Summary
The Internet Age brought about significant changes in the way people conducted business. New business models emerged to replace traditional business models. Google is among the e-business models that emerged to take advantage of technologies and innovation. The search engine giant needs no introduction. The company derives its success from a highly innovative e-business model that depends on online advertisements for revenues. Google has a complex e-business model. The model relies on smart decisions, a highly innovative team, effective use of technology, marketing strategies, excellent products and services, and functional leadership to execute its business strategies. This model has allowed Google to generate billions in revenues through advertisements. The company uses search, YouTube, browser, maps, e-mail, financial sites, and social site, among others to ensure that it has high-levels of a Web presence for advertisers and Internet users.
Introduction
Today, one can conclude that the Internet has taken over the business with the introduction of e-business several years ago. Scholars have referred to this as the ‘Internet Age’ or e-business revolution and evolution (Aldrich, 1999; Evans and Wurster, 1999). E-business has experienced ‘hyper-growth’ facilitated by developments and innovation in Internet technologies. Trading has become simple over the Internet, as various e-business models have emerged to fill gaps. New firms like Amazon, Google, E-Bay, Facebook, SAP, Oracle, and PayPal, among others, have developed because they could effectively conduct their business operations through the Internet. These business models have found new opportunities that were once not possible.
While observers expressed their fascination with the potential of electronic business, critical thinkers were able to develop e-business solutions that could match the demands of modern customers.
A study by Booz-Allen & Hamilton revealed that over 90 per cent of “the top managers believed the Internet would have major impacts on the global marketplace by 2001” (Booz Allen and Hamilton, 1999). This study confirmed that the Internet would revolutionize business and introduce new methods of e-commerce. Such studies helped to clear uncertainties that existed about the capabilities of the Internet in the business environment. Today, many scholars and professionals have observed changes that have taken place in the last few years because of the Internet and e-business models. This article explores Google e-business model as one of the most successful e-business models in the Internet Age.
Criteria for determining successful Internet-based business models
There are many criteria for determining a successful business model. These include the following attributes:
- Increase in revenues
- Growth in profits
- Worldwide presence and expansion into new markets
- Successful acquisitions and alliances
- Differentiation abilities
Specifically, e-business models have unique features that differentiate them from mortar-and-brick business models. These features include:
- Customized Web sites with user-friendly features
- Rare and unique products and services
- Massive investments in technologies
- Constant research and development of new technologies and innovative strategies
- User-friendly transactions
- Result-oriented marketing strategies
Successful e-business models have focused on customer satisfaction and unique experiences because of stiff competition as new e-business models emerge every day. Such high-levels of competition make customers look for businesses that offer solutions to their specific needs. E-businesses have thrived on new technologies as ways of delivering services and products to their customers and audience. E-business models strive to computerize their business processes and maintain and promote personal interaction with customers simultaneously. Successful e-businesses have exploited conventional principles in technology implementation and maintenance. According to Applegate, Internet-based business models have developed in various areas, which include customer services, direct marketing and banners, information and content sales, product sales, and subscription services (Applegate, 2001).
Overall, one must recognize that unique e-business models have relied on several related but different models of e-business together. These strategies allow e-business models to move beyond simple categorization to create diversified products and services for revenue generation and promotion of hybrid models that are cost-effective. Weill and Vitale focused on eight areas of e-business models, which included “direct customer, full-service provider, intermediary, the whole of enterprise, shared infrastructure, virtual community, value net integrator, and content provider” (Weill and Vitale, 2001). These authors based their classification of e-business models on a thorough review of past studies. These scholars reviewed each model to identify competitive strategies, revenue generation strategies, and competitive abilities, among other core factors.
Google e-Business Model
Google Inc., the e-business model, relies on simple algorithms. Today, Google has created a business model that is unique and new to the world. It has grown to be the best search engine in the world. Moreover, Google has several successful applications such as “Google Earth, Google Video, Google Maps, and Gmail among others” (Vertygo Team, 2010), which have continued to attract many users and customers. Google emerged as a new company to take over the market against its main rivals like Excite, Yahoo!, AOL, and AltaVista, among others. Hence, Google had to review its needs and values about what it could offer the market under such circumstances (Weill and Ross, 2009).
