Introduction
The world economy is under the grip of recession. Stock markets show great fluctuations day by day. Recession and the stock market have been the main topics dominating the newspapers since December 2007. Researchers are engaged in discussion about the causes of the recession. As it prolongs, the recession leads to economic depression and later to economic collapse. Many financial analysts have the common opinion that the US is the main cause behind it.
However, contrary to this, there are others who hold that there is no recession in the US economy. Dr. Martin Feldstein, former president of the National Bureau of Economic Research points out “The economy is now in a recession. It will last longer and be deeper than the last two recessions, which lasted only 8 months from peak to trough. It could well be longer and deeper than the recession in the early 1980s that lasted 16 months.” (Feldstein, 1).
Overview of US economic recession
The recession is the decline in the country’s Gross Domestic Product. “According to ‘The National Bureau of Economic Research’ recession is defined as “a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months.” (Economic Recession). Studies show that inflation, currency crisis, speculation, national debt are some of the few causes of the recession. Since 1845, it is marked out that, the US has witnessed 32 cycles of expansions and contractions and four out of them are considered as a recession. The current oil price hike and money supply within the country also have contributed to the recession.
The shock of subprime crisis jointly with retard in mortgages also led to recession i.e. housing market correction and sub prime mortgage crisis has led to recession in the US. The recovery is difficult and it takes time due to the lack of confidence among customers. Drop in the value of houses and decimated pension savings on the stock market have contributed to the lack of consumer confidence. There was a growth of 8.5% in the unemployment rate and there were about 2.6 million job sheds in the US during 2008. The credit crisis, inflation in oil, food, and steel also made the situation worse.
Impact of US economic recession over Canada
US recession spreads all over the world as all countries have trade relations with the US. Recession can have both positive and negative impacts. Even though Canada has come late under the recession, the impact of recession over Canada is a fact,
as the Canadian economy is intertwined with the American economy. Canada is subjected to a sharp decline in exports, the manufacturing sector, etc. Statistics show that “the U.S. shed 598,000 jobs in January, 610,000 jobs in February, and 663,000 jobs in March. Canada shed, respectively, 129,000; 82,600; and 61,000 jobs.” (Yalnizyan, 41). Canada shed more jobs than the U.S when we apply the 10:1 rule of thumb during 2009.
The recession first hit the housing market leaving the natural-based sector behind. The major provinces in Canada experienced a serious decline. Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario, Newfoundland, Labrador are some of the provinces which experienced the largest declines due to the US economic recession. A survey by Phoenix SPI on the impact of recession over Canada has revealed the following findings: 81% of the Canadians believe that the US recession has a negative impact and 42% of the Ontario’s were more likely affected than the Western Canadians.
Ontario housing market
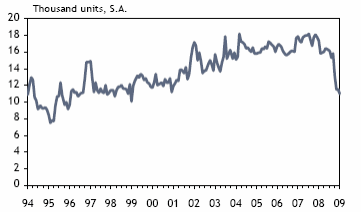
Ontario’s economy is battling against the effects of the US market bend. Overall performance of manufacturing and export sector shows thrashing and there was a decline in the consumer spending activity. Many were subjected to job losses, which led to shelving plans of buying homes and walking out of shopping malls. The housing market sale, during February, has dropped to a ten-year low.
Graph showing Ontario residential unit sales
Recession and Doctor Shortage in Ontario
Some of the facts about the doctor shortage in Ontario are as follows:
- People do not have a family doctor
- Due to the shortage, the number of patients with chronic diseases are increasing in the hospitals
- The Canadian doctors are practicing in US
- Another 2500 doctors will retire today, and the number of doctors per 100000 people will reduce thus ranking Ontario in the eighth position in Canada.
“In the medical profession, Joan Atlin, Executive Director, Association of International Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario (AIPSO) has emphasised the importance of focussing on the doctors shortage in Ontario through a lens of competence and rights-human rights and the Charter of Rights.” (Kwok and Wallis, 136).
Some of the reasons, which Ontario Medical Association points out for the doctor shortage, are increased paperwork and job stress. Statistics show that about 40 percent of their total workweek is spent in filling the forms and paperwork. The bonus given for serving in rural and remote areas has not been raised over the past 30 years, which may sway the cost of living. Due to the lack of medical backup, hospital beds etc, the doctors are unable to give proper treatment to the patients, which make them feel stressed. It is seen that the portfolio held by the physicians has shrunk by 30% and thus many doctors nearing retirement are changing their career plans. Doctors continue to work, and thus in the case of doctor shortage in Ontario, economic recession has helped to solve this problem. (How the Recessions will Help Canada’s Shortage).
