Introduction
LRH Products is planning to attend a major trade show event in Sacramento, CA. For attending this project, plan should be prepared. The project includes activities like updating the trade show display; re-stock the collaterals, giving new orders for the collaterals, transportation of the trade show materials, setting up the display items in the show and travel arrangements. The sales people should be identified and trained for the display. As the marketing head is a new person to the organization, Pat and Terry will be assisting in the trade show project. The main objective of this report is to prepare a work breakdown structure for the trade show. The work breakdown structure includes all tasks and their dependencies, schedule, cost, and other resources required.
Work breakdown structure (WBS) – A general overview
“A work breakdown structure in project management and systems engineering is a tool used to define and group a project’s discrete work elements or tasks in a way that helps to organize and define the total work scope of the project.” (Work breakdown structure, 2009). Work breakdown structure breaks a complex project into individual components in the hierarchical structure. Thus, the individual tasks can be completed without depending upon other tasks with adequate resources. It helps to organize all the operations related to a project in a sequential basis Work breakdown structure is considered as the foundation of project planning. It also helps to identify the CPM and PERT activities of the project. The work breakdown structure helps in project planning, scheduling, budgeting and reporting of the performance of the project.
Construction of work breakdown structure
A work breakdown structure could be constructed in two ways: By bottom up approach and top down approach. In the bottom up approach, all the individual tasks are grouped together based on their relationship with each other. In top down approach, the whole project is broken into detailed tasks or phases. Work breakdown structure could be constructed using excel spreadsheet or with specific WBS software. (Stanek, 2008). 100 % Rule is one of the most important design principles of work breakdown structure. The 100% Rule states that work breakdown structure includes 100% combination of all tasks and activities, which should be completed for the accomplishment of the project.
WBS helps to obtain best solution for the estimation of labor hours, labor costs and other resources cost. Work breakdown structure breaks the total project into smaller units for the successful achievement of the objectives. The format of WBS is as follows
Level 1 – Program, Level 2 – Project, Level 3 – Task, Level 4 – Subtasks Level five – Work package. Here the program refers to the combination of several projects. The second level project is classified into different tasks and sub-tasks. A work package shows the tasks undertaken by a single department or organizational unit.
Work breakdown structure for trade show
Levels of work breakdown structures of trade show
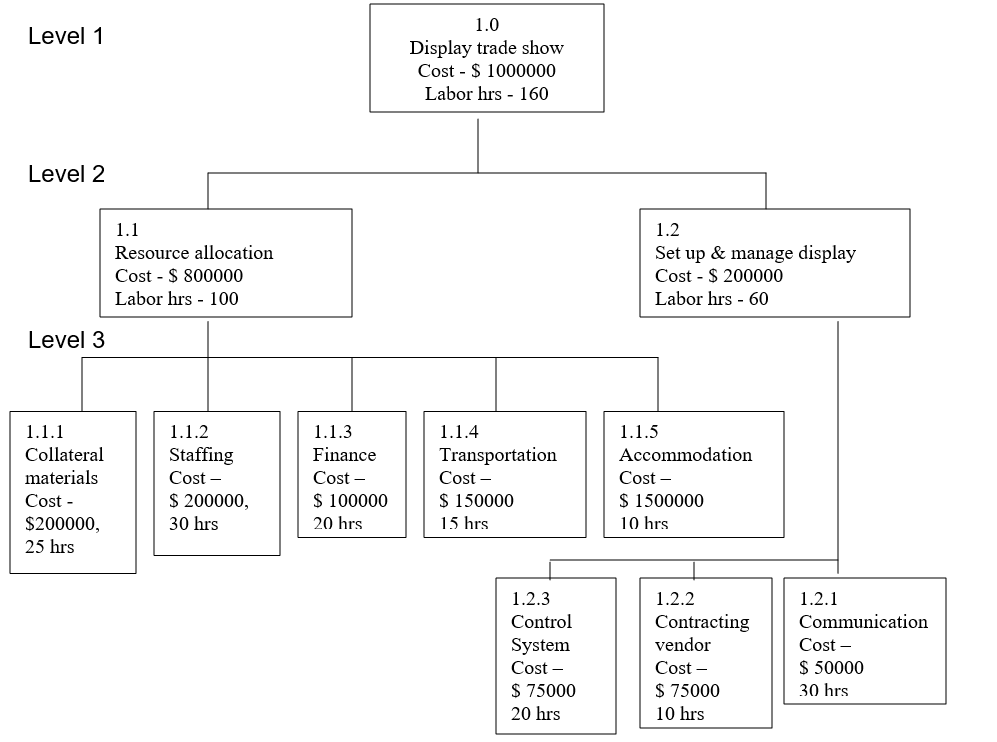
In this case, the work breakdown structure is prepared using top down approach. The tasks in the WBS require resources and an estimation of the labor hours and cost associated with performing the task. After the estimation, the cost is entered in the work breakdown structure. The top level shows ultimate cost and labor hours required for performing the project. The top-level labeled 1.0 is the title of the project. Then whole project is continuously divided until the tasks could be assigned to individuals. Breaking down the work into individual task is decomposition process. The following shows the different levels of work breakdown structure of trade show.
