Introduction
Uber is an on-demand transportation service whose mission is to enhance the accessibility of affordable transport services, which has brought a revolution in the taxi industry all across the world. Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp founded the company in 2009 with its headquarters in San Francisco, California, United States (Uber 2018). Uber has over 50 million-customer base existing in 45 countries globally as of 2014.
The business model has made it possible for people to simply tap their smartphones and have a cab arrive at their location in the minimum possible time. The company is one of those few tech companies in the world that has been valued over $70 Billion. In the establishment of the aggressive culture of the company, Travis Kalanick embraced the utilitarian approach while forsaking deontological ethics and the theory of justice. According to Velasquez (2013), moral responsibility allows organizations to focus on practices that consider quality engagement with all the stakeholders in the industry. Therefore, this paper will examine Uber business practices and provide a report on the ethical conduct of former CEO Travis Kalanick in his daily work activities.
Utilitarianism
The utilitarian theory holds the view that morally right action is the one that produces the most common good. According to Jonsson and Voorneveld (2018), utilitarianism involves the conversion of human beings’ character and productivity into simplistic figures motivated only by their reaction to pleasure and pain. Therefore, under this theory, Uber offers great opportunities to itself, users and drivers to generate abundant income. The top executives of the company have technically adopted, in their decision-making process, a stakeholder-centric approach involving all stakeholders’ business interests.
Analysis of Uber’s Operation Under Utilitarianism
Uber’s entry into the transport business lifted the lid of suppressed customer alternatives on quality and accessibility to transport services. The company utilizes modern technology and low service pay to accommodate customer needs and promote clients’ interest in service utility. In its aim to foster ininvestors’nd employees’ interests, the executives adopted a growth-centric culture through its business slogan that inculcates exciting business progression opportunities of the company. The executive’s chief objective is to attract investors, skilled employees, and promote its competitive edge through increased resource capital base and labor to sustain and enhance the company’s global growth and expansion. This strategic move influenced the company’s rapid expansion in the transport business.
However, the utilitarian theory introduced a toxic culture and ethics to the company. Uber corporate management faced several challenges involving conduct towards its customers, drivers, governments, and business rivals (Dudley, Banister & Schwanen, 2017). Despite the aim to promote the common good for all, Uber compromised its customers’ needs by failing to protect data and privacy issues and embracing a surge pricing policy to exploit its customers during peak periods. This misconduct exposed the company’s selfish interest and the corporate manager’s irresponsibility.
The expansionary ambition led Uber to business controversies with several governments, investors, employees, and rivals. In an attempt to gain a competitive advantage, the company adopted irresponsible business practices that involve underpayment of drivers, booking of fake rides from competitors, and theft of technology from rival companies. Additionally, the company executives engaged in the unprofessional practice of investing in discrediting reporters and silencing company critics. These acts of misconduct and irresponsible behaviors disparagingly negated the adopted theory of utilitarian leadership of the company as it fails to observe the good of the entire community.
However, despite the numerous challenges, Uber is morally correct to adopt the utilitarian approach to business activities. This strategy puts the good of the market as a central principle of sustainable development for all. On the contrary, the company ought to streamline its core objective of ensuring the achievement of utility through driving healthy competition among competitors, observation of policy regulations, community-based response to challenges, and respect for criticism to create a better outcome for the majority
Deontology Theory
Deontology refers to the ethical theory that focuses on the wrongness or rightness of an action. Uber executive management failed enormously in their quest to adjust their business activities to accommodate the company mission and investment objective. The goal of the deontological approach is to determine the duty and morality of human actions (Baumane-Vitolina, Cals & Sumilo 2016).
The company’s mission of providing affordable and accessible transport services forms the fundamental concept in the deontological approach to the development of the business environment. However, the company executives developed dysfunctional culture and inadequate oversight of irresponsible ethics. Travis and his executive team indoctrinated wrong individual ethics on their actions, as well as in handling grievances of their drivers, clients, rivals, and employees.
Analysis of Uber’s Operation From Deontological Point
In handling its clients, the corporate managers placed growth and rivalry ahead of basic humanity. Respect for customers’ privacy is a significant component of any business practice as it safeguards human dignity. Uber never focused its efforts on the recruitment of enough legal and human resource executives to protect both employees and clients’ dignity. The company is on record for underpaying its drivers and executive sexual misconduct, and berating drivers. Additionally, the top executive failed to develop a morally upright culture to address grievances of any magnitude involving gross misconduct of drivers, rape cases, and slow response to driver murder cases. It, however, adopted questionable means to circumvent any attempt of legal suit and criticism.
Among the most notable breakdown in Uber’s business association with its rival companies involves the booking of fake rides and theft of rival technology. The strategy to undo rival company Lyft profit objective through booking fake rides to cut its income is an ethical deviation from healthy competition. Additionally, Uber’s theft of technology in adopting self-driven cars from Google Alphabet company, stab more into the company’s lack of deontological ethics in its business activities. These wrong actions compromise the deontological concept of business engagements to develop a healthy environment for the provision of quality services and sustained growth.
Overall, the former CEO of Uber failed enormously in developing the company’s ethical guidelines. His deontological limitations involved the development of dysfunctional organizational culture, sexual misconduct, unprofessional business engagements, and lack of respect for the rule of law, which greatly affected the company’s development goals.
Theory of Justice
This theory requires that the social structure place liberty on its members while limiting this aspect of social benefit through non-infringement of any member liberty by another. The justice theory does not allow beneficial inequality among the members, social or economic, that promote any of the member’s position over the others (Baumane-Vitolina, Cals & Sumilo 2016). , During Travis Kalanick’s tenure, Uber undertook several strategies to enhance its competitive edge that compromised rival companies’ rights of engagement. Some of the strategies include anonymously booking of fake rides in Lyft, and non-procedurally adopting the self-driven Google Alphabet technology.
