Introduction
Google Incorporation is presently one of the most profitable and competitive technology giants in the United States and across the globe. This organization provides a unique product portfolio designed to attract more users and support their advertisement aims. The available platforms use a free-use model intended to ensure that most of these resources are available to more people.
The company relies on data and adverts to support its wider business strategy. The emerging model is designed in such a way that adverts form the primary niche. With competition becoming a reality in the global technology sector, Google’s future depends on its ability to implement a cost leadership strategy, pursue innovation, and improve its approaches to research and development.
CASE Analysis: Context
Key Elements
The application of an effective generic competitive strategy allows Google to overcome the challenge of competition, attract additional customers, and meet their changing demands. Twigg-Flesner (2021) observes that the differentiation approach is closely related to this company’s competitive approach. Specifically, Google has developed additional capabilities, products, and platforms that have the potential to meet the changing demands of more people. The company ensures that most of these offers are unique and innovative.
For instance, customers can consider a wide range of products, such as Google Chrome, Android, mobile applications, and desktop software (see Fig. 1). The company takes the process of innovation seriously to improve user experience and mitigate the problem of competition. Google Search relies on the use of an advanced algorithm in order to make the company successful. Applying this generic strategy has played a critical role in improving this company’s market share. The promotion of this kind of generic strategy means that the organization will achieve its future aims.

Analysis: PESTEL
Political Factors
The global business environment relies on government policies and guidelines that dictate Google’s operations. In the recent past, several governments have supported free trade arrangements that are influenced by globalization. Google is finding additional opportunities in different parts of the world characterized by stable political environments (MarketLine, 2020). The corporation could consider additional ways to tap emerging markets while avoiding riskier regions characterized by breaches of privacy and hacking.
Economic Factors
The economic forces and trends experienced in different regions determine the overall level of business activity. In different regions, customers and clients rely on globalization and emerging business activities to pursue their aims. During recessions, more people would be unwilling to advertise their services (Siddiqui, 2021). Nonetheless, Google is benefiting from the economic stabilities associated with most of the markets in developing and developed countries (Kim, 2020). Emerging business opportunities and support of upcoming enterprises are powerful trends capable of taking Google closer to its goals.
Social Factors
The fact that Google operates across the globe means that it attracts potential customers with diverse cultural backgrounds. Individuals will rely on the existing social attributes to pursue their aims while relying on online resources. The increasing adoption of social media platforms is a common trend under this category.
The presence of social media networks, such as Facebook, could directly affect Google’s competitiveness (Kim, 2020). The recruitment model should be informed by these unique attributes associated with customers. The force of globalization is compelling more people to merge their cultural perspectives while respecting each other whenever pursuing international business goals.
Technological Factors
As a company directly competing in the global technology sector, Google’s leaders should be aware of the factors associated with this. For instance, more people can acquire handheld devices and access the Internet than ever before (Pereira et al., 2022). Cloud services are influencing the goals and performances of more firms in this sector. The wave of telecommunication and information integration is allowing Google to venture into emerging markets across the globe. The presence of computers, advanced infrastructure systems, and the increasing consumption of technology reveal that unique opportunities exist for marketing Android and sharing its hardware and search engine resources.
Environmental Factors
Google’s business model is designed in such a way that it relies on the Internet for its services. Nonetheless, more consumers prefer to do business with companies that engage in additional activities intended to protect the integrity and sustainability of the natural environment (Kiracı and Çalıyurt, 2022). Emerging policies are compelling firms to focus on recycling methods to reduce the problems of climate change (Muteshi and Kariuki, 2020). More companies are pursuing environmentalism as an emerging tactic for attracting more stakeholders and liaising with ethical suppliers. Green reporting is a new trend that is allowing companies to meet the changing demands of their customers.
Legal Factors
Regulatory requirements is becoming a norm in different sectors today. Most companies operating online should consider existing confidentiality, privacy, and intellectual property (IP) laws. Governments are introducing strict restrictions to protect personal information against any form of theft or cybercrime (Fellmeth, 2020). The international community is compelling corporations to impose stricter privacy measures (Sergio, 2022). Google, therefore, needs to consider these issues, embrace emerging regulations, and enhance proper IP protection measures. These efforts can make it easier for Google to compete successfully in the ever-changing online business environment.
