The Sun coast remediation dataset was used in this study to perform ANOVA and t-tests hypothesis testing to evaluate whether there is a statistical difference between groups. Excel tool pack was used as a statistical software to perform data analysis.
Independent Data t-Test
An Independent t-test is a parametric test used to test if there is a mean difference between independent groups. This study involves two independent variables: group A prior training scores (IV1) and group B revised training scores (IV2) (Khatun, 2021). The aim of performing an independent t-test on IV1 and IV2 is to evaluate if there is a significant difference between the two groups.
Hypothesis
H0 (null hypothesis): There is no statistically significant difference in the mean value of the dependent variables between the IV1 and IV2 groups.
H1 (alternative hypothesis): There is a statistically significant difference in the mean value of the dependent variables between the IV1 and IV2 groups.
Table 1: Independent t-Test Results
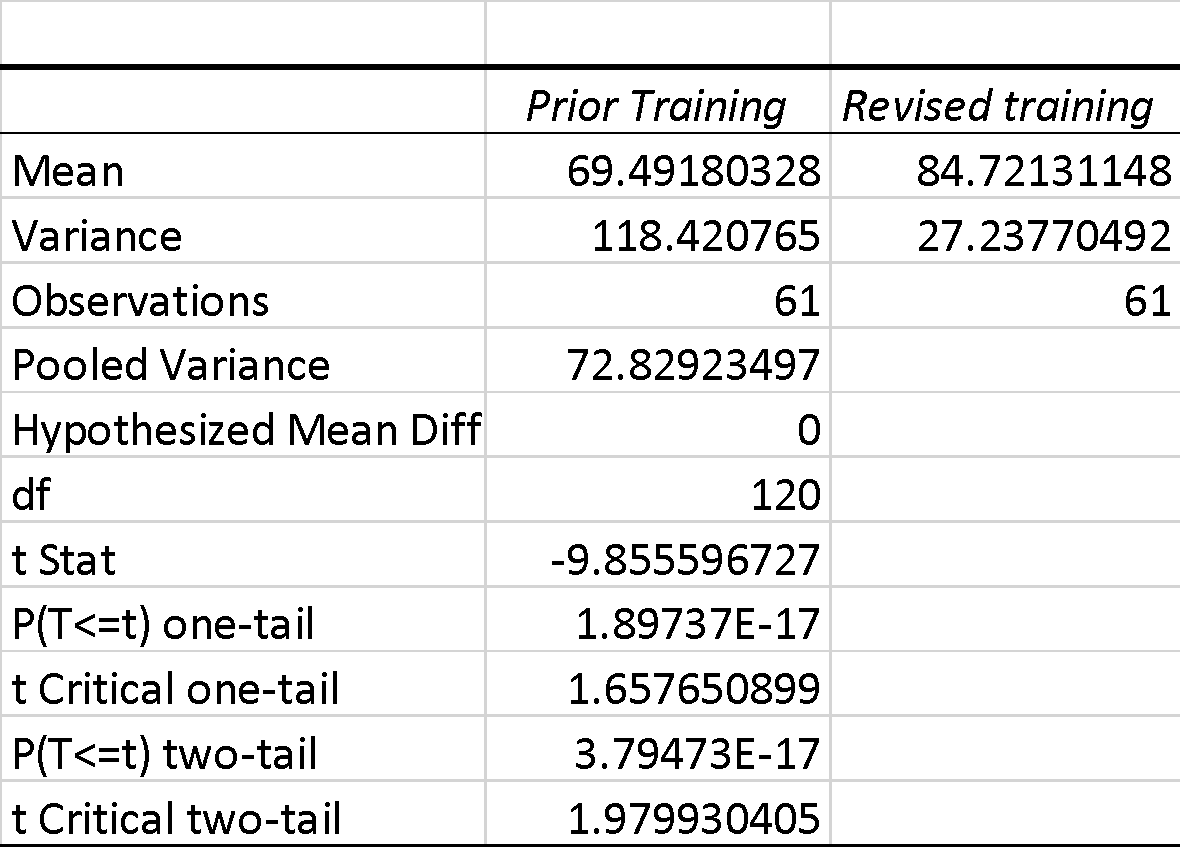
Interpretation
Results from the table show that the mean values of prior training are lower than revised training. In addition, the p-value is 1.897× 10-17, which less than the alpha level of 0.05. Due to this, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis to conclude that the means values of dependent values between IV1 and IV2 are statistically significant (Khatun, 2021). Due to improvement in the company’s mean scores, it should consider replacing prior with an updated safety training program.
