Targeted Organisation
The selected firm is Virgin Atlantic. Headquartered in Crawley, Virgin Atlantic is one of the leading airline companies in the United Kingdom and across Europe (Notis 2015). The company transports millions of passengers to over thirty destinations across the globe. The corporation was established in 1984 by and is owned by Virgin Atlantic Limited. The current chairman of this firm is Stephen Murphy. The firm was founded by Richard Branson and its current chief executive officer (CEO) is Craig Keeger (Virgin Atlantic 2016, para. 2). The firm’s current number of employees is above 9,200.
The firm offers a wide range of services and products to the targeted customers. To begin with, the company transports millions of passengers to over 30 destinations. The company offers logistical services to different consumers. The company’s courier product is called VEX (Atras 2013). This service targets customers who want to transport shipments below 32 kgs. The firm transports pets from one place to another. These include cats and dogs. These products and services make it easier for the company to realise its potentials.
The company engages in strategic relationships with different partners. A good example is the current partnership with WNS (Virgin Atlantic 2016). The corporation has developed a powerful business strategy that is guided by the emerging needs of the consumers. For instance, new leisure markets have emerged in the developing world. That being the case, the company’s business strategy is therefore aimed at supporting the needs of more customers. The firm purchases new aircrafts that can add value to the customers. These strategic processes have continued to drive effectiveness and efficiency at the company.
Virgin Atlantic’s Macro Environment
Virgin Atlantic’s business performance is affected by a number of external forces. In order to achieve the targeted business objectives, the corporation must always analyse the major factors that can affect performance (Atras 2013). The discussion below outlines the major forces associated with Virgin Atlantic’s external environment. These aspects of the macro environment can be analysed using the PESTEL model.
Political Factors
The European continent is characterised by politically stable nations. Consequently, the political climate experienced in Britain and other nations can support the company’s goals. Virgin Atlantic has been operating flights to a number of countries across the globe. The “abolishment of the Traffic Distribution Rules is currently making it easier for the company to expand its operations” (Atras 2013, p. 4). The firm has been operating flights in different nations in Asia and Africa. However, the issues experiences in countries such as Yemen and Syria might affect the firm’s operations adversely.
Economic Factors
These forces can have both positive and negative implications on the performance of a business organisation. Several issues such as recession and inflation rate continue to dictate the performance of many firms in the United Kingdom and beyond. The financial crisis of 2008 forced Virgin Atlantic to undertaken new strategies in order to remain profitable. For example, it reduced its prices and targeted new destinations. The recession experienced in specific countries might affect the hospitality and tourism industries. Consequently, such issues might affect the company’s business performance (Atras 2013). Virgin Atlantic has recently minimised its flights in an attempt to deal with redundancies and inflation. The United Kingdom’s exit from the European Union (EU) might result in economic changes and subsequently affect the company’s profitability.
Social Factors
The economic changes experienced in different countries are encouraging more people to engage in various social activities. Domestic and foreign tourism can make it easier for the firm to achieve its goals. More members of the society are presently travelling to different locations across the globe. The increased use of social networks is encouraging people to travel from one place to another (Notis 2015, p. 13). Such social changes influence the performance of companies such as Virgin Atlantic.
Technological Factors
The aviation industry is always characterised by modern technologies in order to support the diverse needs of more customers. In order to minimise accidents, companies in the industry embrace the use of advanced technologies. At Virgin Atlantic, modern technologies are acquired in an attempt to improve the quality of services available to different customers. Similarly, different “governments use such technologies to improve security and safety of different aircrafts” (Virgin Atlantic 2016, para. 4). Such technologies are “being used by competitors to entertain passengers” (Notis 2015, p. 38).
Environmental Factors
Many customers are supporting the business models of companies that protect the integrity of the natural environment (Notis 2015). Virgin Atlantic has been forced to engage in a wide range of activities that can support the sustainability of the natural environment. For instance, Virgin Atlantic has been associated with a number of corporate social responsibilities. For example, the firm supports the needs of disabled persons. The company also uses environmentally-friendly vehicles. Such vehicles are used to transport some of its passengers.