Situation
Situation analysis is an evidence-based approach used to apply various tools and models to monitor the existing relationship between a company and its overall external and internal forces. Such factors have the potential to affect organizational performance and subsequent profitability (Fligstein, 2021). The application of such frameworks allows investigators to get a clear picture of the macro-environment and how to address notable threats to competitiveness (Mansaray, 2019). Some recommended tools for Google include SWOT analysis, Porter’s generic forces, financial ratios, and Value Chain Analysis (VCA).
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Google has unique attributes that make it a reputable brand in the global technological industry. First, it is associated with the best search engine, making it a market leader, thereby attracting an increasing number of customers. Second, Google has established a powerful business model that supports the continuous generation and attraction of user traffic to most of its platforms (Verhoef et al., 2021). Third, the ability to generate revenues from display and advertising platforms makes it possible for the company to remain competitive. Fourth, the company has unique software products and operating systems that are revolutionizing the sector, such as Android.
Weaknesses
Despite the presence of unique features and products that make Google an outstanding company, it has unique weaknesses that could impact its future performance. For instance, the established business strategy allows the corporation to depend primarily on adverts (Yi, Park and Kim, 2019). This approach reduces the chances of attracting more users and maximizing profitability (Ongaro and Ferlie, 2019). In the recent past, the company has been reporting a decline in the rate of its adverts, a trend that could have negative consequences (MarketLine, 2020). Additionally, most of the developed products and software are not designed in such a way that they are compatible with emerging devices.
Opportunities
Several opportunities exist that have the potential to support and sustain Google’s business model and future performance. The first one is the fact that more mobile phone companies are still producing high-quality products relying on Google’s Android operating system (Benzaghta et al., 2021). The second opportunity is the emergence of additional niches and trends that make it possible for Google to diversify and invest in other segments that do not rely solely on advertisements (Levenson, 2018). The third one is the fact that Google Play is becoming a one-stop shop for most of the software systems and apps associated with the company (Valacich, 2022). Finally, the benefits of cloud computing have the potential to support this company’s business model and future goals.
Threats
The ever-changing nature of the technology industry means that Google will continue to grapple with emerging challenges or threats. First, competition is becoming a reality due to the strategies Facebook and other social media platforms are putting in place (see. Second, most of the products emerging in the industry are capable of directly competing with those of Google, such as the ones associated with Amazon and Apple (Chen, Liu, and Gong, 2021). Third, mobile computing is changing the use of Google’s search engine, a trend that could affect its future attractiveness (Sukri and Yusoff, 2019). Legal issues could have detrimental impacts on this company’s profitability.
Porter’s Five Forces
Competitive Rivalry
Google operates in an ever-changing industry characterized by large and competitive corporation, such as Apple, Amazon, and Facebook. The diverse nature of most of these companies makes it easier for them to produce revolutionary products and increase the overall level of rivalry in various market segments. Customers in this field can switch from one product or platform to another with ease (Kusumawijaya, 2020). These trends indicate that the power of competitive rivalry for Google remains strong and capable of affecting its current and future goals.
Bargaining Power of Customers
Google’s superior products are irresistible to most of the customers while making it easier for them to pursue their aims. The company has a wide portfolio capable of segmenting and meeting its needs. The small size of such consumer groups makes it impossible for them to compel the company to make significant changes in the available products or business model (Fartash et al., 2018). The company determines the quality of content and information users can upload or share on some of the available platforms (Kim, 2020). These stakeholders continue to demand and rely on such products to pursue their needs. Consequently, Google’s intensity of this force remains low to moderate.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The existing statistics reveal that Google has established a unique business model that reduces the overall involvement or power of suppliers. For instance, the company can receive supplies from more players at reduced prices (Yeshitila et al., 2020). The increasing availability of resources from different suppliers weakens this force.
The small size of most of these partners makes it impossible for them to affect the company’s performance (Islami, Mustafa, and Latkovikj, 2020). Some of them include suppliers of hardware systems that support the established business model. Consequently, the intensity of this force for Google is weak, thereby making it incapable of disorienting its overall business model.
The Threat of Substitutes
Some of the substitute products that customers can select from include print media, television, and social media platforms. Google’s leaders have realized that such resources could affect the overall level of competitiveness and reduce revenues. Kulick (2021) indicates the switching costs for most of these substitutes would remain moderate.
Additionally, the substitutes are available and accessible to an increasing number of customers (Sukri and Yusoff, 2019). However, the expensive nature of print media and TV adverts could explain why Google might continue to remain dominant in the sector. These attributes reveal that the nature of this force remains moderate for Google.