Dependent Sample t-Test
The dependent t-test compares the means of two measurements taken from the identical object. When performing the dependent t-test, the dependent variables were measured for one group, pre-exposure, and post-exposure to an independent variable, to identify a statistical difference (Khatun, 2021). Furthermore, the study’s dependent t-test was designed to see if hemoglobin levels had risen while workers were performing lead remediation.
Hypothesis
H0 (null hypothesis): There is no statistical significance in the lead levels in the blood, pre-exposure and post-exposure
H1 (alternative hypothesis): There is statistical significance in the lead levels in the blood, pre-exposure and post-exposure.
Table 2: Pre-Exposure and Post-Exposure Results
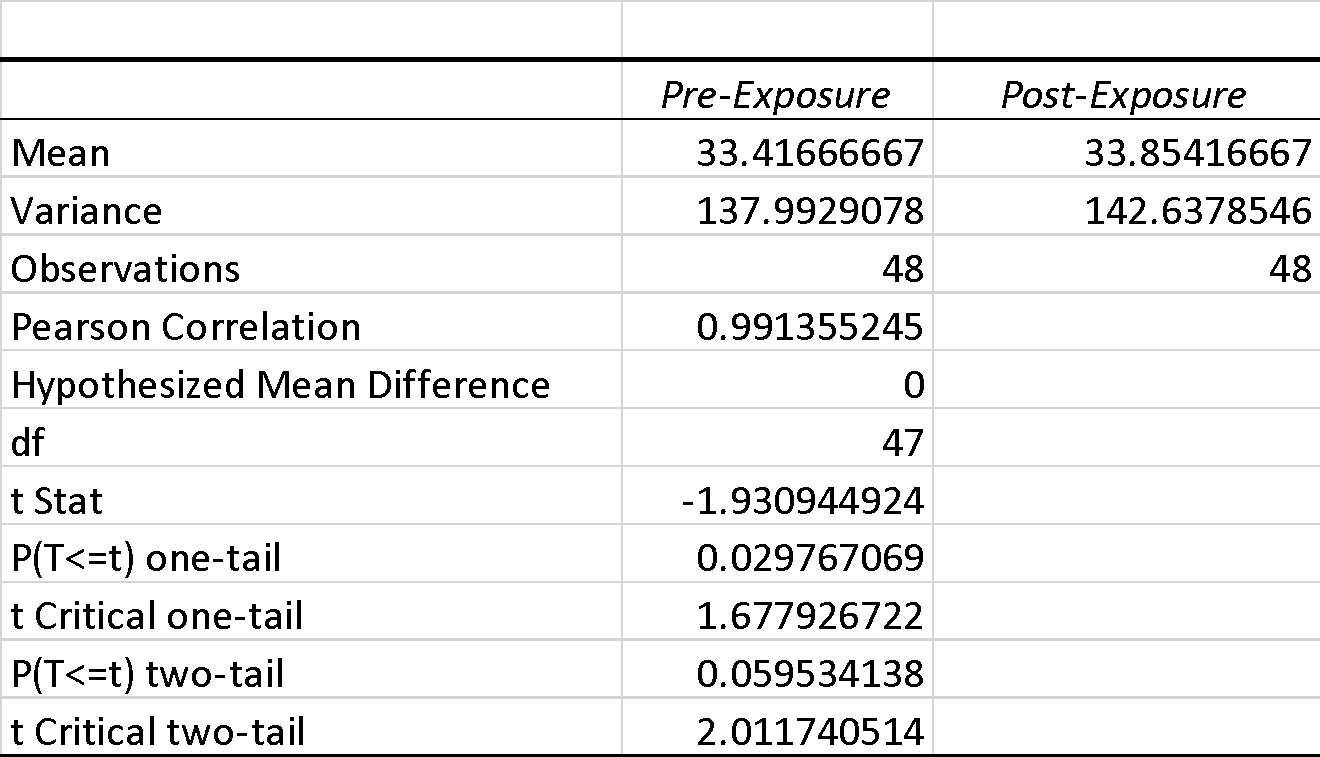
Interpretation
Table 2 shows that the p-value is 0.06, more than the 0.05 alpha level. As a result, the alternative hypothesis is rejected, and the null hypothesis is accepted, resulting in the conclusion that there is no statistical significance in the lead levels in the blood of personnel working at the lead cleanup job site before and after exposure.