Analysis of Uber’s Operation Under the Theory of Justice
Uber’s concept of booking fake rides to cut on rivals Lyft income failed this theory of justice. The company’s executive intended to enhance its profitability while reducing its rival earnings by breaking the customers’ fair choice situation of service. The fake bookings negatively affected the economic position of Lyft, leading to the undue advantage of Uber in establishing its market niche and expanding its market share.
Uber significantly negated Lyft’s capacity to conduct its business activities in the market and compromised its rights of operation. Additionally, the theft of self-driven technology from Google parent corporation Alphabet is unlawful and breaks the rights to justice in the transport industry. This theft portrayed Uber’s wicked acts of selfish interest and disrespect to other industry players’ rights. These immoral acts of theft and participation in fake bookings broke Uber’s objective of utilitarianism, seeking to achieve the common good for all. In this view, the company must review its business skills and approaches to accommodate a fair play in the market that enhances product quality for customers, revenue for investors, and income for employees and sustained global growth.
Semiotic Square
The brand language transforms an organizational image into inventory. According to Rossolatos (2017), brand image constitutes one of the most extensive operationalized constructs in marketing theory and practice. Uber’s semiotic square cuts across the theories of Justice, the association of utilitarianism approach to service delivery, which promotes the common good for all with the contrary deontological concept of business development and fosters the promotion of rightful business activities.
Application of Semiotic Square to Uber
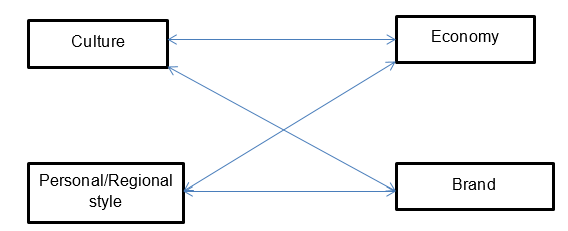
The theory of justice influences the company’s culture and economic position. Promoting customer’s awareness of gross misconduct significantly affects customer perception of the company’s culture and loyalty. An organization’s culture is fundamental to fostering a market share, influencing customer choices, and enhancing sustained growth. Therefore, Uber must transform its business culture by establishing its competitive objective on fair market rules.
Utilitarianism and deontological ethics are the basic components of company branding. Velasquez (2013) explains that business ethics creates an outstanding image of responsibility in customers, which is essential in developing customer brand loyalty and preference over competitors. The brand combines the elements of organizational culture and economy, which are essential in the identification of products or services. Based on previous knowledge of brands, consumers predict and build their trust in a product, which influences their subsequent product choice. The consumers, in exchange for their trust in the brand, expect the fulfillment of promises and expectations of performance.
Personal and regional style defines the other elements in the system. This element is essential in binding together all the three theories ascribed to by the company. Personal and regional style significantly influences the establishment of an organization’s culture, brand, and economic elements under a single unit of an organizational image. Therefore, Uber must strive to rebrand its regional and entire organization image across the globe through consolidating its efforts while respecting the rights of rivals, employees, customers, and drivers.
Rationale for the Personal Positioning of the Company
In a personal view, Travis Kalanick’s approach to leadership of the company defied all the essential ethical considerations involving individual and organization practices and could not drive Uber’s growth and development agenda.
Travis undermined the company’s legal establishment rights by imposing his own and those of the top executive individual lives on the company’s life. The CEO placed top management’s life objectives at the center and as the core driving force of the company’s business practices. His unprofessional conduct destroyed the company’s brand, culture, and image through a series of personal mistakes, including lawsuits, the unprofessional resolve of customer complaints, and destructive competitive tactics. These personal mistakes destroyed his capacity to steer Uber to sustained global growth and development.
Rights and Duties of Uber in UK
The UK government stripped Uber of its London business license due to the legal view of the basis that the company’s business establishment is not appropriate to operate as the hire of private cars (Uber, 2018). The critical element in the nullification was the lack of integrity in its partnership with customers and the market. The duties of the company thus remain limited to operating its business activities within the capital.
Conclusion
Uber is an on-demand transportation service that revolutionized urban transport and became the model for platform companies, which connect customers and contract suppliers through software. The company’s founding CEO, Travis Kalanick emphasized his leadership approach to utilitarianism and failed to observe rightful and fair acts in his business engagements with employees, drivers, and rival companies. These personal failures streamed down to the company’s culture that subsequently led to a series of challenges in growth and expansion. Therefore, Travis Kalanick’s deviation from ethical considerations makes him not fit to drive Uber’s growth and development agenda.
Reference List
Baumane-Vitolina, I, Cals, I & Sumilo, E 2016, ‘ Is ethics rational? teleological, deontological and virtue ethics theories reconciled in the context of traditional economic decision making’, Procedia Economics and Finance, vol. 39, no.1, pp.108-114.
Dudley, G, Banister, D & Schwanen, T 2017, ‘The rise of Uber and regulating the disruptive innovator’, The Political Quarterly, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 492-499.
Jonsson, A & Voorneveld, M 2018, ‘The limit of discounted utilitarianism’, Theoretical Economics, vol. 13, no. 1, pp.19-37.
Rossolatos, G 2017, ‘Brand image re-revisited: a semiotic note on brand iconicity and brand symbols’, Social Semiotics, vol. 18, no. 90, pp. 1-17.
Uber 2018, Finding the way: creating possibilities for riders, drivers, and cities. Web.
Velasquez, M 2013, Business ethics: concepts and cases, Pearson Education, London.