Legal Factors
The aviation industry is characterised by a wide range of legal frameworks, regulations, and requirements. These laws are critical towards maximising safety and ensuring that different stakeholders are responsible for their actions. Many governments have implemented stringent measures to protect their citizens. The ongoing wars in different parts of Asia have forced many governments to implement new laws in an attempt to minimise cases of terrorism (Notis 2015). This analysis shows clearly that Virgin Atlantic operates in an industry that is heavily regulated by different governments (Carter 2014). Experts have also indicated that new laws and regulations will emerge in the future. Britain’s exit from the EU will definitely force the corporation to sign new pacts with different airports across the continent.
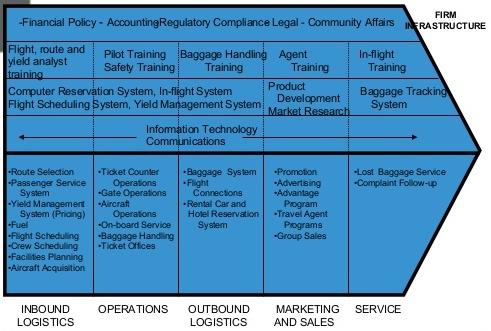
Porter’s Value Chain
Virgin Atlantic can be described as a system because it is characterised by different processes (Notis 2015). The corporation acquires and uses numerous resources in order to achieve the targeted goals. That being the case, Virgin Atlantic undertakes a wide range of value chain practices in an attempt to realise the targeted profits. Using the case of Virgin Atlantic, the discussion below gives a detailed analysis of the primary activities in Porter’s Value Chain.
Inbound Logistics
The term inbound logistics refers to the processes used to acquire raw materials from different suppliers and use them to add value to the targeted clients. Some of these practices include storage and use of fuel, provision of drinks and foods, and accommodation (Virgin Atlantic 2016). At Virgin Atlantic, facility planning is a powerful strategy aimed at supporting the needs of different customers. For example, upper class customers (or passengers) are provided with limousine services. Security measures are taken seriously in order to increase the trust of many customers. Some UK passengers are provided with complementary airport transfer in Virgin Limousines or Volvos (Virgin Atlantic 2016). These inbound logistics make it easier for the company to serve more customers.
Operations
Virgin Atlantic’s website indicates clearly that “the corporation is the second largest long haul airline in the United States” (Virgin Atlantic 2016, para. 5). It is also one of the largest carriers and providers of excellent passenger services in Europe. It has continued to serve millions of citizens in North America. In the recent past, Virgin Atlantic has been operating flights to many destinations in Africa, India, the United States, the Caribbean, and the Far East (Carter 2014). Because of such services, the firm has earned many awards in different categories. The company uses its resources to support these operations.
Outbound Logistics
Virgin Atlantic provides adequate facilities to support its customers. An amenity kit is “always available for every outbound journey” (Notis 2015, p. 4). The customers are provided with different newspapers. The facilities tend to increase for passengers who prefer the upper class (Virgin Atlantic 2016). Upper class customers receive airport transfers thus making the outbound logistics admirable and impressive (Carter 2014). The passengers are transported in Limousines or Volvos. The outbound logistics at this firm are therefore exemplary and admirable.
Marketing and Sales
Marketing is a powerful strategy that supports the firm’s objectives (Notis 2015). The first thing taken seriously at the company is advertising. The “corporation advertises its services and products using television channels, posters, direct mails, magazines, and taxi presses” (Virgin Atlantic 2016, para. 6). The company uses promotional strategies to attract more customers especially during low seasons. Virgin Atlantic’s club membership ensures the targeted passengers earn points depending on the distance covered. Such points can be exchanged for a wide range of rewards such as free flights. The company uses competent agents to sensitise more customers about its superior services. Promotional schemes, campaigns, and educational events are also embraced at the company.
