Background of the Company
Unilever is one of the most influential multinational corporations in the world that specialises in producing personal care products and cleaning products as well as food and beverages. The company was founded after the merger of Lever Brothers and Margarine Unie in 1929, and it operates in more than 190 countries of the world. Still, the history of the corporation’s units is even longer because the British Lever Brothers was founded in the 19th century as became popular as the soapmaker (Unilever 2015). The merger of the British company with the Dutch producer of margarine products was an important step to create the multinational corporation.
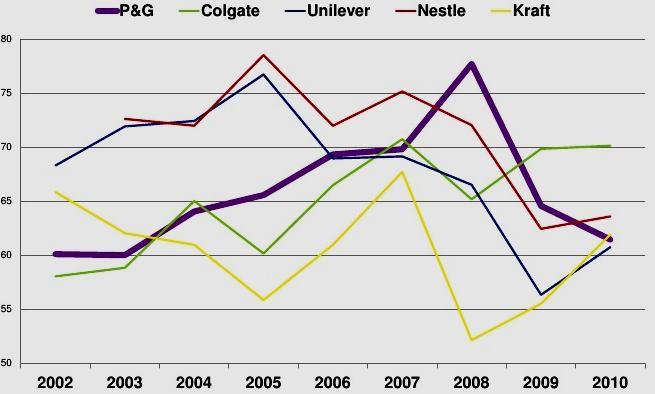
Today, Unilever ranks the third influential consumer goods producer in the world after Procter & Gamble and Nestle with the annual revenue in more than €49 billion (Unilever 2015). Developing more than 400 brands, Unilever orients to the further progress of the company in spite of the competition in the industry. In addition to such main competitors as Procter & Gamble and Nestle, Unilever also competes with Kraft, Mars, Colgate, and Henkel (Figure 1).
Analysis of the Mission Statement
Unilever’s mission is to help people “good, feel good and get more out of life” as well as to contribute to the “sustainable growth” (Unilever 2015). Unilever’s mission reflects the basic principles of the company’s orientation to the persons’ well-being, and it accentuates the necessity of focusing on the sustainable growth. Thus, it is possible to state that the company’s mission demonstrates that the company responds to the needs of consumers, its strategy is correlated with the modern tendencies.
Industry Analysis
Market structure determines the aspects of the competition within the industry. The typical market structures are the monopolistic competition, perfect competition, monopoly, and oligopoly. The industry in which Unilever operates is characterised by oligopoly because the global market is dominated by the products of such corporations as Unilever, Procter & Gamble, and Nestle (Proctor 2014).
Ansoff Matrix for Unilever
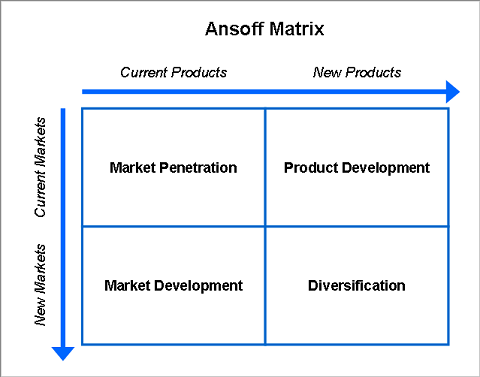
Market Penetration Strategies
Unilever increases the market share and focuses on the price and quality balance for customers.
Market Development Strategies
Unilever focuses on the geographic expansion.
Product Development Strategies
Unilever focuses on product improvement and extension and proposes new products for the current markets.
Diversification Strategies
Unilever is constantly diversifying the range of proposed products. The main focus is on the sphere of research and development t o propose innovative products (Hill & Jones 2009, p. 24).
Porter’s 5 Force Theory
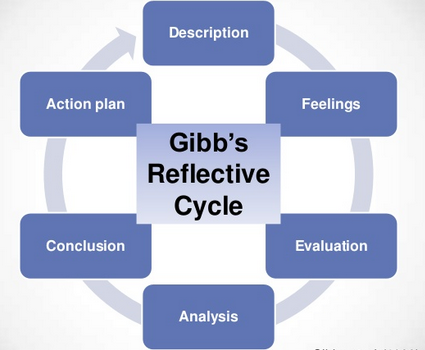
Gibb’s Model
Unilever is a company that builds its marketing and management strategies according to the principles of the Gibb’s Reflective Model where the main focus is on the consumer’s perception of products and the associated brand loyalty.
Reference List
Hill, C & Jones, G 2009, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach, Cengage Learning, New York. Web.
Lamb, C 2008, Marketing, Cengage Learning, New York. Web.
Moore, K & Pareek, N 2006, Marketing: the basics, Taylor & Francis, New York. Web.
Pride, W & Ferrell, OC 2008, Marketing, Cengage Learning, New York. Web.
Proctor, T 2014, Strategic marketing: an introduction, Routledge, New York. Web.
Unilever . 2015. Web.