The Threat of New Entrants
The global technological sector is allowing more companies to emerge and invest in the sector. Most of these newcomers will not require huge startup costs due to the existence of the Internet, affordable infrastructure, and cloud computing services (Wang Z. et al., 2020). The cost of developing new brands and products is quite low (Lanzolla and Markides, 2021). Emerging companies will find ways to fulfill the major legal requirements if they are to become operational (Quezada et al., 2019). Based on these attributes, it becomes quite clear that Google faces a moderate force from possible new entrants.
Value Chain Analysis (VCA)
Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is a framework that analysts apply to evaluate the major activities defining a firm’s value chain in order to pinpoint existing opportunities and areas for improvement. According to the VCA model, Google’s primary activities are designed in such a way that they support performance. Most of the value arises from the company’s inbound logistics (Wirtz, 2020).
The company’s search engine allows users to generate positive results, thereby reducing inbound costs as a critical aspect of its business strategy. The use of revolutionary equipment makes it possible to support business activities (see Fig. 2). In terms of operations, the company competes in over 40 countries across the globe. Its headquarters offer the best organizational culture for workers.
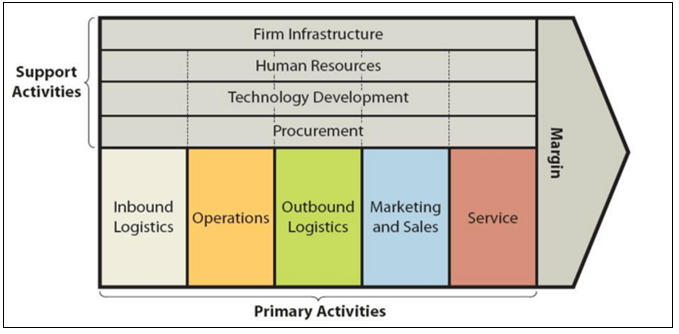
Outbound logistics is missing since the company relies on advert integration and online search to support the needs of the customers. The marketing model revolves around the use of both offline and online channels of communication to attract and inform an increasing number of customers (Gul, 2020). Its promotional expenses have increased significantly to over 3 billion US dollars in 2015 (MarketLine, 2020). Under the service category, Google offers forums that allow users to identify and address emerging technological issues. Additionally, the corporation provides proper customer support to ensure that more individuals are satisfied.
Financial Ratios
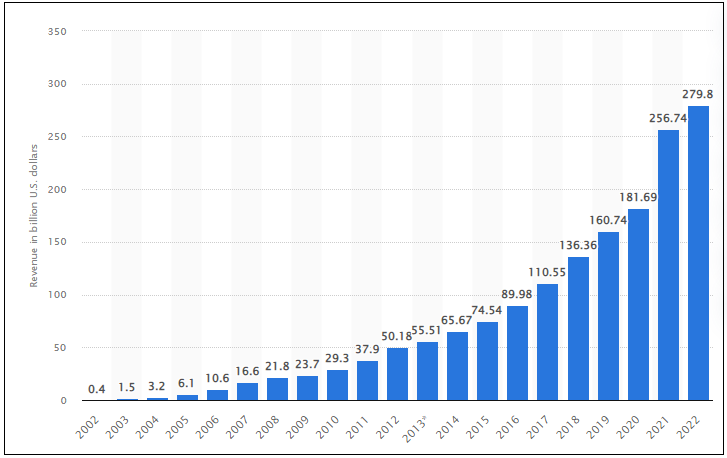
Google stands out as one of the most successful companies in the world today. For instance, the latest financial records indicate that the organization reported revenues amounting to 279.8 billion US dollars (see Fig. 3). The advertising segment contributed around 224.5 billion US dollars to this figure (see Fig. 3).
Alphabet, Google’s parent corporation, recorded a market capitalization of more than 1.39 trillion US dollars (Farida and Setiawan, 2022). In 2021, Google reported revenues of around 256.74 billion US dollars (see Fig. 3). From the presented chart, it is agreeable that the company has been increasing its annual earnings since 2002 (see Fig. 3).
Price-to-Sales Ratio
Alphabet’s financial ratios show clearly that Google has been performing excellently. For instance, the last three financial year periods reveal that the parent company’s price-to-sales ratio (P/S) has been averaging 6.01. This figure indicates that the company is performing excellently and above the industry value of around 4 (Soelaiman and Ekawati, 2021). This ratio is essential since it reveals the value investors will place on revenues earned in terms of US dollars.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) for Google in 2019 was 0.08 (MarketLine, 2020). This figure shows conclusively that the corporation relied on its financial gains to fund most of its business activities. In 2020, the recorded D/E increased significantly to around 10 percent. Valacich (2022) indicates a figure of less than 100 percent would be appropriate for a given business corporation. More investors have been keen to do business with Google, thereby supporting its overall competitiveness.
