Conceptual/Theoretical Model
In most countries, particularly in developing nations, tourism is one of the significant sources of revenue and the main contributor to economic growth. Tourism also plays a vital role in promoting economic growth by contributing to the gross domestic product (GDP) (Shih and Do 2016, 371-372). East Timor (also known as Timor-Leste) is one of the world’s youngest countries after having got its independence in 2002 from Indonesia. The country’s tourism sector is still at the infancy stage, owing to continuous conflict and clashes between various security agencies and the government. However, despite its dormancy, the tourism sector in Timor-Leste, just like in any other Southeast Asian countries has an immense potential to contribute to the country’s economic growth and significantly boost its GDP growth for sustainable development.
Research Data
Data Description
The panel data on tourism growth in Southeast Asia used in this study comes from the World Bank. The GDP growth data covers 11 countries on the Asian continent1 including annual net tourism income as well as an annual number of travelers entering the respective countries from the year 2000 to 2018. The data set also included two variables coded Receipt and GDP. The Receipt variable represented international tourism receipts in US Dollars that included expenditure of international inbound visitors on items on the reporting countries, including expenses on national carriers and international transport. The GDP variable represents the annual GDP of countries in US dollars. In order to make inferences specifically for Timor-Leste, a dummy variable called TimorLeste was created, which coded data as “1” if the country was Timor-Leste and “0” if otherwise. Another variable called ReceiptsMn_TimorLeste was created to estimate if the impact of tourism was different from all the other countries in Southeast Asia. It was created by multiplying ReceiptsMn with the dummy variable TimorLeste.
Table 1: Variable description table
Summary Statistics
The mean international receipts in Southeast Asian countries was $7.5 billion, with a standard deviation of $10.5 billion. Similarly, the mean GDP in South Asian countries was $167.14 billion, with a standard deviation of $212,041 billion. The significant standard deviations indicate that the data entries are widely spread around the means.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics for Southeast Asia
In Timor-Leste, the mean international receipts were $35.64 million, with a standard deviation of $22.01 million. The mean GDP was $3.83 billion, with a standard deviation of $1.4 billion. This implies that the mean GDP and international receipts of Timor-Leste were lower than the average GDP of Southeast Asian countries during the observed years.
Table 3: Descriptive statistics for Timor-Leste
Correlation Analysis
Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the two variables was 0.5605, which implied that there was a significant correlation between the variables. This can be explained by the fact that South-Eastern countries, in general, are highly dependable on the income obtained from international tourists. The results of correlation analysis suggested that a regression model can provide significant insights for predicting GDP using international tourism receipts.
Table 4: Pearson’s correlation between variables
Regression Model
The regression result presented in Table 3 below shows that the regression model had R2 (R-squared) of 0.3141, which indicated that 31.41 percent of the variability in the dependent variable (annual GDP) could be explained by the independent variable (international receipts). The regression model was not statistically significant,
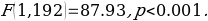
This result showed that the model could statistically significantly predict the dependent variable. According to the regression result, the regression model will be as shown in an equation below:
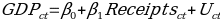
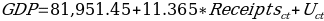
The regression model above shows that there is a positive association between international tourism receipts and GDP, which supports the findings of Nguyen, who established that the GDP growth in developing countries is directly proportional to the amount of receipts received from international tourists. (Nguyen 2015, 4).
Table 5: Linear regression model without dummy variable (in million dollars)
The regression model presented above does not include a dummy variable, which is designed to predict the impact of international receipts on the GDP of Timor-Leste. The results for the second regression analysis with a dummy variable are presented in Table 6 below.
Table 6: Linear regression model with the dummy variable (in million dollars)
Considering the results of the analysis, the regression model that could predict national GDP using the information about the international receipts is as follows:
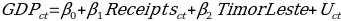
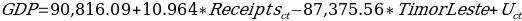
The model demonstrates that there is a positive correlation between international tourism receipts and GDP, and an increase in $1 million of receipts leads to a $10.96 million increase in annual GDP of countries. The constant, however, is different for Timor-Leste and the rest of the Southeastern countries.
In order to understand if the effect of tourism receipts was different in Timor-Leste in comparison with other countries in Southeast Asia. The model that could estimate the difference was as follows:
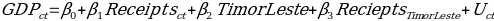
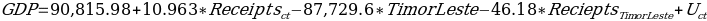
The results of the regression analysis are presented in Table 7 below:
Table 7: Linear regression model with the dummy variable and Reciepts_TimorLeste (in million dollars)
The results of the regression analysis revealed that the tourism receipts do not produce a significantly different effect on GDP in Timor-Leste in comparison with other countries in Southeast Asia (p=0.984).
Limitations of the data discovered
Although the data file was obtained from the World Bank database, which is a reputable institution, it had two significant limitations. First, there were missing observations in variables for some countries. For instance, Vietnam lacks information about GDP in three years. Secondly, the data presented on the World Bank website is the official information, and the actual data may differ.
Bibliography
- Nguyen, Anh Tru. (2015) “Examining the Relationship between Tourism and Economic Growth in Southeast Asia: A Vector Autoregressive Model Approach.” International Tourism and Hospitality Journal 1, no. 2: 1-17.
- Shih, Wurong, and Ninh TH Do. (2016) “Impact of Tourism on Long-Run Economic Growth of Vietnam.” Modern Economy 7, no.3: 371-376.
Footnotes
- Timor-Leste, Vietnam, Thailand, Singapore, Philippines, Myanmar, Malaysia, Lao PDR, Indonesia, Cambodia, and Brunei Darussalam.