One-Way ANOVA Test
ANOVA test is used when comparing more than two means in a study. In addition, the mean comparison in the ANOVA test should contain independent variables. In this study, an ANOVA test is performed to evaluate if there is a statistical difference between consulting project return on investment on air, soil, water, and training.
H0 (null hypothesis): There is no statistical difference between the mean return on investment for air, soil, water, and training.
H1 (alternative hypothesis): There is a statistical difference between the mean return on investment for air, soil, water, and training.
Table 3: ANOVA Table for Air, Soil, Water, and Training
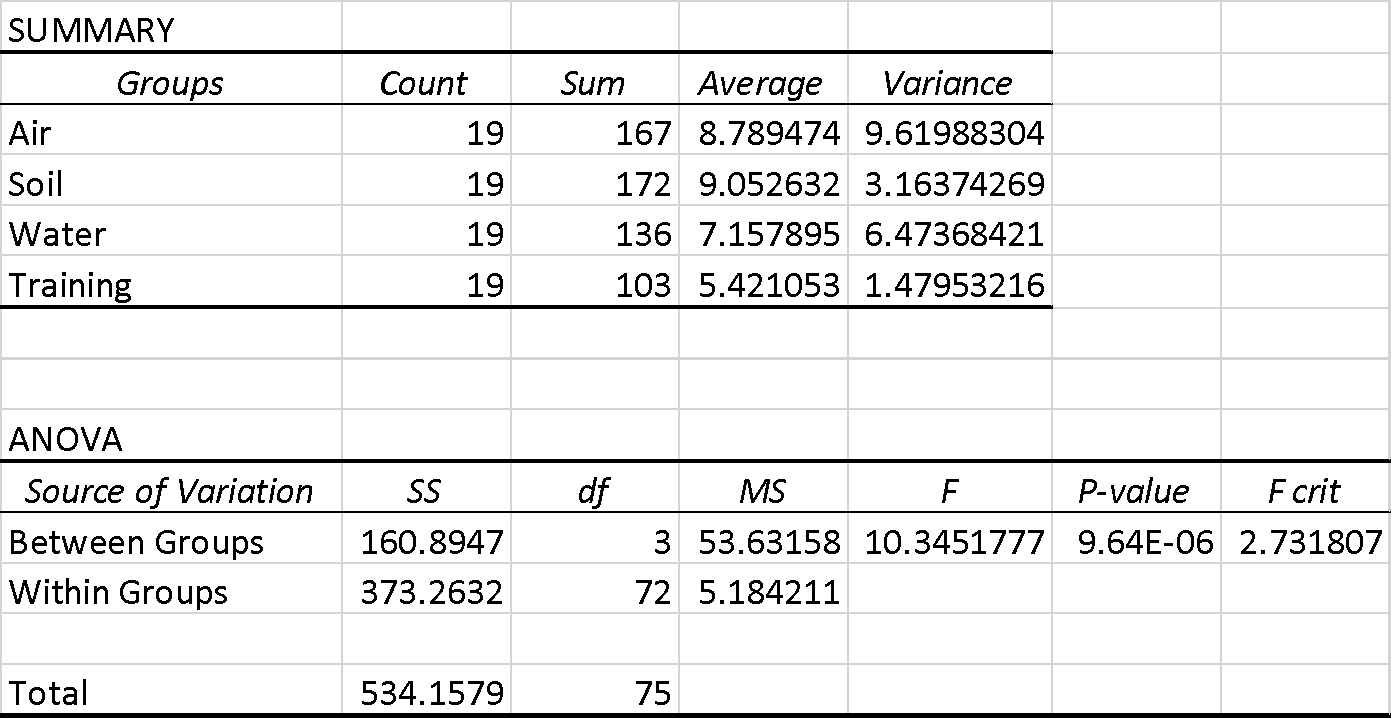
Interpretation
Table 3 shows that when the soil project was implemented, the mean return on investment was the highest (m=9.1%). In addition, the second highest was the air with 8.1%, and the last project was training with a mean of 5.4 %( Khatun, 2021). Further on, the results between the four groups were F (3, 75) =10.35, p=9.64 ×10-06, which is less than the 0.05 alpha level. Due to this, we reject the null hypothesis to conclude that there is statistical significance between air, soil, water, and training.
Reference
Khatun, N. (2021). Applications of normality test in statistical analysis. Open Journal of Statistics, 11(01), 113-122. Web.