Introduction
Subway is a fast food franchise that has quickly conquered the world in the last 56 years. The goal set by Subway in every market it comes to is to become a leader in terms of the number of establishments and the preferences of local consumers. The concept of Subway restaurant chain is a franchise with local entrepreneurs who have received specific training in the franchise business management program. Thus, the company contributes to the development of the regional economies of many countries, because investments in real business allow entrepreneurs to securely place their income in their regions. Dominko (2021, pp. 1) even states that “Subway is America’s largest fast-food chain by the number of locations,”. Subway franchise is not exclusive – a separate franchise agreement is concluded for each restaurant, so a new franchisee can open a restaurant even in the city where Subway restaurants are already open. Entrepreneurs are provided with information support based on more than fifty years of experience which gives them the ability to advertise their restaurant in all countries according to a single advertising and marketing plan.
However, such a strategy has proven to be challenging for franchisees throughout the years. The company exists on the franchise fees and royalties, and it has the legal right to set the rules by which the franchisees are expected to operate their shops. Recently, the company released a new version of their franchise contract agreement that many franchisees had called “draconian”. New contract provides Subway with the rights to control operation hours, places on the franchisees the requirement to participate in all promotions, and bans any and all negative feedback on the company. This contract lasts now 20 years, and if the franchisees do not want to accept it, they will be required to increase their royalty payments from 8% to 10% percent. In 2020, Subway closed 1882 of its stores, and the franchise opening cost has grown to $207,050 – $476,900, states Luna (2021). These changes are related to the current state of Subway business – after Fred DeLuca, the company’s confounder and CEO of 50 years, died in 2015, the business has experienced significant management troubles.
The situation has angered the franchisees, as they are forced to operate their businesses now by much stricter rules. Ji and Yoon (2021) also suggest that organisational competitiveness comes from the utilization of strategic human resources nowadays, which the company seems to operate poorly. This poses a significant problem to Subway both in USA and other countries, as well, especially in regard to the company’s steady decline in shop count and profits in the last 5 years.
Active SWOT Analysis
Environmental analysis serves as a tool for entrepreneurs to monitor external and internal factors of a business in order to anticipate potential threats and new opportunities. Specifically, analysis of the external environment allows an organization to timely predict the emergence of threats and opportunities, and develop situational plans in case of unforeseen circumstances. Simultaneously, the internal analysis helps the managing lead create a strategy that will allow the company to achieve goals and turn potential threats into profitable opportunities.
SWOT analysis remains one of the most effective tools in strategic management. The essence of the SWOT analysis is to assess the internal and external factors of the company, and evaluate the risks and competitiveness of the product in the industry. Gürel (2017, p. 994) claims that “while external analysis focuses on the environmental threats and opportunities facing an organization, internal analysis helps an organization identify its organizational strengths and weaknesses”. However, one needs to prioritize the most important analysis factors, giving them more focus in order to avoid the data dispersion. To determine the degree of dynamism of the external environment of the company, it is necessary to consider how it affects the activities of the Subway company.
The external environment can influence the company by both direct methods and indirect ones. The direct impact environment includes several factors such as suppliers, customers and competitors. In turn, the environment of indirect impact includes the general state of the economy, scientific and technological progress, socio-cultural changes and the political situation in the country. Despite the fact that there are several large players in the fast food market, the chances of new companies emerging are quite high. This risk is justified by several indicators. First of all, the barriers to entry into the industry are practically absent for new Subway restaurants, as the franchise strategy has lower requirements for opening a store. Also, the term of the initial investment is still not too high, as, for example, it costs up to 2 million dollars to open a McDonalds store (Olita 2020). Moreover, due to the openness of this service sector and Subway’s overwhelming influence, there is full accessibility to various distribution channels for new franchisees.
Subway’s Strengths
While facing an undeniable decline in the last several years, Subway still has a set of significant advantages that allow the business to stay among the leaders in the fast food market. Fist important strength of Subway is the franchising structure of its business, which provides a sustainable protection from such expenses as operational costs, and production- and labor-related risks. Moreover, this strategy also allowed Subway to quickly achieve a global level of operations: according to official Subway website (2021), there are 21,000 franchisees with 43,600 stores of Subway worldwide. In 2017, Subway was ranked by Forbes as 92nd in the World’s Most Valuable Brands rating (Forbes 2021). This provides a steady and stable base for future development. The wide assortment of products offered by Subway is another advantage of the business, as it allows the franchise to operate simultaneously in different markets. Moreover, Subway branches tend to be significantly smaller than similar fast food chain branches and require significantly fewer staff and equipment. This makes them profitable in small towns or other places where opening of a McDonald’s store does not pay off.
