Introduction
The UK-based Tesco is a grocery and general merchandise multinational retailer organization with its headquarters located in Hertfordshire, England. Besides being the 15th most valuable retail brand globally, Tesco is also among the most valuable brands in the UK. Additionally, Tesco is the leading grocery retailer in the United Kingdom with a consistent share of over 25% of the market share and grouped as one of the big four supermarkets together with Morrisons, Asda, and Sainsbury’s. The company was originally founded by Jack Cohen in 1919 and has recently diversified in retail sections and geographically (TESCO, 2022). It sells a wide variety of products, including beauty products, consumer electronics, home-ware, groceries, among other products.
Tesco has a hierarchical organizational structure considering the huge size of the business scope. Its structure is constructed with five committees, including Audit, Corporate responsibility, Nominations, Disclosure, and Remuneration committees answerable to Tesco PLC Board. In store level, the company contains up to four management layers in some large stores in. The four layers comprise the Regional manager in the first level, store manager in the second, personnel, food trading, and non-food trading managers in the third level. Moreover, the fourth layer includes the electrical section, clothing section, personnel assistant, ambient food, and fresh food section managers (Tesco, 2021). Group Chief Executive Dave Lewis leads eleven members of the Tesco Executive committee. The company’s Board of directors comprises ten members, and significant changes within the board were made in the financial year 2014/2015. The change made included the appointment of Allan Stewart as the new Chief Financial Officer, Dave Lewis as the CEO, John Allan as the Board Chairman, the appointment of 3 new Non-Executive Directors, and the retirement of 4 Non-Executive Directors
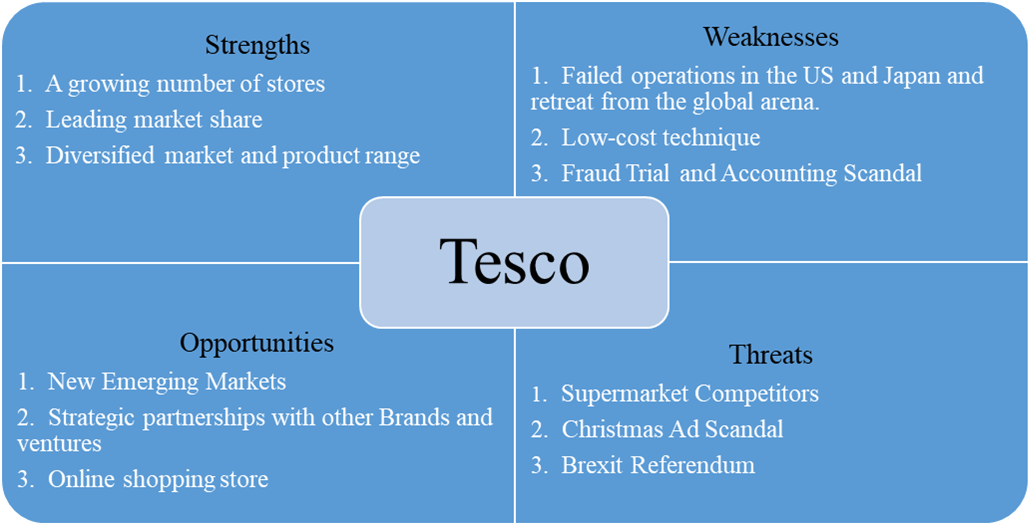
The SWOT was produced by identifying the factors that enabled the company to gain a competitive advantage in the market. Furthermore, there are challenges that the organization is facing, and it is struggling to solve them. Together with the market’s volatility, these factors help in the creation of the SWOT. The strengths were identified by determining what factors contributed to its competitive advantage the resources and assets it contains. The weaknesses were identified by determining where the company can improve and what factors hinder its growth in the market share. Threats were identified by considering what the company’s rivals are doing well, their market share, and the regulations that can threaten their business. On opportunities, they were identified by determining how the company can expand its operations, the demographics the company is not focusing on, and how it can explore new market segments. The data concerning the SWOT analysis was collected from statistical sites such as Statista, journals, the company’s website, and their annual reports and other websites.
Strengths
A Growing Number of Stores
This is an important strength to Tesco Company because it now operates 6966 retail grocery stores globally from 3751 stores in 2008. As a result, the addition of stores all over the world has led to continued increase and growth in its revenue every year. In 2020, the company had made sales worth 53.4 billion pounds and won the Grocer award of the year 2020 at Grocer Gold Awards. Their operating stores in 2021 amounted to 4,673, with franchise stores included worldwide (Bedford, 2022). Of the total seven thousand stores worldwide, approximately four thousand are located in the United Kingdom.