In the year 2007, Google became the fifth largest firm in the US based on its market capitalization. At the same time, the company shares price went up beyond $700. Today, it’s stock market capitalization is over $880.
In 2011, the company had over $37.9 billion in terms of revenues. Google derives most of its revenues from the finance and insurance industry, as shown in the below table (Miller, 2012).
Table 1: Some of the major revenue streams for Google, 2011
These industries spent most of their advertising dollars on Google Ad in 2011. Top ten industries spend more than 60 per cent of their advertisement budget on Google. These multiple sources of revenue highlight one major characteristic of successful e-business models.
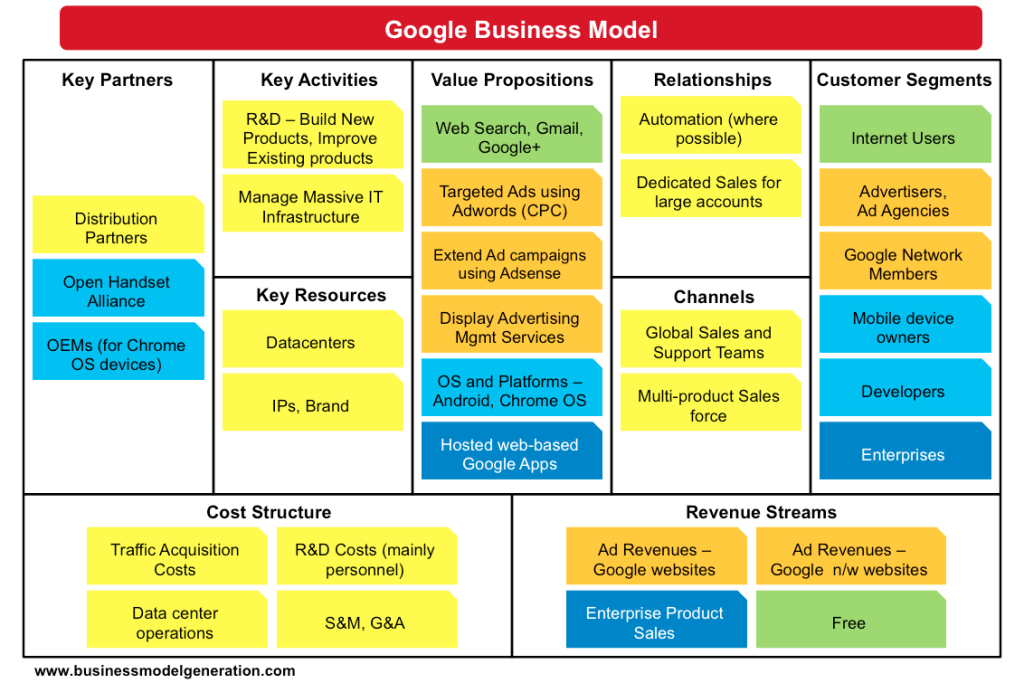
Why the Google e-Business Model is successful?
It is imperative to understand the e-business model of Google to understand why it is a successful model that has resulted from Internet technologies, innovation, and creativity.
Search engine
Spencer observes that the “current pre-dominant business model for commercial search engines is advertising” (Spencer, n.d). According to Alexa ranking, Google search engine is the most popular search engine today. This shows that the company leads to search engine applications and usages. Google has become synonymous with Web browsing (‘Google it’ as many users refer to whatever they would like to search on the Web). It is no longer search for information among users, but rather “Google it”.
Google also relies on a highly innovative team to drive its e-business model. One can easily observe this on the number of products and services that Google offers to its clients. The company uses a simple, lean user interface to make its search engine easy and fast to load. This is what search engine pioneers failed to observe in their technologies. Search engines have evolved, but developers like Yahoo! created slow search engines due to several links and banner ads, which made them exceptionally slow for users.