Lastly, Subway uses an advanced marketing strategy, maintaining a steady presence on every advertising channel: social media, TV, podcasts, and even radio. Horst and Murschetz (2019, p. 1) highlight that the convergence of strategy and entrepreneurship adds to organizational success through developing visions and facilitating strategic planning. An analytical approach is used to ensure the relevance and efficiency of every marketing move, and the company uses the whole variety of modern advertising tools to reach its customers.
Subway’s Weaknesses
The main current weakness of Subway is that its continuous expansion in the last 50 years led the business to an unpleasant situation. Due to the historically low initial investment costs – for example, $139,550 to $342,400 last year (Luna 2021) – the overwhelming amount of the shops have caused a collapse in sales. Many stores were too close to each other, generating a too strong competition inside the company. The sales continued to decline in the period from 2015 to 2021. Olito (2020, pp. 35) adds that “in 2019, Subway’s sales dropped $210 million from the previous year to $10.2 billion, and the company closed another 1,000 stores.” This was one of the outcomes of DeLuca’s death which prompted significant changes in the managing lead, many of which were unsuccessful in the end.
The recent changes in the contract rules also prompted many of the company’s franchisees to sell their stores by a low price, as well as raised heated discussions in the media. Many of franchisees have spoken up about the situation, and discouraged other potential store owners from taking up Subway’s offer. Taylor and Luna (June 10, 2021, pp. 22) state that “franchisees could have to pay three years’ worth of royalties and advertising fees if they leave the system prematurely”. Some sources speculate that the new contract is an attempt to make Subway a more appealing buying target. The rumors claim that the current owners of the business, Elizabeth DeLuca and Peter Buck, want to sell the company due to its inner structure continuously crumbling after Fred DeLuca’s death. A constant stream of scandals and complaints associated with Subways proves to have an overall negative effect on the business.
Subway’s Opportunities
Subway’s current opportunities remain ambiguous in nature. Recently, the company has performed a brand refreshing Eat Fresh Refresh campaign to boost the sales. According to Subway’s press release (2021, p. 1), “the top-performing quartile, representing over 5,000 restaurants, experienced a 33% increase in sales and the top three combined quartiles, about 16,000 restaurants, averaged an increase of nearly 14%”. Thus, it is safe to say that the company still has potential for further market expansion: for example, with more vegan options and overall portfolio expansion. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemics has showed the population’s need worldwide for food delivery, therefore, another opportunity lies in establishing of a steady delivery service.
Subway’s Threats
The innovations of Suzanne Greco, who became the CEO of Subway after the death of her brother Fred DeLuca, did not provide much in terms of company’s development. In 56 years of its existence, the company’s menu almost never changed, and many consumers became tired of the same food over the time. The constant closing of shops and decline in sales Subway experiences nowadays are a result of many factors, the main of which were the business’ aggressive expansion and Fred DeLuca’s authoritarian method of leading the company. Today, the main competitors of Subway USA are McDonalds, KFC, and Domino’s Pizza, each of which have proven to respond better to the changing needs of population. For example, McDonalds has more than 13,000 drive-thru restaurants against Subway’s only 600 (Olita 2020). Kentucky’s Fried Chicken (KFC) has also began to introduce more healthy food choices, offering the customers vegan alternatives.
It can be concluded that the company needs a new strong strategy for further development, as it is clear that today’s Subway way of operating franchise does not reflect the real market situation. Currently, Subway lacks significant advantages that would make its products more desirable to customers than the competitors’. Moreover, company’s flawed politics in regard to treating their franchisees also does not work in Subway’s favor.