- Level 1: the ultimate project trade show.
- Level 2: here the project is mainly divided into two tasks – resource allocation, and set up and manage display. For a trade show, various pre-show activities should be conducted like arranging the collateral materials, staff, finance, vehicles for transportation, accommodation etc. In the set up and managing task, onsite display is arranged to be attractive for the audience.
- Level 3: here the tasks are divided into sub-tasks. The resource allocation task is divided into sub-tasks like arranging collateral materials, staff, finance, transportation vehicles and accommodation. Set up and manage display is divided into communication, vendor contracting, and control system.
The following figure shows the levels work breakdown structure of trade show.
- Display trade show
- Resource allocation
- Collateral materials
- Check the stock level
- Estimate the requirement
- Order for new
- Check the supplied materials
- Packing of materials
- Checking of all materials packed
- Staff
- List all sales staff
- Screening
- Selecting the staff
- Training
- Deciding uniform for staff
- Taking measurement
- Procurement of uniform
- Allocating to staff
- Finance
- Sources of funds
- Estimation of cost
- Transportation arrangements
- Inviting quotations of vehicles for transportation
- Review of proposal
- Finalize it.
- Arrangements for accommodation
- Estimation of the guests arriving for the trade show
- Identify the alternatives for accommodation.
- Evaluate the alternatives based on cost and services
- Choose the accommodation areas.
- Set up and manage display
- Communication
- Contracting with vendors
- Identify the vendors
- Select vendors for all key show materials.
- Control system
- Make the warehouse arrangements for storing the materials
- Transportation of materials to the site
Cost breakdown structure of trades show and estimated labor hours
Let the allocated budget for the overall project be $1000000. As the top down approach is used, we can allocate the task budgets according to the scope of the individual tasks. Budget is allocated for the entire project and then the cost is rolled into the individual phases. “A task appearing in the WBS may be broken down into several subtasks in further project planning. However, if a project task cannot be traced to a task appearing in the WBS, the task is out of scope and should not be performed without an official modification of the WBS.” (The work break down structure 2008). As the trade show project begins 10 weeks ago with 16 hours per week, then total labor hours is 160 hours. The task budget and the estimated labor hours are shown in the following work breakdown structure.
Conclusion
In day-to-day dynamic environments, we can see many projects. Therefore, each project should be carefully planned and scheduled for its successful completion. Work breakdown structure is an efficient tool for planning and allocation of resources like cost, labor hours. It also helps in project control. Normally work breakdown structure occupies a tree structure. Usually a work breakdown structure is used for small projects, as the tree structure would be complex for large projects.
Reference
Stanek, Rich. (2008). Project management tools WBS, OBS, & RAM. TRIUMF. Web.
The work break down structure: An important point. (2008). IT Economics Corporation. Web.
Work breakdown structure. (2009). Absolute Astronomy.com. Web.