Google understood what customers wanted in their search engine. This is what many pioneers did not include in their models. Users wanted to get a search engine rather than banner ads that contributed to users’ challenges. Google created a user-friendly search engine that was reliable and fast. The company avoided a general portal search engine that dominated previous versions of search engines. Google understood this concept and delivered it to users.
Advertising
Google offers some free services to Internet users. However, the company generates most of its revenues from advertisers who want to appeal to online customers. In this context, Google has assisted such advertisers in relaying their messages to Internet users through Google AdWords. This is a unique idea that Google introduced to sell advertisements to online customers. The company used the Cost-per-click concept to calculate what advertisers would pay for the service. In other words, advertisers will only pay Google when visitors click on the displayed advertisement (Chau and Crawford, 2013).
According to Levy, AdWords could be “the most successful business idea in history” (Levy, 2009). AdWords can analyze Google search to demonstrate the most popular advertisement words used in sponsored links. He notes that AdWords is “the world’s biggest, fastest auction, a never-ending, automated, and self-service advertisement concept” (Levy, 2009). It is the most profitable e-business model for Google, as Levy notes that AdWords generated $21 billion in 2008 (Levy, 2009).
Academics note that Google based its online advertisement model on economic concepts. This explains why the Google search engine has dominated the market by capturing over 60 per cent of it (Levy, 2009). Also, Google relies on auction theory to analyze its operations. All these concepts exploited a simple algorithm.
Google also has Google AdSense program. This platform allows advertisers to reach Google Network members. Members receive a given amount of revenue from Google because of the displayed advertisement banners on their Web sites. The company also offers Display Advertising services based on the technology of the DoubleClick. This form of advertising service has video, images, text, and other components of multimedia to create interactive advertisements. These advertisements are common in specialized Google pages like finance, YouTube, and Google Network member Web sites.
Based on such success, it is important to understand technologies and innovation, which have worked for Google.
Technology and Innovation
Google uses algorithms for its search engine technology. This helps the company to determine its PageRank and Hypertext-Matching. PageRank technology indicates how each page is important in the ranking, and Google considers “500 million variables and 2 billion terms to determine how a page will rank in the search engine” (Google Inc, n.d). Hypertext-Matching Analysis helps in the analysis of pages and their contents to provide accurate results based on the users’ search query.
According to Weber, Google must rely on such algorithm technologies to ensure that it has “scale, speed, and efficiency to serve its rapidly growing number of users” (Weber, 2008).
Google advertisement model is unique. The pay per click concept revolutionized Web-based advertisement. This was a risky and innovative e-business model, which has generated billions of revenues for Google. AdWords has remained a significant source of Google’s revenue.
Innovative strategies have allowed Google to create some unique Web applications. The company offers most of these services at no cost to users. Some great new applications consist of the Android operating system, Google Maps, Google Scholar, Gmail, and Google Earth, among others.
Technology has been the driving force behind these innovative services and products. The company is among the leading technology giants in the world. The search engine has made Google the most preferred search tool, among other search tools. Users can get fast responses to the information they need. The company has kept various forms of data on Web sites. This allows Internet users to get information in forms of texts, images, audio, videos, and others.
Google created Android for mobile devices. Android is a free software application for mobile technologies. Handset manufacturers can download and install various versions of Android in their devices, while software developers can develop new applications for Android. This has attracted growth as several mobile devices run on Android today. The company also developed Google Chrome, which is a Web browser for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). Developers can install these software applications, or users can download, install, and update at no cost.
Today, Google works with several OEMs to ensure that many computers run on Google Chrome operating system. The company has developed several applications to serve corporate and individual clients. These are mainly Google applications, such as Google Doc, Google Sites, Google Calendar, and Google Scholar, among others. These are freely available applications.
