Time has become the main goal in today’s rapidly developing world. Technological progress gives people the opportunity to distribute it economically and intelligently. One of the tools for this is taxi services, which have become widespread in society. One of the most successful companies providing services for the transportation of people is Uber. Case analysis of this company affecting its policies, prices, risks and opportunities can contribute to its further development and greater understanding of the sphere in which it operates.
Taxi is a service that provides a service for transporting people to the desired destination. This service is very popular due to its comfort and time saving. With the development of Internet technologies, the prevalence of this service has increased significantly, as special applications have appeared. Moreover, an important point is the cost of services. It is affordable and most people can afford to order a car if necessary. The company’s transportation services are most in demand in cases when there is no opportunity to use or there is no own car. Taxis are used both on short distances and on long ones. It should also be added that recently this service is in demand for the transportation of various goods. Cars are often rented to transport correspondence, animals and much more.
The Uber Company
The appearance of Uber on the market has radically changed the existing taxi company. Before the introduction of such service, people called a special dispatch number. Dispatchers, in turn, accepted the application and called taxi drivers to go to the address. The fare for trips consisted of several aspects; the passenger paid for the delivery of the car, then according to the meter about a dollar per mile and the same amount per minute of the driver’s work. Thus, such trips often turned out to be quite expensive for the population. On the other hand, they were quite logical, since they covered the costs of the office with dispatchers, the driver’s work and the maintenance of the car.
The emergence of the opportunity to order a taxi through a mobile application has given even greater prevalence and popularity and transparency of Uber. It gave people the opportunity to set the necessary route and immediately find out about the cost of the trip. The choice of non-cash payment also greatly simplified the calculations. Lam and Liu (2017) state that “ridesharing platforms, such as Uber, differ from traditional taxis in key aspects, such as real-time smartphone app-based matching, dynamic pricing that balances real-time supply and demand, and flexible driver work arrangements” (p. 376). Due to the growing demand and the development of the economy, this service must be constantly improved. This is done through new more comfortable customer service conditions. Moreover, the ever-growing competition of taxi services directly affects the reduction of tariffs, which helps to attract more and more individuals.
Uber’s business model can be characterized by innovation in the taxi market. On the other hand, it caused many problems for the company. Despite the fact that most perceive Uber as a transport company, the organization is considered a developer of special software. This development provides intermediary services between the driver and the passenger. Thus, any driver can use the application to find customers and provides transportation services without being an employee of Uber. Therefore, not being a company providing taxi services, Uber is not obliged to obey the laws related to this industry and pay the appropriate taxes. This opens up the opportunity for the organization to provide services cheaper than its competitors. Moreover, Uber independently sets all fares and determines which cars can register and operate, and which drivers are prohibited from taking tips.
It is noted that Uber resorts to rather dubious tactics, which may negatively affect its work in the future. Furthermore, the inefficiency that Uber has taken advantage of is the involvement of intermediary relationships with drivers. The company has an advantage from this aspect, since it sets the prices itself, and drivers are obliged to agree with them. Moreover, at this time there is a simultaneous reduction in the cost of the trip for the passenger and an increase in the commission from the driver.
Surge Pricing and Price Discrimination
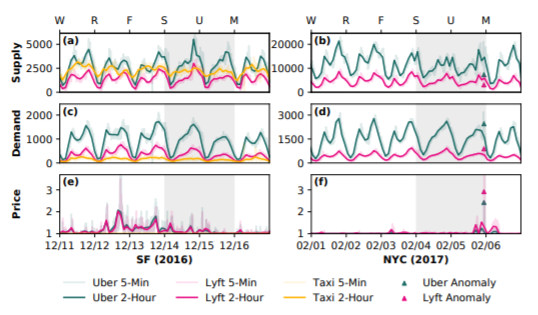
The jump in prices for Uber services is directly dependent on the level of demand and supply of the company. This is due to the fact that during an increase in demand for the transportation of people or goods and an insufficient number of available cars, the cost of the trip increases. Such a change in price may be due to several factors. Firstly, many prefer to wait until the price drops. Secondly, many drivers, wanting to make a big profit from work, ply in certain areas. The increase in the cost of Uber rides affects the alignment of supply and demand (Appendix 1). “Arbitrary price increase isn’t Uber’s endgame; it applies its calibrated model to respond to times and areas of high demand” (Lee, 2017).This is done by redistributing drivers to areas with high demand, affecting the price reduction due to an increase in the number of cars.
The policy of increasing prices practiced by Uber contributes to the development of such a phenomenon as price discrimination. It consists in setting different prices for various types of consumers in the absence of rational reasons. Surge pricing is characterized as “a price at a particular zone is temporarily raised above the regular price” (Guda & Subramanian, 2019, p. 1995). In order to implement such a pricing strategy, an organization must have a monopolistic position in the chosen field. This is due to the fact that only such a situation can make it possible to dictate prices (Belleflamme et al., 2020). However, as already mentioned, Uber is not the only company in the field of transportation services. The main goal pursued by companies using this strategy is to increase profits by assigning a difference, which comes from the difference between the potential willingness of the client to pay a certain amount and the actual price paid.
Moreover, the development of new innovative technologies aimed at collecting and analyzing data from users of various applications contributes to the more frequent use of ways to set specific prices for services. In taxi services, pricing in services such as Uber is directly affected by the marginal costs of providing services and various special characteristics of customers. Moreover, a combination of external factors, such as weather conditions, traffic situation, time of day, makes its contribution. They have a strong influence on how much users are willing to pay for certain services.