Active Strategy
An active change strategy is now necessary for Subway. According to Taylor and Luna (April 10, 2021, pp. 7), “corporate employees and Subway franchisees state that a lack of long-term vision has persisted, and that Chidsey’s – Subway’s current CEO hired in 2019 – clearest priority is cutting costs”. The changes should begin within the company – new products and offers should be introduced, seeing as the recent brand refreshing campaign was fairly successful. Well-designed marketing communication strategy established within the company could gently introduce the renewed menu that would provide a competitive advantage to the company. According to Williams et at. (2018, p. 43), “the true benefit for a firm appears to lie not in any one particular action but in a conglomeration of strategic thinking approaches”. Additionally, the regulations related to the franchise operation should be reassessed; currently, they harm the franchisees and repel new potential store owners.
Financial Performance
Although currently, Subway is rightfully considered one of the largest quick-service networks across the US, the revenue of the company remains not as beneficial. Hence, over the years 2015-2019, the company’s sales have decreased by nearly $1 billion (Figure 1). As of now, the company has claimed a $10 billion annual revenue rate, demonstrating a steady drop. The company posts no public data online as far as financial performance is concerned, so it is impossible to create a real-life comparison of the revenue before and after the pandemic.
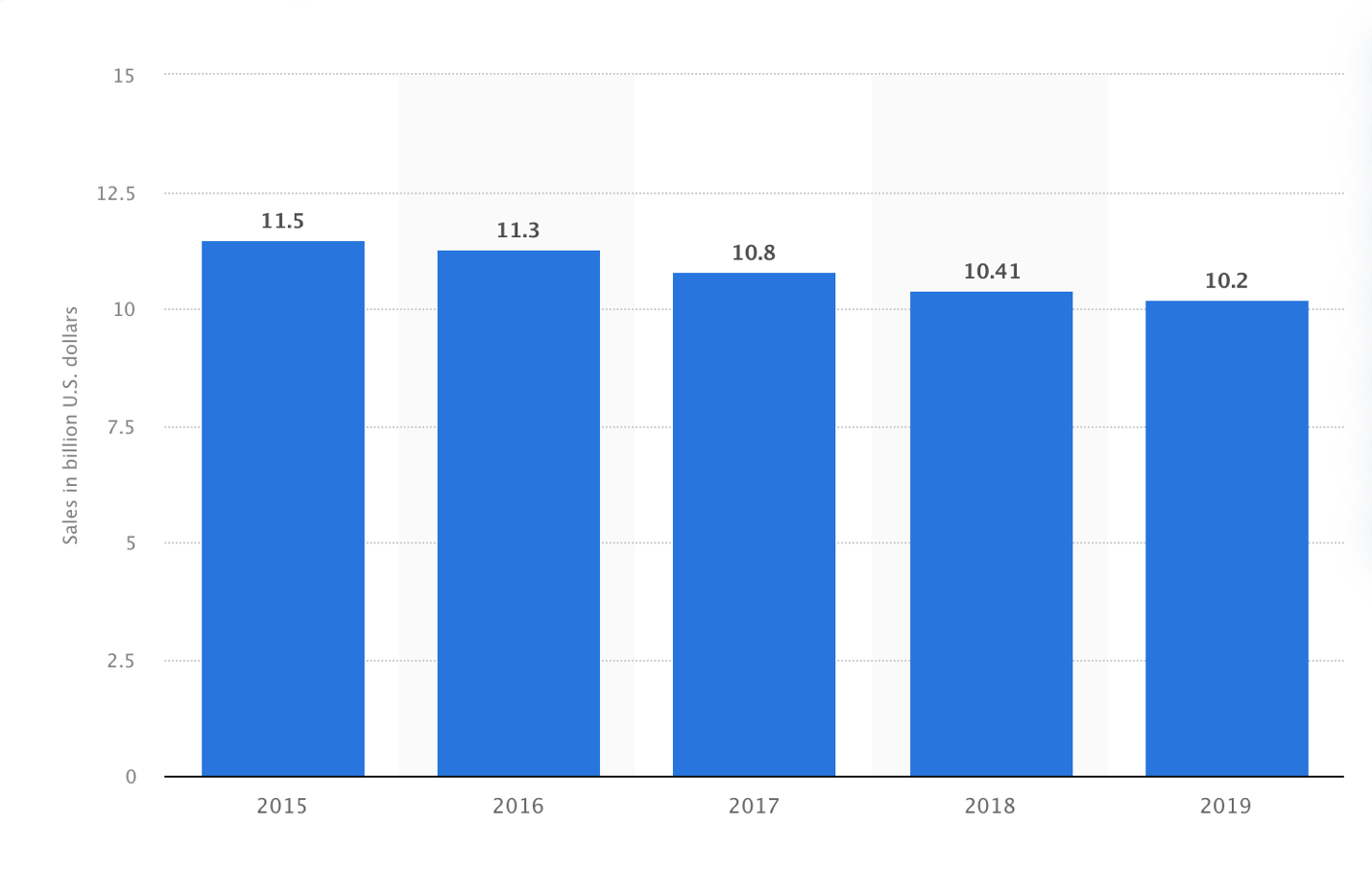
As far as the competition is concerned, the Restaurant Business’s Top 500 quick-service restaurants list placed Subway in the sixth position. The major marketing competitors in the field include McDonald’s, Starbucks, Taco Bell, Wendy’s, Chick-Fil-A, and Burger King. While the latter companies generate very close sales outcomes over the year, varying between $10-11 billion, Starbucks’s 2019 US sales were allegedly twice as high, whereas McDonald’s sales constituted nearly $40 billion, with $98 billion of global sales (Top 500, 2020):