Services
The services provided to Virgin Atlantic’s customers are usually improved using continuous innovation (Chaffey & White 2010). Research and development (R&D) is embraced at the company to come up with new initiatives that can add value to more customers. The company has been recognised globally because of the superiority of its services. The firm offers upper-class suite to its customers. This suite is characterised by comfortable beds. This fact explains why the company is admired by many customers from different parts of the world. Passengers from the airport can use the firm’s limousine services (Notis 2015). Continuous improvement is taken seriously in order to ensure enhanced services are available to the targeted customers.
How Virgin Atlantic Can Deploy Information Technology
The current situation shows clearly that Virgin Atlantic is a leading provider of exemplary services to many passengers. The firm analyses the diverse needs of its customers in order to design the most appropriate business strategies (Chaffey & White 2010). The corporation uses its resources to deliver desirable and timely services to more customers. However, the above analysis shows clearly that some gaps continue to affect the company’s profitability. The increasing level of competition and complexity continue to affect Virgin Atlantic’s performance. The company can use information technology (IT) to improve its business processes and enhance competitiveness.
Modern information systems can be used to analyse the current productivity, performance, and profitability. Such information systems will present evidence-based data to make the most desirable decisions. Decision support systems (DSSs) can help the managers at Virgin Atlantic to come up with powerful ideas that can transform the company’s business strategy (Virgin Atlantic 2016). The company will implement new practises and processes that have the potential to support the diverse needs of the customers.
Modern IT has the potential to support the concept of lean. The lean approach is used to identify the major gaps affecting the firm’s performance. The model can help Virgin Atlantic identify and reduce wastes (Virgin Atlantic 2016). Information technology systems can be used to gather data from different departments and processes. More passengers can be encouraged to present their views about the company’s strategies. By so doing, the corporation can address the major gaps affecting its performance.
The satisfaction of the passengers is one of the major strategies towards improving the level of profitability. The firm can use modern technologies to provide superior services to its customers. A new business model should be developed to address the needs of more passengers. Such technologies can be used to improve the level of security and safety (Chaffey & White 2010). The provision of 4G internet and handheld devices to the passengers will support the firm’s business model. Such measures will improve the company’s business processes and eventually deliver the best results.
The R&D department at Virgin Atlantic can embrace the use of IT to come up with innovative systems and applications to guide more passengers (Scarborough & Cornwall 2014). For instance, new apps showing new products and services at the corporation can make it possible for more customers to realise their potentials. Such apps will also improve the firm’s marketing and advertising strategies.
The company has the potential to benefit significantly from modern social media networks. Many successful companies are currently using social media platforms to advertise their services and attract more customers. Some of these social networks can be used to communicate and inform more people about the products provided by the company (Scarborough & Cornwall 2014). By so doing, Virgin Atlantic will ensure more people are informed about the company’s business model.
Modern technologies can be combined to form a powerful online community. Such communities are widely embraced by corporations that want to initiate powerful debates about their unique products. The use of an online community will ensure every individual is updated about the services, discounts, and products associated with the company (Notis 2015). These initiatives will play a positive role towards enhancing the company’s competitive position.
References
Atras, A 2013, ‘Virgin Atlantic’s branding on social media: leveraging brand attitudes and brand activity’, Brand Base, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-13, Web.
Carter, J 2014, Marketing Plan Example: Virgin Atlantic Little Red, GRIN Verlag, London.
Chaffey, D & White, G 2010, Business Information Management, Financial Times Management, London.
Notis, I 2015, ‘Virgin Atlantic Airways: a look inside the airline’s green initiatives’, CU Scholar, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-45, Web.
Scarborough, N & Cornwall, J 2014, Entrepreneurship and Effective Small Business Management, Pearson, New York.
Virgin Atlantic 2016, Web.
Appendix