Price-to-Earnings Ratio
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is a useful framework that analysts apply when comparing the share price of a given organization with its earnings for every share. Since 2020, Google has been reporting a P/E ratio of around 29.02 (GorjianKhanzad and Gooyabadi, 2022). This figure is a clear indication that its value is around 15 times higher than the industry average. This means that the company continues to report a higher valuation in relation to its average earnings (Sewpersadh, 2023). The organization might continue to attract more investors and eventually remain competitive in its business sector.
Problems
Despite being a leading competitor in the global technology industry, Google is presently facing unique challenges that might affect its future profitability. First, the existing organizational culture has been characterized by major malpractice whereby the leadership focuses mostly on aberrant geniuses to support product development (Yuniati et al., 2021). This approach discourages more people, thereby compelling them to find better opportunities elsewhere.
Second, the completed analysis indicates that Google is attracting competition from existing companies such as Facebook, Apple, and Amazon (Alshmrani, 2021). These trends explain why Google needs a superior model to retain and meet the demands of more customers. Third, the problem of data privacy has the potential to attract new challenges unless proper mechanisms are put in place.
Solution
The best solution to address most of the challenges affecting Google is the use of a cost leadership strategy. Under this model, the corporation should consider an effective strategy to reduce the charges for its online-based adverts (Wurthmann, 2019). This is possible if the organization pursues the best economies of scale, supports technological advancement, and exploits existing industry opportunities (Donthu and Gustafsson, 2020).
The ultimate business aim should be to realize and support cost leadership. This achievement means that the company will attract and retain an increasing number of customers, thereby overcoming the current challenge of competition (Casañ, Alier, and Llorens, 2021). The emerging revenues will be utilized to improve data privacy and take the corporation closer to its business aims.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Google is a competitive company that operates in the global technology industry. Its wider product portfolio, progressive business model, and software apps support the company’s strategy. However, additional strategies are necessary to ensure that Google addresses most of the identified threats and weaknesses.
The consideration of a cost leadership strategy could ensure that the company overcomes competition while encouraging more clients to place their adverts at reduced charges. Those in leadership can consider evidence-based ways to improve the existing organizational culture and empower all employees. The organization will need to engage in R&D to deliver additional products that resonate with the changing demands of the targeted customers while responding directly to the issue of rivalry in the industry.
Reference List
Alshmrani, H.M. (2021) ‘An analytical view of Amazon success in the worldwide’, Life Science Journal, 18(6), pp. 71-90. Web.
Benzaghta, M.A. et al. (2021) ‘SWOT analysis applications: an integrative literature review’, Journal of Global Business Insights, 6(1), pp. 55-73. Web.
Casañ, M.J., Alier, M. and Llorens, A. (2021) ‘A collaborative learning activity to analyze the sustainability of an innovation using PESTLE’, Sustainability, 13(16), pp. 8756-8771. Web.
Chen, X., Liu, Y. and Gong, H. (2021) ‘Apple Inc. strategic marketing analysis and evaluation’, Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 203(1), pp. 3053-3061. Web.
Donthu, N. and Gustafsson, A. (2020) ‘Effects of COVID-19 on business and research’, Journal of Business Research, 117(1), pp. 284-289. Web.
Farida, I. and Setiawan, D. (2022) ‘Business strategies and competitive advantage: the role of performance and innovation’, Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), pp. 163-178. Web.
Fartash, K. et al. (2018) ‘The impact of technology acquisition & exploitation on organizational innovation and organizational performance in knowledge-intensive organizations’, EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(4), pp. 1497-1507. Web.
Fellmeth, A.X. (2020) Introduction to international business transactions. Northampton: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Fligstein, N. (2021) ‘Innovation and the theory of fields’, AMS Review, 11(3), pp. 272-289. Web.
GorjianKhanzad, Z. and Gooyabadi, A. (2022) ‘Digital strategizing: the role of the corporate culture’, Open Journal of Business and Management, 10(1), pp. 2974-2995. Web.
Gul, M. (2020) ‘Digital business strategies and competitive superiority’, International Journal of Business Ecosystem & Strategy, 2(1), pp. 17-31. Web.