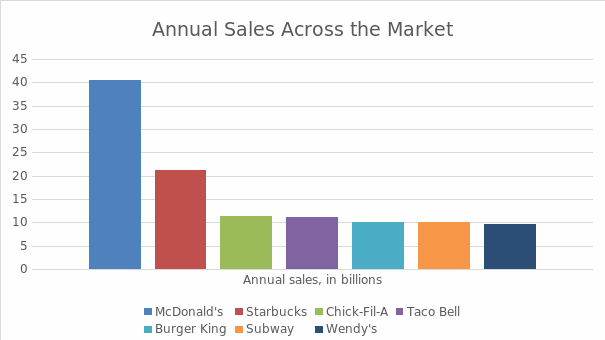
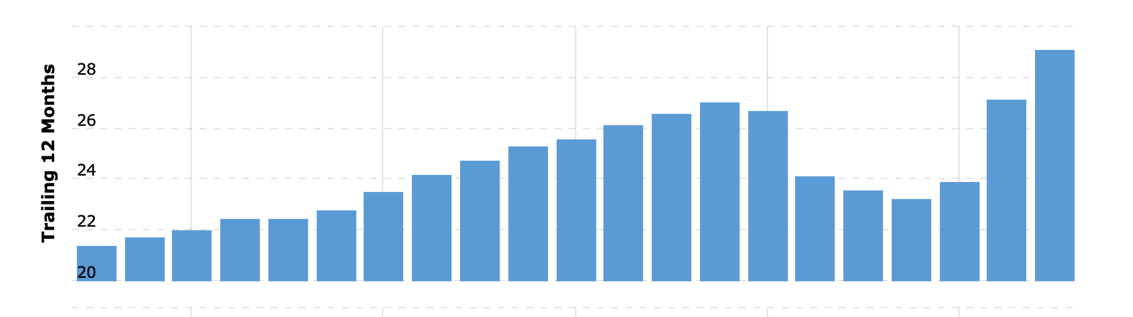
One of the potential reasons for such a tendency is Subway’s chosen strategy of cost leadership in the segment. For example, when taking Starbucks, the price range for the products presented is relatively higher compared to the market. However, with the product differentiation and marketing tactics, the revenue of the network has increased significantly over the past two years, constituting nearly $29 billion in revenue:
For this reason, it can be rightfully assumed that the competition on the market, financially speaking, is alarming for Subway, as there is a demand for rapid reconsideration of the company’s revenue and marketing strategies. The issue is especially relevant in the context of the ongoing pandemic, as fast-food chains tend to lose money on delivery commissions paid to online food delivery services like Uber Eats and Door Dash. According to the average rates, Subway tends to pay from 15% to 30% of delivery commission per each order placed on the delivery app. Such an obstacle is only one of the few obstacles in terms of entering the quick-service market. Other market entry challenges include:
- Procurement challenges. Cost efficiency is key in quick-service industry, and small services tend to have lower probability of cost-efficient raw goods procurement, creating a challenge of gaining revenue and establishing competitive prices;
- Location. The proximity of the fast-food chain is one of the most evident competitive advantages of such companies as McDonald’s, Subway, and Starbucks. The new entrants’ inability to afford locations with good customer passability creates an obstacle in sales and cheaper marketing;
- Product differentiation. The decades of quick-services’ existence transformed the industry into a full-scale restaurant industry with various options and customer preferences. For this reason, the creation of a product competitive to an established brands is highly challenging and cost-demanding.
