Group Activity
This analysis will dwell on the quarterly meeting of the AIDs (Immune Deficiency Syndrome) Monitoring and Support Committee held on August 13 2011 at the Medicare Hospice conference room.
Type of Group
This is a professional group that was mandated to oversee the implementation and evaluation of a healthcare project that was established in the year 2010. This project was established to monitor the progress of the healthcare facility in the aspects of AIDS prevention, treatment and the efficacy of the AIDS support group.
Group Participants
- AIDS Specialist (AS)
- AIDS Support Group Chairperson (ASGC)
- AIDS Support Group Coordinator (ASG)
- AIDS Support Group Spokes Person (ASGS)
- AIDS Treatment Coordination Officer (ATCO)
- Senior Hospice Counselor (SHC)
- Disease Control Analyst (DCA)
- Senior Hospice Nurse (SHN)
Goals/Purposes of Group
The overall goal of this committee was to ensure that all Medicare Hospice patients suffering from AIDS receive high-quality medical services through proper treatment, follow-ups and professional counseling from the AIDs support group. Specific goals include:
- Monitoring the progress and effectiveness of the AIDS support group.
- Monitoring the progress of AIDS patients’ general health condition.
Member Commitment and Cohesiveness
Baring in mind that the members of this group volunteered to be part of the committee, all the members were committed and determined to ensure that the group achieved its overall goal. For example, members of this group are united with a passion for ensuring quality healthcare services for patients affected and infected by AIDS. Therefore the unity in the group is a clear indication of cohesiveness (Blais & Hayes, 2011).
Leadership Style and Role
This group embraced a democratic leadership style that allowed all the members to actively participate in the decision-making process. In addition, the team nominated a chairperson (AIDS Specialist) who coordinated the meeting and offered professional guidance on contentious medical issues that the group considered while making individual suggestions.
Type of Decision Making
The group employed a collective decision-making process. This process requires that all members come up with a solution to the issue under discussion. This is later followed by group deliberations on all the presented solutions before settling on one option through voting.
Examples of Member Behaviors/Participation
The level of participation in this group was very high. However, the level of participation for the support group representatives was quite low as the three members largely relied on the directions of the other group members. The chairperson was tasked with coordinating the meeting and maintaining order during discussions. Also noted includes the Senior Hospice Counselor’s domineering behavior.
Group Interaction Pattern
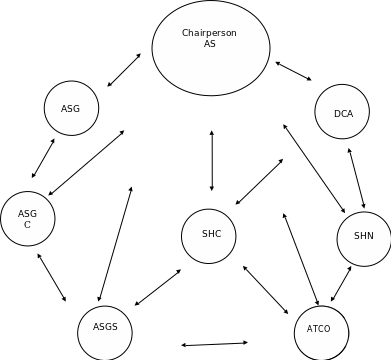
The interaction pattern of this group was majorly controlled by the chairperson (AIDS Specialist). He initiated all the agendas while members frequently directed their views to him and sometimes to the other group members. This is illustrated in the sociogram.
Power in Group
In this group, it was apparent that though the leadership and decision-making process were democratic and participatory, the chairperson and the Senior Hospice Counselor seemed to control some of the major agendas through their repeated interruptions throughout the meeting. The rest of us had average powers while the three Support Group Representatives had no powers at all.
Group Effectiveness
The group was very effective, for instance, the meeting started on time with all members present and all the outlined agendas were discussed comprehensively and decided upon. Therefore, the group was very effective in terms of achieving the goals of the meeting.
Improving Group Process
As outlined earlier, the group had a power and participation issue. If I was the group leader, I would have dealt with the issue by ensuring that all members participate equally by allowing all members equal opportunities to air their views. Domineering would be highly discouraged as members will only be allowed to communicate or air out their views under my directions. This will ensure that all members feel equally important in the group, therefore, ensuring equal participation and distribution of powers (Blais & Hayes, 2011).
Sociogram
The initials represent the respective members of the group as indicated on the participants list.
References
Blais, K. K., & Hayes, J. S. (2011). Professional nursing practice: Concepts and perspectives (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.