The company provides six different store formats to clients with diverse sizes and product ranges. For instance, Tesco superstores are standard giant supermarkets that trade primarily in food products and a much smaller variety of non-food products compared to Extra stores. Additionally, most of its annual revenue was generated from its primary market, the United Kingdom (Aiello, Quercia, Schifanella and Del, 2020). The company contains over four thousand stores in the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom alone.
Leading Market Share
Tesco dominates or leads the Grocery retail market of the United Kingdom among the big four supermarkets with a market share of twenty-seven percent. Recently, Tesco has become the most popular supermarket in Ireland. As of January 2022, Tesco had a 27.9% market share of total grocers in the United Kingdom compared to its competitors such as Sainsbury’s with a 15.6% market share, Asda with a 14.4% Morrisons with a 9.9% market share, thereby holding the largest market share. Having a leading market share enables the company to record increased company economic sales (Bedford, 2022).
Diversified Market and Product Range
This strength is essential to the company as its diversification strategy has proven to be very successful for the organization. On product range, the organization trades in home-ware items, mobile phones business, school uniforms, music downloads, and DVD rentals, clothing range, fair cotton trading, electronics, health, car and dental insurance, and financial and telecom services. Due to its geographical diversification, retailing and related activities have become possible outside the United Kingdom, including Japan (Aiello, Quercia, Schifanella and Del, 2020). It also operates in the United States of America, Poland, China, Malaysia, India, The Czech Republic, South Korea, Turkey, Thailand, South Korea, Slovakia, Republic of Ireland, and Hungary. Currently, the organization is one of the world’s largest retailers, with 6,800 plus locations across Asia and Europe (Kar, Bansal and Mishra, 2021). Most of the company’s growth comes from acquisitions, as Tesco started acquiring other organizations in the 1950s (Bedford, 2022). As of June 8, 2020, Tesco has a market capitalization of 28.4 billion dollars, and its total revenue reached 81.8 billion dollars for the 2019 fiscal year.
Weaknesses
Failed Operations in the US and Japan and Retreat from the Global Arena
The failed export operations of the company forced it to shut down stores in the United States after five years and in Japan after nine years. Tesco opened its first Fresh & Easy stores in November 2007 in California. However, the shopping experience at Fresh & Easy for Americans was different from what they were accustomed to. These stores were small stores made for people who needed to shop every day, such as Brits who lived in big cities but a regular American consumer desired to buy their groceries in bulk, or vast amounts that could last or take them two to three weeks every time they shopped. According to the Americans, there were many self-service check-outs and TV dinner options (Zeller, 2017). The business could have performed better because most Fresh & Easy markets were open mainly in the western United States, particularly in states that were struck by terrible unemployment during the recession, such as Nevada, California, and Arizona.
The retailer also invested approximately 250 million pounds in Japan under the name Tsurakame since July 2003 but did not succeed. The Japan project only had a market share of one percent of the Japanese grocery share market. The company reported that Japanese customer demands were challenging to meet and that Japan was challenging to trade in because of its high costs (Son, Baek, Park and Kim, 2018). Tesco had to move out of Japanese and American markets due to their failed operations in the two countries in 2012. This is because the company could not carry out its plans effectively offshore and export operations. It ended up selling its operations in Poland, Malaysia, Hungary, China, Thailand, Slovakia, and China in 2020 due to poor planning (Zeller, 2017). While the global or the international business is expected to contribute more to the company’s income, the organizations continue to be heavily dependent on the United Kingdom market.
Low-Cost Technique
A low-cost technique is an approach in which a company sells its products and services at a very low price but satisfies its customers in the process. Tesco tried to employ this strategy, but it cost the organization due to low profit (Rosnizam et al., 2020). This strategy can cause a decrease in the organization’s profit margins as much as it is the price leader in the United Kingdom.
Fraud Trial and Accounting Scandal
The company has been involved in various legal battles with organizations such as Weatherford and Varco for trespassing on some of their patents. As a result, the company’s legal fees for tackling the violation charges have increased, and any statements or news that can be proven true can adversely impact the organization and its reputation. Tesco was found guilty and charged with fines in 2017 due to misrepresentation of profits and false accounting declarations to avoid paying taxes (Rosnizam et al., 2020). The company can also impact its finance if it receives more fines due to increasing lawsuits.
Opportunities
New Emerging Markets
As much as the organization has expanded its business operations in fourteen countries, there are some enraging markets such as Turkey and Indonesia that Tesco can expand their business to. Expanding their businesses in emerging markets can be a profitable opportunity or chance for the organization (Rosnizam et al., 2020). This is because growth in the market would lead to a dilution of rival’s advantages enabling the company to improve and expand its competitiveness compared to its rivals (Zeller, 2017). Also, Tesco has been provided with the ability to reach a newly developing market because of a government free trade agreement and the introduction of new technology standards.