Despite these obstacles, the market of quick-service remains overwhelmed with new entrants, as opening a small business is relatively easy and convenient tax-wise. However, small restaurants are of no direct competition to large companies like Subway, and the major competition is tracked between large enterprises. One of the most evident economic features of a product in a fast-food industry is high price elasticity. Fundamentally, price elasticity of demand (PED) is a measurement that shows how a slight change in pricing may change customer behavior and consumption of a product. For example, the price of a standard Subway breakfast comprised of bacon, eggs, and cheese is nearly $4. A very similar McDonald’s menu position costs nearly $3.5, given that the portion is much smaller. However, once Subway’s price increases by even 15%, the customer’s retention rate may be affected. The average customer of a fast-food chain is price sensitive yet not highly loyal. For this reason, having chosen the strategy of cost leadership in the market, Subway enforces the price elasticity for the segment, as they make it their distinct feature in the food industry.
Up to date, Subway has not been subject to the competition investigations. McDonald’s, one of its primary rivals in the market, however, has a series of competition investigation inquiries worldwide on the matter of breaching antitrust laws (Chee, 2021). Fundamentally, antitrust laws are created to promote competition in the market and prevent the markets from monopolization. Subway has been exploiting competition rather than seeking illegal ways to infringe the industry. It remains rather challenging that Subway has no explicit data on annual revenue and long-term financial performance. However, based on the revenue and sales data over the past five years, it becomes evident that Subway has a negative revenue tendency followed by competition, pandemic context, and lack of marketing incentives. In order to change the pattern, the company needs to closely examine its opportunities.
Subway’s Perspectives
Currently, Subway still has a strong position on the market, maintaining its place among the leaders of the fast food industry. Olita (2020) states that in 2020, Subway had total of more than 22,000 restaurants, which is a significant number for a franchise that has been experiencing serious losses. However, this leadership is majorly based on the achievements and strategies from the past. The most important element of strategic management and planning in the company is the analysis of the external environment, as well as the monitoring of the industry market. Wandhwani et al. (2020) claim that historical assumptions play one of the crucial roles in entrepreneurship research. Currently, the US market is experiencing a steady uprise, and the number of competitors grows exponentially. Kolmar’s (2021) insights add that, with almost 200,000 fast food restaurants and the expected 2021-2027 CAGR rise of 5,1% in America, there is a lot of competition, both local and international, for Subway. Thus, to increase the brand’s influence and anchor Subway’s position on the market, steering the company away from further decline and sales loss, a new strategy should be implemented.
Fast food belongs to a few types of activity, the volumes of which are little subject to changes in the context of economic downturns. To increase its market share, as well as increase the flow of customers, Subway should take steps to develop a strong promotion campaign, similar to Eat Fresh Refresh. It is necessary to stand out against the plethora of competitors, thus, the company needs to create new offers which would attract the customers. The advertising should focus on the strengths of the company and develop them intensively in order to ensure a stable financial and material position of the restaurant. Within the framework of modern marketing, the relationship between the fast food restaurant and the client is changing. Earlier, restaurants and cafes offered customers a standard set of services. Now they are forced to constantly develop new types of products that are addressed to specific groups of customers – mainly to certain categories of individuals.
As Subway already has a strong market presence, it would be wise to employ the market infiltration strategy – setting a deliberately low price range for new products and analyzing the first reactions of the customers. As an example, Subway could offer an Indian vegan wrap and set the price for it lower that for existing vegan offers. The market infiltration strategy fits Subway’s business the best, because it generates market acceptance and ensures the required level of trial purchases. In perspective, the market infiltration also maximizes sales in the short term and achieves a high market share, which then would gently lead to increase in prices. A sustainable competitive advantage lies in the fact that Subway offers its customers more individualized fast food, more attuned to their needs and tastes. The competing fast food chains such as McDonald’s do not provide such specific services, and their business models are not fit for this approach. This ensures that Subway’s new offers will not be copied by competitors in long-term perspective.