Islami, X., Mustafa, N. and Latkovikj, M.T. (2020) ‘Linking Porter’s generic strategies to firm performance’, Future Business Journal, 6(1), 3-17. Web.
Kim, H. (2020) ‘The analysis of innovation management in Google’, Journal of Economics and Management Studies, 3(4), 10-19. Web.
Kiracı, K. and Çalıyurt, K.T. (2022) Corporate governance, sustainability, and information systems in the aviation sector. New York, NY: Springer.
Kulick, A. (2021) ‘Corporate human rights?’, European Journal of International Law, 32(2), pp. 537-570. Web.
Kusumawijaya, I.K. (2020) ‘Understanding entrepreneurial intention: the prediction of entrepreneurial behavior’, International Review of Management and Marketing, 10(4), pp. 35-42. Web.
Lanzolla, G. and Markides, C. (2021) ‘A business model view of strategy’, Journal of Management Studies, 58(2), pp. 540-553. Web.
Levenson, A. (2018) ‘Using workforce analytics to improve strategy execution’, Human.
Maheshone (2021) ‘Over 271 Google products & services you probably don’t know’. Web.
Mansaray, H.E. (2019) ‘The role of leadership style in organizational change management: A literature review’, Journal of Human Resource Management, 7(1), pp. 18-31. Web.
MarketLine (2020) ‘Google Inc.: revolutionary business model needs to evolve’. Web.
Muteshi, D. and Kariuki, A. (2020) ‘Corporate strategy, networking and firm performance in Africa’, Expert Journal of Business and Management, 8(2), pp. 139-146. Web.
Ongaro, E. and Ferlie, E. (2019) ‘Exploring strategy-making in ‘non-new public management’ public services settings: the case of European Union agencies’, Administrative Sciences, 9(1), pp. 23-40. Web.
Pereira, V. et al. (2022) ‘Evaluating talent management in emerging market economies: societal, firm and individual perspectives’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(11), pp. 2171-2191. Web.
Quezada, L.E. et al. (2019) ‘Measuring performance using SWOT analysis and balanced scorecard’, Procedia Manufacturing, 39(1), pp. 786-793. Web.
Sergio, R. (ed.) (2022) Managing cases: thriving organizations in the new normal. Chennai: Notion Press.
Sewpersadh, N.S. (2023) ‘Disruptive business value models’, Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 12(2), pp. 1-27. Web.
Siddiqui, A.A. (2021) ‘The use of PESTEL analysis tool of quality management in the health care business and its advantages’, American Journal of Biomedical Sciences & Research, 14(6), pp. 507-512. Web.
Soelaiman, L. and Ekawati, S. (2021) ‘The role of social media in enhancing business performance’, Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 653(1), pp. 400-404. Web.
Statista (2023) ‘Annual revenue of Google from 2002 to 2022’. Web.
Sukri, S. and Yusoff, R.Z. (2019) ‘Technology strategy: literature review and issues’, International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 8(6), pp. 67-84. Web.
Twigg-Flesner, C. (2021) Foundations of international commercial law. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis Group.
Valacich, J. (2022) Information systems today: managing in the digital world. New York, NY: Pearson.
Verhoef, P.C. et al. (2021) ‘Digital transformation: a multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda’, Journal of Business Research, 122(1), pp. 889-901. Web.
Wang, Z. et al. (2020) ‘Multidimensional perspective of firms’ IT capability between digital business strategy and firms’ efficiency: a case of Chinese SMEs’, SAGE Open, 10(4), pp. 1-15. Web.
Wirtz, B.W. (2020) Media management: strategy, business models and case studies. 2nd edn. New York, NY: Springer Shop.
Wurthmann, K. (2019) ‘The essential mix: six tools for strategy-making in the next decade’, Journal of Business Strategy, 40(2), pp. 22–33. Web.
Yeshitila, D. et al. (2020) ‘Situational and mixed business strategy analysis for market competitiveness: an exploration in context of Africa’, International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness, 15(1), pp. 106-120. Web.
Yi, H.K., Park, S. and Kim, J. (2019) ‘The effects of business strategy and inventory on the relationship between sales manipulation and future profitability’, Sustainability, 11(8), pp. 2377-2394. Web.
Yuniati, E. et al. (2021) ‘Talent management and organizational performance: the mediating role of employee engagement’, Management Science Letters, 11(9), pp. 1-6. Web.