Google has a global sales network across the globe. The company sales and support teams focus on its key products and services that include mobile, display, and search. In most cases, customers rely on self-serve strategies, which allow customers to customize and handle their processes with minimal company’s assistance. The company has a support team throughout the world. These teams of technicians assist customers in deriving value from Google applications. Also, the sales team focuses on relationship building with major firms across the world.
Focus on Costs and R&D
The company’s business models focus on four critical areas for growth. These include Research and Development (R&D), sales and marketing, Traffic acquisition, and data centre. Google has massive investments in R&D. This allows the company’s engineers to develop new products and enhance the usability of the available ones. The company has millions of servers that handle billions of requests daily. Google has invested and maintained its data centres despite high costs. The company also incurs expenses by compensating its Google Member Web sites, which run the AdSense advertisement scheme. Google must also compensate others who help it to distribute Google Toolbar to users. These are critical applications, which help the company to drive large traffics to its servers. The company must also maintain its global sales and marketing department.
Over 95 per cent of Google’s revenues originate from advertisement activities. Although the company has focused on applications for mobile devices, such attempts, and OS for mobile devices have not generated major incomes for Google. In fact, in 2010, experts questioned Google’s ability to “generate revenues from its Nexus One phone business model because it based the business model on a vision that was not possible in the US phone market at the time” (Gohring, 2010).
Industry observers believe that Google’s main source of revenues will continue to grow from its new applications and investments. These include Google Glass and entry into the mobile phone business. Moreover, the company may get success from wearable computer products and several recent acquisitions. Google has an effective e-business model that relies on strategies (McKeen and Smith, 2011).
What makes Google e-Business Model Unique?
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Google has more than 60 per cent of the search market shares. The company has enough servers to handle over a billion requests each day. The company has maintained its data centres through massive investments. This strategy has created economies of scale and scope for sustainable competitive advantages. In other words, new entrants in search engines cannot match such large investments.
Also, Google has a robust R&D department, which leads the market through innovative products. Hence, this model has worked well because no competitor can match Google in sustainable competitive advantage.
Porter and Barney presented the most significant concepts in business strategies (Porter, 1991; Barney, 1991). Porter notes that the “low-cost and differentiation advantages that firms enjoy on the product market ultimately stem from initial conditions and managerial choices” (Porter, 1991). Porter observes that executives’ decisions have critical effects on drivers of the business, which are usually resources that employers must work on in order to create low costs and establish differentiation among competitors. Eisenhardt and Sull note that it is simple to identify such business advantages in a company’s position “on the product market, in its resource base or in the key processes – all of which could be referred to as components of a business model” (Eisenhardt and Sull, 2001).
Unique network presence
The Google search engine serves any user. Advertisers have been able to gain competitive advantages from Google because of millions of users who rely on the Google search engine. Also, the focus on Android application will allow Google to create a larger base of users for its advertisement customers. The company’s focus is on mobile advertisement as consumers switch to mobile devices.
Google relies on words that Internet users enter in the search engine to generate traffic. The company ensures that its computers monitor the activities of users. It then uses the keywords people use to generate traffic for the advertiser.
Revenue predictability
Google created a self-serve system for customers to generate maximum revenues with minimal investments. However, it is not simple for competitors to understand possible revenues that Google may generate in subsequent years because the company has managed to keep such information as private and has never disclosed such data. From them. Moreover, it is equally difficult to determine the growth of Google’s customer base. As businesses move online, one can be sure that Google’s e-business model will continue to generate huge revenues, and the company will benefit significantly.
Customer retention strategy
Google has a simple way of keeping its customers. The company aims to create lifetime value from its customers. In other words, Google has locked-in its users by providing all applications, which can serve their various needs while on the Internet. For instance, the company has more than 350 million users of its e-mail application. Google has created other applications, such as photos, video, and image sharing platforms, blogs, and document hosting to keep these users. Customers, including corporate customers, have noted that it is simple to use Google applications in their Web activities. This is a form of locking and retaining customers.
However, one must observe that Google sources of revenue are mainly its advertisement clients. This is like a single source of revenue. However, Google created a system in which its customers can only accept the imposed rate of advertisement without bargaining because it is a form of self-auction service.