Conclusion
After 56 years of successful development, Subway’s concept and brand have a strong position in the fast food business. The company positions itself as a chain of restaurants promoting a healthy lifestyle and offering an alternative to traditional fast food. Subway’s concept promotes healthy, low-calorie nutrition based on fresh vegetables, quality meat products and freshly baked breads. Target audience perceives Subway as a fast-food chain where they can order a more individualized and healthy meal, as opposed to a more or less similar offers from McDonald’s, Burger King, and Wendy’s. Subway is a strong brand that has maintained its leading position on the fast food market for decades. However, nowadays, the business experiences significant losses due to ineffective managing strategies and marketing failures. It can be concluded that Subway needs to adjust its marketing strategy to the current trends in food industry, and reevaluate its regulation choices. Changes should be made in the product offers that would provide the business with the much needed competitive advantages it currently lacks.
Reference List
Bruhn, M. & Schnebelen, S. (2017) ‘Integrated marketing communication – from an instrumental to a customer-centric perspective’, European Journal of Marketing, 51(3), pp. 464–489.
Chee, F. Y. (2021) McDonald’s faces Italian antitrust probe into franchise terms – document. Web.
Dominko, M. (2021) America’s largest fast-food chain is on a downward spiral, reports say. Eat This Not That. Web.
Forbes (2021) Subway. Forbes. Web.
Gürel, E. (2017) ‘SWOT analysis: a theoretical review’, Journal of International Social Research, 10(51), pp. 994–1006.
Hole, Y., Pawar, S. & Bhaskar, M.P. (2018) ‘Service marketing and quality strategies’, Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences (PEN), 6(1), p. 182.
Horst, S.-O. & Murschetz, P.C. (2019) ‘Strategic media entrepreneurship’, Journal of Media Management and Entrepreneurship, 1(1), pp.1–26.
Jankoff, C. (2021) Leading innovation and change. The Risk Doctor. Web.
Ji, Y. & Yoon, H.J. (2021) ‘The effect of servant leadership on self-efficacy and innovative behavior: verification of the moderated mediating effect of vocational calling’, Administrative Sciences, 11(2), p.39.
Kanten, I.K. & Darma, G.S. (2017) ‘Consumer behavior, marketing strategy, customer satisfaction, and business performance’, Jurnal Manajemen Bisnis, 14(2), pp.143–165.
Katsikeas, C., Leonidou, L. & Zeriti, A. (2019) ‘Revisiting international marketing strategy in a digital era’, International Marketing Review, 37(3), pp.405–424.
Kolmar, C. (2022) 19 US fast food industry statistics [2022]: revenue, trends, and predictions. Zippia. Web.
Luna, N. (2021) Subway’s ‘dirt-cheap’ startup costs for franchisees just increased by thousands even as the company’s unit count declined by 1,600. Business Insider. Web.
Olito, F. (2020) The rise and fall of Subway, the world’s largest fast-food chain. Business Insider. Web.
Pitta, D.A. (2010) ‘Product strategy in harsh economic times: Subway’, Journal of Product & Brand Management, 19(2), pp.131–134.
Sales of Subway restaurants in the United States from 2015 to 2019 (2022) Statista. Web.
Soegoto, E.S. & Utomo, A.T. (2019) ‘Marketing strategy through social media’, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 662, p.032040.
Sorescu, A. (2017) ‘Data-driven business model innovation’, Journal of Product Innovation Management, 34(5), pp.691–696.
Starbucks revenue 2006-2021 (n.d.) Web.
Subway Sales Department (2021) Subway® restaurants’ historic brand refresh results in positive sales momentum. Subway. Web.
Subway (2021) Frequently asked questions. Subway. Web.
Taylor, K. & Luna, N. (2021) Subway franchisees say a new contract forces them to sign away their ability to criticize the struggling chain. Business Insider. Web.
Taylor, K. (2021) Rumors are flying that subway is up for sale as the distressed sandwich chain lays off hundreds to cut costs and abandons franchisees. Business Insider. Web.
Top 500 (2020) Web.
Wadhwani, R.D. et al. (2020) ‘Context, time, and change: historical approaches to entrepreneurship research’ Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 14(1), pp.3–19.
Williams, R.I. et al. (2018) ‘The relationship between a comprehensive strategic approach and small business performance’ Journal of Small Business Strategy. Web.