Strategic Partnerships with Other Brands and Ventures
Tesco has been making alliances with other brands in search of growth to put forward better services and products to facilitate clients better. Developing these strategic alliances with reputable organizations can provide a perfect chance or opportunity for the company. It will give the company the ability to provide more products and attract more clients or customers. Additionally, in the regions where Tesco is not excelling, there is a good chance and opportunity for joint ventures (Rosnizam et al., 2020). The local organizations can offer profound market information or knowledge which can aid in enhancing performance in such regions. There are a few stores in Tesco Company that are underperforming in certain countries. If it makes alliances with the local businesses and obtains information about the local market, its performance can increase significantly.
Online Shopping Store
Tesco has adopted current technologies like Scan & Shop application and radio-frequency identification technology, which is an online mobile payments system known as PayQwiq also the self-checkout system. These technologies have enabled the company to increase their offerings on the client’s satisfaction shopping experience that is convenient and faster check-out (Rosnizam et al., 2020). Tesco dominates the United Kingdom’s online grocery shopping. They contain a mobile app for online customers, which will continue to attract more shoppers to the company. The organization can continue to utilize this opportunity by upgrading and growing its home delivery services and online shopping business (Khan, 2020). The company can utilize Artificial Intelligence to observe an act and environment to deliver better customer services.
Threats
Supermarket Competitors
In the United Kingdom, the grocery market is very competitive, and Tesco’s Competitors can pose a threat to the organization. Tesco has been on top of the United Kingdom grocery market but is now facing competition from other organizations. Giant supermarkets such as Aldi, Carrefour, and Walmart are among the rivals of the Tesco organizations and continue to grow and develop (Guo and Wang, 2019). Additionally, Tesco’s market position is threatened with the rise in performance and growth of Aldi, Carrefour, and Walmart. It is challenging for Tesco to win a price war with Aldi and Lidl. These two rivals are also commonly known as discounters, making it difficult for Tesco to compete with them on price matters. These two company’s pricing policies also have a significant effect on the organization’s profits.
Christmas Ad Scandal
Tesco group launched a Christmas ad in 2017, which is supposed to be funny. However, the Christmas ad ended up offending many people instead. Individuals reported that it was a direct attack and disrespectful towards the Christian faith. Commercials and television ads should be free of criticism of every demographic (Khan, 2020). As a result, the company faced social media backlash where individuals boycotted the store due to their opinion on the disrespectful act of Tesco against the Christian faith.
Brexit Referendum
The current pursuit of the United Kingdom on a no-deal Brexit could lead to the suspension of the European Union’s free trade agreement. As a result, the United Kingdom will be forced to trade with the European Union in line with World Trade Organization regulations. Implementing new rules can lead to increased custom inspections, tariffs, and quotas. Also, Brexit could have a huge impact on imported food sold in supermarkets (“Tesco”, 2022). The unsuccessful movement of imported goods to the United Kingdom from the European Union negatively impacts the Supply chain of Tesco Company due to Brexit executing restrictions at the entry ports.
Recommendations
There are areas that Tesco can improve to ensure that they overcome the situations it is facing and continue its business growth. The following are critical recommendations that can help the company improve and grow.
Before Entering a New Market, Tesco Should Conduct In-Depth Market Analysis and Market Research to Prevent Losses and Failure
This can be best illustrated by the company’s failed operation in Japan and the United States. In Japan’s case, the company did not consider the cultural differences between Japan and the United Kingdom. Additionally, the company did not acquire sufficient information concerning the structure of the Japanese market, the purchase behaviors of clients, and their respective preferences. Much of this information includes that Japanese customers prefer high-quality products and outstanding service in their shopping experience. As much as Japanese clients or customers love to purchase items from the United States of America and Europe, they also require that they obtain the products in an appealing way associated with the Japanese mindset.
Moreover, Japan contains many long-established and family-owned grocery stores that make a focal point for the community appreciated for the personal touch they provide. Therefore, the organization’s failure in the Japanese and USA markets was primarily because the company did not identify core business forces such as significant social changes, cultural differences, and economic conditions and trends. As a result, Tesco can follow the learned trends to meet the client’s demands. It also needs to have the ability to describe the industry and its viewpoint, including the marketing practices.
