 2018).
- Nursing Professional Identity – Nursing professional identity refers to the unique characteristics and qualities that define a nurse’s sense of being a member of the nursing profession. This identity is shaped by a combination of personal and professional experiences, values, beliefs, attitudes, and the knowledge and skills gained through nursing education and practice (Clements et al., 2016).
Outline
The paper will essential has five main parts. These will include the background to this issue of professional identity, followed by the search strategy for the paper. The next section of the paper will examine the appraisal of evidence sources. The potential implications for the research on this issue will then be assessed based on its relevance to nurses, with a conclusion providing a summary of the paper and future directions for nurses and their professional identity.
Background
Nursing and midwifery education delivery and quality assurance have been contentious in the United Kingdom. In the last 30 years, pre-licensure healthcare education has seen significant changes (O’Connor et al., 2021). Clinical placement and undergraduate students have been the topic of study, and the results underline the importance of providing undergraduates with real-world exposure and quality placements (Vabo et al., 2022). There is a link between the quantity, quality, and overall experience of these clinical rotations and the extent to which nursing students come to love and enjoy the job. Given the widespread problems in attracting and keeping nurses, it is crucial to understand what traits might increase the retention of competent professionals and students. Even though there is a clear association between work commitment, professional identity, and retention, there is a shortage of research on the views of first-year student nurses as they develop their professional identities. This research attempts to analyse the experiences that first-year nursing students through as they create their professional identities.
Search Strategy
The literature review question is: How does the first-year university experience impact the development of nursing students’ professional identity, core competencies, and clinical classroom perceptions? Relevant information was meticulously extracted from education, healthcare, psychology, and medical databases. These databases were PsycINFO, Embase, Medline, EBSCO, and ERIC. Just Google was employed as a search engine. These databases were selected due to their wealth of medical and health journal articles. Characteristics of the study included the English language and literature from 2017 to 2023. There were both single and multiple phrases used to search for articles. Consider as inclusion criterion time, keywords, language, availability, content, scientific fields, and accessibility. Among the search keywords utilised were nurses, nursing students, the nursing profession, professional identity, undergraduate nursing programmes, journey, professional socialisation, identity, and combinations of these categories.
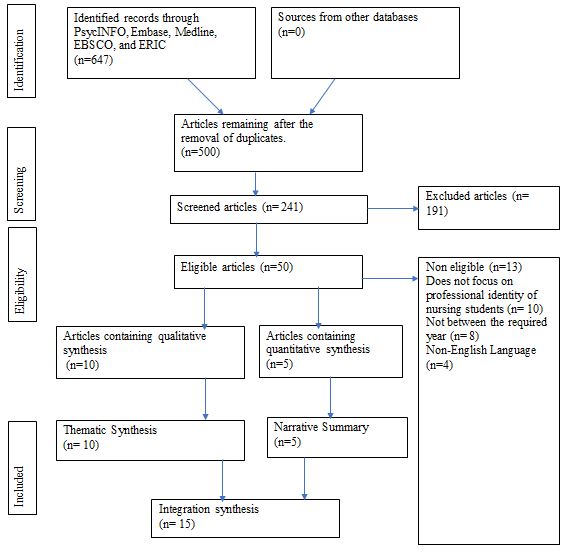
Appraisal of the Sources of Evidence
To illustrate the distinctions between the methodological methods, the included studies were evaluated using the research critic framework. Three articles were deemed to be of excellent quality, while twelve were considered to be of medium quality.
Potential Implications
The research study provides valuable insight for beginning students. It is essential to emphasize advanced learning techniques, including group discussions, clinical simulation, case studies, and professional ideals like professionalism and activism. A person’s work life is a continuous learning experience in which they acquire new values. In contrast, students might undergo a significant socialization process crucial to developing nursing professional values throughout school. The formative years of a nurse’s education are vital to developing professional ideals.
Conclusion
The paper has examined professional identity as a piece of a person’s more significant identity. Similarly, the study has identified a lack of reflection on the perspectives of first-year student nurses as they create their professional identities. However, a strong correlation exists between job dedication, professional identity, and retention. The study therefore aimed at analysing the experiences that nursing students go through in developing their professional identity as freshmen. A nursing professional identity develops as a result of a student’s active participation in social situations with nursing professionals and the student’s subsequent application of the profession’s culture, values, knowledge, and skills.
Reference List
Green, G. (2020) ‘Examining professional values among nursing students during education: A comparative study’, Nursing Forum, 55(4), pp. 589–594. Web.
Green, J.L. (2018) ‘Peer support systems and professional identity of student nurses undertaking a UK learning disability nursing programme’, Nurse Education in Practice, 30, pp. 56–61. Web.
Maginnis, C. (2018) ‘A discussion of professional identity development in nursing students’, Journal of Perspectives in Applied Academic Practice, 6(1), pp. 91–97. Web.
O’Connor, S. et al. (2021) ‘Co-production in Nursing and Midwifery Education: A systematic review of the literature’, Nurse Education Today, 102, p. 104900. Web.
Thomas, L., Hovdhaugen, E. and Sweetman, R. (2023) ‘Professional or student identity and commitment? Comparing the experiences of nursing students with literature on Student Success’, Tertiary Education, and Management [Preprint]. Web.
Vabo, G., Slettebø, Å. and Fossum, M. (2021) ‘Nursing students’ professional identity development: An integrative review’, Nordic Journal of Nursing Research, 42(2), pp. 62–75. Web.