Economies of Scale and Economies of Scope
Economies of scope and economies of scale are two concepts that help determine the reason for lower costs for large companies. The main aspect of economies of scope is the average total price for the provision of certain services. Economies of scale concentrate on the cost benefits that an organization receives with an increased level of provision of a certain service (Nickolas, 2019). When receiving positive consequences from this aspect, the company is characterized by average costs, due to the fact that they decrease with an increase in the volume of services provided.
Economies of scale are successful for an organization in the context of what is characterized by low average costs. This is due to the fact that they are distributed to various services. In the case of Uber, the main resource is the mobile Internet platform. The cost of its development is the main aspect for the organization, as well as legal costs and fines awarded to the company due to complaints from both users and drivers. However, the advantage for the company is that they can noticeably succeed with the inverse relationship between fixed costs and the number of services provided. Therefore, the higher the level of service provided, the lower the costs for it.
Game Theory to Uber’s Market
Game theory is presented as an important aspect of modern economics. Its main advantage is that it helps to make effective management decisions in conflict situations. Such a case can be considered a certain problem affecting several parties-participants with opposite interests. Game theory and the application of its concepts contributes to the successful planning of the company’s economic activities. Moreover, it helps the rational allocation of resources and the preservation of the competitiveness of the organization. Uber, in turn, can use the theory of the game in the formation of pricing policy.
In addition, it should be noted that game theory is an effective tool for the development of a company’s strategy and business model. When developing a pricing policy, taking into account this theory, Uber should take into account such aspects as opponents, consumers and complementors (drivers). In order to outperform its main opponents, the company uses a strategy of increasing prices with an increase in demand for transportation services. Moreover, the game takes place directly between the organization and its drivers, since one of the main goals is their retention and loyalty to work at Uber.
Expansion and Policy Issues
Another essential aspect to consider is Uber’s potential for international expansion and potential trade policy issues. In examining this aspect, the policy that Uber undertakes to determine the needs of consumers and the sale of its products is of particular interest. Thus, by expanding its services, the company contributes to the spread of global expansion. This is due to the fact that currently, in addition to transporting people, the company is expanding its services, for example by introducing UberEats services. Moreover, by developing and improving its work and strategy to conquer markets, this innovation has become an effective tool. Uber became the first company to apply the “on-demand” policy on an increased mass scale.
The main aspect of the on-demand economy is the fact that it is getting access to goods and services at the moment the consumer needs. Orders are received online, and their execution and receipt are offline. The success of the company depends on the technology of the satellite navigation system, which shows all available drivers on the screen in the application. In addition, all operations related to money take place directly in the application. Thus, finances do not transfer to external sources and remain inside the application. However, the main problem in this case is the increased costs. Uber spends billions of dollars on operational services and technical support, research, development and depreciation.
Incentive Pay and Principal-Agent Problem
The incentive system of Uber was introduced to increase the motivation of taxi drivers. Thus, the company charges this incentive fee of about nine dollars on behalf of drivers on all trips to the airport. Moreover, this amount goes directly to the driver, and not to the intermediary company. Incentive payments were also presented to compensate for the usual and time costs associated with airport maintenance, including returning from the airport without a passenger. The amount is charged at commercial rates, regardless of what is paid, and is not withheld by Uber. Sometimes there are cases when this amount of the fee may be more than the paid cost of the trip.
The problem of the relationship between the principal and the agent, which is promoted by Uber with its policy, is one of the most important for the economy. This is due to the fact that during the development and functioning of organizations, a management problem arises. That is, there is a conflict of interests between the principal and the agent, which contributes to the development of conflict situations. Thus, many drivers of the company have recently begun to complain that they do not receive an insensitive fee, which causes controversial situations.
Asymmetric Information Issue
Information asymmetry is a valuable aspect of the work of any organization and all spheres of society as a whole. The reason for this is the level of technology development of modern society and the increased importance of information in it. The essence of asymmetry lies in the fact that there are often cases when participants in economic relations have different amounts of information about the service, which are the key object of the relationship. This leads to the fact that one of the sides of economic interaction has an informational advantage over the other. The expansion of Uber’s influence and influence in the market can only occur if there is low information symmetry and if there are specialized departments that can reduce its negative consequences.
The asymmetry of information contributes to the reduction of competition and the acquisition of a monopoly, which can increase the level of price discrimination. This is stimulated by the fact that all economic agents have only a limited amount of information at their disposal. Thus, insufficient data about the object, the implementation of the transaction and possible consequences has several reasons, one of which is the cost of resources. Thus, the agent of economic relations will not pay for information more than the level at which marginal costs exceed the level of marginal revenue from use. In conclusion, it is worth noting that the asymmetry of information creates a situation of abuse of the participants of the transaction by insufficient awareness of others.
References
Belleflamme, P., Lam, W. M. W., & Vergote, W. (2020). Competitive imperfect price discrimination and market power. Marketing Science, 39(5), 996-1015.
Guda, H., & Subramanian, U. (2019). Your Uber is arriving: Managing on-demand workers through surge pricing, forecast communication, and worker incentives. Management Science, 65(5), 1995-2014.
Jiang, S., Chen, L., Mislove, A., & Wilson, C. (2018). On ridesharing competition and accessibility: Evidence from Uber, Lyft, and taxi. Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, 863-872.
Lam, C. T., & Liu, M. (2017). Demand and consumer surplus in the on-demand economy: the case of ride sharing. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 17(8), 376-388.
Lee, J. (2017). How Uber leverages supply and demand in their pricing model. Learn Hub. Web.
Nickolas, S. (2021). Understanding economies of scope vs. economies of scale. Investopedia.
Appendix 1