Planning the design for medical supplies warehouses, developing storage, and elaborating retrieval methods, companies are left to make a decision on their own. Very little guidance has been provided for storing pharmaceuticals in the warehouses. However, there are several recommendations for keeping them safe before they get to the pharmacies. The proper layout of a warehouse will ensure effective functioning, receiving, and delivery of the goods. Due to the fact that the pharmaceuticals are very sensitive to multiple factors such as external contamination or temperature changes, they have to be kept in a “first-in-first-out” condition to avoid any threat. Sometimes, even the lighting and other insignificant aspects can influence medicines (Abideen & Mohamad, 2019). Furthermore, drugs must be placed in a dry devoid of humidity place, or else, they will expire or lose its potential (SciSafe, 2019). Besides, their expiration date should be considered as a primary factor for sorting them out. Therefore, these aspects of the products chosen imply that many factors must be considered prior to setting up the medical warehouse.
Effective inventory control is vital in drug storage, primarily because they are exposed to various threats. These measures must be taken in order to avoid financial and other losses. For instance, medicine potency is dominantly dependent on temperature regulations; therefore, failure to maintain the proper temperature during storage of pharmaceutical goods can lead to significant product losses. Having a refrigerated section in the warehouse allows companies to avoid massive wastage. Moreover, it is essential to monitor the temperature in those zones because there are chances of gaps. Taking into account the fact that medicines must be stored in a dry place, warehouse owners must ensure a high degree of protection of the premises from moisture intrusion (Abideen & Mohamad, 2019). What is more, many pharmaceuticals have a short expiration date; therefore, they should be sorted out according to the date stamped on its package. For example, inventory control can be performed using identification codes previously inserted into a computer program to check which ones should be marked as “out of stock”. Eventually, it is reasonable to mention that since the pharmaceuticals are very sensitive, inventory measures should be conducted quite often to ensure a safe environment for storing them.
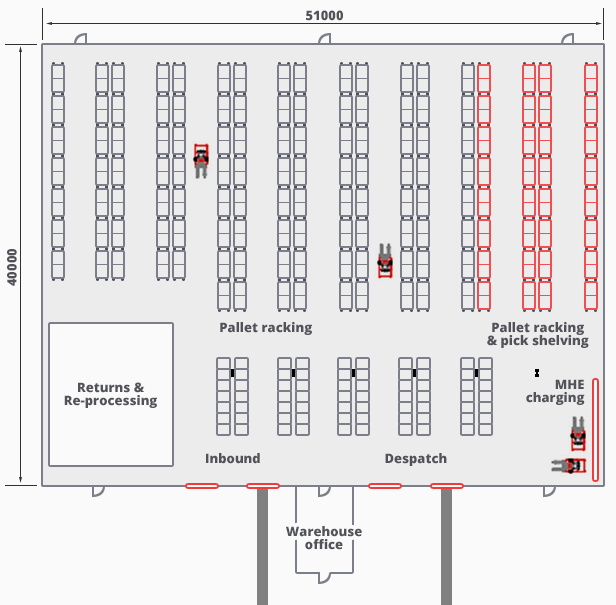
A “through” pattern of a warehouse can be implemented because it adheres to the consideration of accessibility. As the pharmaceuticals demand the “first-in-first-out” system, this design’s linear order can ensure its productivity because the goods will travel in a single direction. The flow consideration, which presumes an adequate sequence of operations, should be included here as well. Since the “through” warehouse layout comprises multiple channels that flow one way, there is less risk that someone can grab the wrong product (De Koster, Johnson, & Roy, 2017). What is more, the throughput capacity is also identified in the case of storing pharmaceuticals. Different lines of this warehouse layout may have a temperature control function, not overlapping other areas. Because drugs are dependent on climatic changes, receiving and dispatching areas should be weatherproof. Finally, the product specification consideration might be the most important as it presumes that drugs must be kept in an out-of-reach safe environment (De Koster, Johnson, & Roy, 2017). As a result, the “through” design may be best suited for pharmaceutical storage, as it provides temperature control zones, linear order, and the flowing capacity, which guarantees accurate product organization and configuration.
References
Abideen, A., & Mohamad, F. (2019). Supply chain lead time reduction in a pharmaceutical production warehouse – a case study. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing, 14(1), 61-88.
De Koster, R., Johnson, A., & Roy, D. (2017). Warehouse design and management. International Journal of Production Research, 55(21), 6327-6330. Web.
SciSafe. (2019). Understanding the importance of temperature control in pharmaceutical stability. Web.
Warehouse Design