In addition, Google does not depend on a single industry for revenue generation. It focuses on several industries. This helps the company to avoid risks associated with a high dependency on a few revenue streams.
The Google e-business model runs strategic partnerships through Google Network members. These companies can reach millions of users through Google platforms (AdSense). In turn, the company has to share incomes with its affiliates. These are members, which would find it impossible to conduct any business without Google AdSense. At the same time, the company has strong grips on traffic acquisition partners. These partners are responsible for driving Internet traffics to Google Web sites. They are major sources of revenue for the company.
However, it is important to note that Google has created win-win situations for all its partners and affiliates. Moreover, the company does not rely on them to generate its revenues. In other words, these partners need Google to be in business.
The company culture insists on innovation. Google has excellent leadership that fosters creativity, which leads to the development of new products and services. The company leadership has focused on new approaches to profit generation and in situations where leadership encourages developments of new business models with interests (Austin, Nolan, and O’Donnell, 2009). Johnson notes that “in built-to-transforms companies, managers recognize that becoming is a part of being and that the road to the next big thing can be traveled only by those with open minds” (Johnson, 2010).
Conclusion
Google has used a solid e-business model to create innovative solutions, which have captured a significant share of the Internet advertisement business. The company has used AdWords and AdSense models and a search engine that analyses what users enter in their browsers. In turn, Google delivers what advertisers want their clients to see.
Google offered free services to Internet users to develop traffic from them. Advertisers soon realized the value that Google created for them. From Google’s innovative approach to an online advertisement, one can conclude that technological strategies and innovations are tools that can transform any form of a business model.
The company understood how to capture and retain customers, create sustainable competitive advantages, exploit emerging technologies, acquire a stake in potential partners, and not to rely on several affiliations it has with other companies. Hence, Google has learned to generate its revenues from multiple industries. Analysts believe that Google will explore other revenue opportunities as many businesses migrate to online platforms.
Reference List
Aldrich, D 1999, Mastering the Digital Marketplace: Practical Strategies for Competitiveness in the New Economy, John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York.
Applegate, M 2001, Emerging e-business models: lessons from the field, Harvard Business School, Boston.
Austin, R, Nolan, R and O’Donnell, S 2009, Adventures of an IT Leader, Harvard Business Press, Cambridge.
Barney, J 1991, ‘Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage’, Journal of Management, vol. 19, pp. 99–120.
Booz Allen and Hamilton 1999, Competing in the Digital Age: How the Internet will Transform Global Business, EIU, New York.
Chau, L and Crawford, A 2013, Why Google’s Business Model Works. Web.
Eisenhardt, M and Sull, N 2001, ‘Strategy as simple rules’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 107–116.
Evans, P and Wurster, T 1999, ‘Getting Real About Virtual Commerce’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 77, pp. 84–98.
Gohring, N 2010, Experts question Google’s phone business model. Web.
Google Inc. n.d., Google Corporate Information. Web.
Johnson, M 2010, Seizing the White Space: Business Model Innovation for Growth and Renewal, Harvard Business Press, Boston.
Levy, S 2009, Secret of Googlenomics: Data-Fueled Recipe Brews Profitability. Web.
McKeen, J and Smith, H 2011, IT Strategy, 2nd edn, Prentice Hall, New York.
Miller, M 2012, How Google Made $37.9 Billion in 2011. Web.
Porter, M 1991, ‘Towards a dynamic theory of strategy’, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 12, pp. 95–119.
Spencer, C n.d., A look at Google’s business model. Web.
Vertygo Team 2010, Google Marketing Strategy. Web.
Weber, T 2008, A decade on Google’s Internet economy. Web.
Weill, P and Vitale, R 2001, Place to Space, Harvard Business School Press, Boston.
Weill, P and Ross, J 2009, IT Savvy: What Top Executives Must Know to Go from Pain to Gain, Harvard Business Press, Cambridge.