Automotive industry crisis in Ontario (in Canada)
Close relationship with US also led the Canadian auto industry into trouble due to Automotive Products Trade Agreement and North American Free Trade Agreement. The financial crisis led the car dealers into the risk of job losses to tens of thousands of people due to the decline in the car sales in North America. The rise in price of raw materials and oil price hike also made the situation worse. “The plight of the “Detroit Three” is being addressed by the U.S., Canadian and Ontario governments, which have so far collectively committed nearly US$29 billion in financial assistance.” (Provincial Outlook, 5).
Graph showing the motor vehicle sales
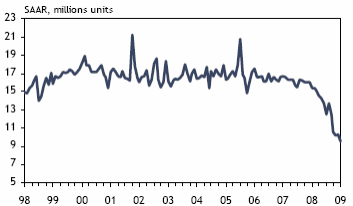
(Provincial Outlook, 5). During the fiscal year, Ontario government has announced a deficit with C$500 million shortfall. “Real GDP is forecast to decline by 1.9% in Ontario in 2009 — the second largest drop among provinces behind Alberta — but rebound to a growth rate of 2.4% next year. Of even greater significance to the 2010 outlook will be the anticipated recovery in the United States, supported by that country’s own unprecedented fiscal and monetary stimulus.” (Provincial Outlook, 6).
Transformation of British Columbia, from correction to contraction
With global recessionary forces weighing higher GDP shows a decline of 1.5% this year. There was a sliding trend in the housing market, redundancy rate and consumer spending. After 1986, the job market has shown a longest losing streak by losing 35000 jobs. The commodities market was also knocked down. Survey of investment intentions by Canada’s Private and Public Investment pointed out domestic weakness because nearly 10% of non-residential capital spending was set to plunge in this year.
Energy funk and economic slump in Alberta
There is a significant twist in the Alberta economy. According to Statistics of Canada’s P&PI survey, there was more than 15% fall in the non-residential capital spending in this year. Downturn in the oil and gas sector has reduced the consumer spending in the retail stores. GDP is expected to decline by 2.3% and there is slump in the housing construction with dropping to a 13 year low.
Nova Scotia- and recession
Even though there was a softening in the domestic economic conditions, the unemployment rate has risen to 8.8% as against the previous figure of of 7.6%. There was also deterioration in the housing market with revising 0.4% down in the economic growth of Nova Scotia. The province is expecting to outperform despite of the recession, as the spending on Deep Panuke natural gas project is to increase C$760 million
Saskatchewan and recession
The economic growth of Saskatchewan was cut to 0.9% from 2.8% during 2009 due to the greater weakness in the commodity prices than expected. There was a record high price in the key export commodities of Saskatchewan in the earlier 2008. This has contributed to the residential investment activity and boost in demand for housing. As the future price is expected to go high, there is an anticipation of increase in the capital spending.
Weathering the recession in Manitoba
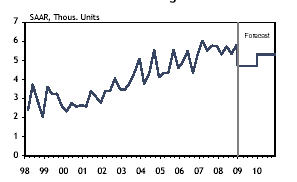
The economic growth has been 0.5% in the current year, which was 1.9% in the previous year. There was a decline of 4.4% in the non-residential capital expenditures. The housing market is expected to decrease in 2009.
Graph showing the Manitoba housing market
Conclusion
It is seen that recession had both negative and positive impact. The positive impact is that recession has helped to reduce the doctor shortage in Ontario. However, all other cases have shown the negative impact. The world economy cannot be separated from US economy, and thus has to face the deepening effect of US recession. While looking at the history we can see that US economy, over the past 40 years has experienced six recessions. The period of recession varied from six to sixteen months. It was on December 2007, that the recession began in United States-declared by Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
Starting from 2007 December, it has been over 18 months; the current recession is expected to extend for a long period due to the contraction in the housing market and financial crisis. Decline in the employment rate, real income and industrial production shows that this recession could be the most severe. By 2010, world anticipates the recovery of US economy and strengthening of Canada. We cannot forecast the future and cannot determine when recession will start or end. However, we are not still far from another Great Depression.
Works Cited
Economic Recession: Mumbai Space. 2008. Web.
Feldstein, Martin. What is a Recession? Liber8: Economic Information Newsletter. 2009. Web.
How the Recessions will Help Canada’s Doctor Shortage. KevinMD: Medical Web log. 2009.
Kwok, Siu-Ming., and Wallis, Maria A. Daily Struggles: The Deepening Racialization and Feminization of Poverty in Canada. Canadian Scholars’ Press. 2008.
Provincial Outlook: Recession Virus Spreading Quickly. RBC. 2009. Web.
Provincial Outlook: Recession Virus Spreading Quickly: Ontario- Battling the Recession. RBC. 2009. Web.
Yalnizyan, Armine. Exposed: Revealing Truths about Canada’s Recession: Notes. Growing Gap. 2009. Web.