Upgrade its e-commerce and online business sites to offer a satisfying shopping experience for customers
Tesco can also implement a different effective marketing strategy to improve its marketing strategies such as earned media, co-branding and affinity marketing, internet marketing and viral marketing, and social networks. With the implementation of an effective marketing strategy, the company will be able to potential new customers.
The Company Should Also Keep Up With the Latest Technology
Technology has become among the important things in modern life society. Keeping up with the latest technology gives the company the ability to improve the customer shopping experience. In business operations, technology plays a vital role in business operations as its change impacts the methods, work cultures, and systems. The newest technology utilization can boost business operations, and the company has a role to always follow the latest technology since it continues to change and improve over time. Various retailers are thinking of cashier-less stores, and technology can aid the organization in growing its retail presence to ensure the company can decrease its dependence on online shopping at a faster rate and a lower cost compared to building its stores. Customers need to take products off shelves, scan their phones and proceed to walk out and receive a receipt for the products they purchased. By implementing the system, Tesco will be able to compete comfortably with other retail giants, including Walmart and Amazon.
Take Customer Feedback on Launching of New Ads and Schemes
Tesco should always take into account the client’s feedback when they decide to launch new ads on advertising the company. Based on the customers ‘ responses, this will help guide the company on where it should improve and what it should continue to maintain. If they receive negative responses, they should try to adjust the contents of their ads to ensure that the customers are satisfied with the contents of the ads. This, in turn, will help avoid disapproval from the public as this will lead to decreased sales leading to a drop in profits.
Tesco Evaluation
Tesco is one of the top four retail supermarkets in the United Kingdom. It dominates the Grocery retail market with a 27.9% market share as of January 2020. The company has also diversified its market range due to the continuous increase in its number of stores worldwide. However, its environment is surrounded by other big competitors, including Morrisons, Asda, and Sainsbury’s. There are also uncertainties involved that might affect its business, such as the emergence of new competitors, changes in market price, and changes in tastes and preferences of the customers within the market. It has been able to diversify its product range and increased the number of market stores worldwide. They also have a technical advantage that helps them market their products globally. It also did not succeed in implementing the low-cost technique. In addition, it also encountered failed operations in the United States of America and Japan, forcing it to retreat from the two countries. The company was also faced with fraud trials and an accounting scandal.
Future Strategies for the Organization
TESCO (UK Company) requires a new strategy that could aid in attracting more potential customers and potential investments because of the challenges associated with the strenuous political and economic situation in the UK. It can implement pricing strategies, product differentiation, corner a young market, improve customer service, grow sales from new products, and have a technological advantage. TESCO should consider utilizing the pricing strategy to ensure its performance improves to attract more customers and increase its revenue in the long term. To ensure the success of the pricing strategy is attained, the company should focus on a cost leadership strategy. A cost leadership strategy is an approach that is primarily implemented to increase the profit margin of an organization by producing standard and high-quality products and selling them at a lower price compared to its competitors. This is an excellent strategy because a company will increase revenue when the popularity of a product increases because of its low pricing.
Cost Leadership Strategy
Cost leadership strategy can be used by emphasizing efficiency at each level of the value chain, including production, sales, manufacturing, and customer service. It can be used to obtain a competitive advantage in two ways (Wada, 2018). One of which is having the same pricing as the competitors but benefiting from the advantage of cost leadership, leading to maximized profits. These profits could be helpful in the future or help in maintaining market share (Islami, Mustafa and Topuzovska, 2020). The second way is by permanently or temporarily lowering the price of products to grow the market share.
Using a cost leadership strategy comes with its strengths, one of which is it can lead to an increased market share of the organization. This is because items with an acceptable value but sold at a lower price are more likely to be considered for purchase first. This strategy also improves the sustainability of the company (Kharub, Mor and Sharma, 2019). This is because fewer financial threats could potentially put the company out of business when the prices or costs are lower for the organization. Sustainability becomes a significant advantage when economic circumstances worsen (Eric, 2017). For instance, there is a decline in the economy when a trade or price war happens.
Another strength is that it creates more revenue that can be utilized for growth. Cost leadership strategies enhance the availability of more capital resources. The higher margins allow the company to retain capital from each transaction, although the retail cost of products or services is low (Upadhyay and Adhikari, 2020). This creates an accumulation of resources over time that can be utilized for various purposes. Lastly, a cost leadership strategy also provides better profits for the organization since it is mainly focused on creating low-cost operations within the market (Bryksina, Golovina and Legotin, 2018). It becomes possible to attain higher profit margins by reducing production and development costs. In addition, a company can gain more profits when competitive pricing is available with higher margins compared to what other organizations achieve.
In addition to strengths, cost leadership strategy also has a negative side. One of the weaknesses is that it can be a risky approach as competitors are likely to imitate the method immediately after the organization determines it. Another weakness is that organizations that utilize this strategy rely on a high sales volume to ensure that the company continues to maximize profits (Lauer, 2019). Additionally, it is challenging to maintain quality perceptions when the marketing strategy of a company depends on offering low-cost products (Anwar and Shah, 2020). As a result, companies will need to find a means of offering low-price products while sustaining a positive image and enhancing brand loyalty. It is also difficult to adapt to market changes when using cost production to market its products. This is because customer preferences are always changing and shifting, making it difficult for the organization to use its advanced technology to reduce production costs.
Cost leadership strategy can be adapted and strengthened by developing an advanced technology that helps decrease operating costs and increase efficiency, allowing the company to increase production while lowering prices. It can also be adapted by gaining a source for raw materials. A company can potentially decrease the overall production cost and increase value to their products by gaining control over the source of raw materials. Another way to achieve a cost leadership strategy is by creating economies of scale (Suleman, Rashidirad and Suleman, 2019). This can be done by increasing mass production leading to a low production cost for each item. A company can also increase its purchasing power where more money is given to the suppliers to obtain unique deals that become beneficial (Ali and Anwar, 2021). Lastly, the company can increase its operating efficiency by completing more tasks at a lesser cost and period.
Reference List
Aiello, L., Quercia, D., Schifanella, R. and Del, L., 2020. Tesco Grocery 1.0, a large-scale dataset of grocery purchases in London. Scientific Data, 7(1), pp.1-11.
Ali, B. and Anwar, G., 2021. Porter’s generic competitive strategies and its influence on the Competitive Advantage. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, Management and Science, 7(6), pp.42-51.
Anwar, M. and Shah, S., 2020. Entrepreneurial orientation and generic competitive strategies for emerging SMEs: Financial and nonfinancial performance perspective. Journal of Public Affairs, 21(1), pp.1-17.
Bedford, E., 2022. Topic: Tesco PLC. Statista. Web.
Bryksina, N., Golovina, A. and Legotin, F., 2018. Implementation of cost leadership strategy by Russian medical companies of laboratory diagnostics. Leadership for the Future Sustainable Development of Business and Education, pp.189-198.
craft.co. 2022. TESCO. Web.
Eric, B., 2017. Generic strategies and strategy dynamics. Comprehensive Strategic Management, pp.127-159.
Guo, L. and Wang, Z., 2019. Ratio analysis of J Sainsbury plc financial performance between 2015 and 2018 in comparison with Tesco and Morrisons. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 09(02), pp.325-341.
Islami, X., Mustafa, N. and Topuzovska, M., 2020. Linking Porter’s generic strategies to firm performance. Future Business Journal, 6(1), pp.1-15.
Kar, S., Bansal, R. and Mishra, S., 2021. Tesco: Entry and expansion strategy in India. Emerging Economies Cases Journal, 3(2), pp.65-76.
Khan, M., 2020. A Case Study on Tesco Customers’ Satisfaction and Loyalty. Web.
Kharub, M., Mor, R. and Sharma, R., 2019. The relationship between cost leadership competitive strategy and firm performance. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 30(6), pp.920-936.
Lauer, T., 2019. Generic strategies, outpacing and Blue Ocean – discussing the validity of three strategic management theories using case studies from airlines and grocery retail. Theory, Methodology, Practice, 2019(1), pp.57-66.
Rosnizam, M., Kee, D., Akhir, M., Shahqira, M., Yusoff, M., Budiman, R. and Alajmi, A., 2020. Market opportunities and challenges: A Case Study of Tesco. Journal of The Community Development in Asia, 3(2), pp.18-27.
Son, J., Baek, J., Park, H. and Kim, C., 2018. The localized merchandising for international retailers: a study of Tesco’s failure in Japan. THE RITSUMEIKAN BUSINESS REVIEW, 56(5), pp.259-276.
Suleman, M., Rashidirad, M. and Suleman, S., 2019. The applicability of Porter’s generic strategies in pure online firms: A case study approach. Strategic Change, 28(3), pp.167-176.
TESCO, 2021. Annual Report and Financial Statements 2021. pp.12-220. Web.
Upadhyay, J. and Adhikari, P., 2020. Generic competitive strategies on organizational performance in Nepalese Commercial Banks. Pravaha, 25(1), pp.87-94.
Wada, T., 2018. Capability-based cost leadership strategy of Japanese firms. Annals of Business Administrative Science, 17(1), pp.1-10.
Zeller, D., 2017. The Retail Industry: Expanding in the Global Market. Web.