Company Profile
Bovis Homes Group PLC (Bovis Homes) is a leading home construction company in the UK, which is located in New Ash Green, Kent. The company started its construction business in 1965 and achieved significant growth. Its stock symbol is BVS, which is listed in FTSE250 on London Stock Exchange (LSE). The company’s vision is “Proud of every home; built by people who care” (Bovis Homes Group PLC, 2018). The primary activities of the company are designing and building homes for private investors and landlords (Bovis Homes Group, 2017). In this report, the company’s financial position is assessed along with a discussion of its dividend policy. Furthermore, the report provides news related to the company and their analysis. Finally, stock value assessment is performed by calculating the net asset value of the company and a recommendation is made regarding investment in its shares.
Profitability Analysis
It is crucial for any business to generate a positive return on shareholders’ investment, which is only possible if the company is generating a profit from its operations (Kelly and Williams, 2014). From Table 1 provided below, it could be indicated that the revenue of Bovis Homes had increased in the last five years as the demand for homes in the UK increased significantly. The company had focused on less risky greenfield sites, which assisted in generating high-profit margins. It could be noted that the company’s operating profit increased by almost 300% during 2012-16. Furthermore, the company incurred low-interest expense that helped it to generate a high net profit after tax in all these years. However, it could be noted that the net profit of the company reduced by £7.16 million in 2016. Although the UK home construction industry had been growing in the last five years, there were many claims made by the company’s customers regarding the quality of construction. In 2016, the company’s ex-CEO, David Ritchie resigned from his position after eight years after a profit-warning was issued by the company. It reflected poor management and strategies to take advantage of the positive market conditions (Ralph, 2017).
Table 1: Profitability KPIs. Source: (Morning Star, 2018; Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
Various profitability ratios are calculated, and their values are provided in Table 2. It is clear that the company had a strong profitability position from 2012 to 2015. However, it did not sustain its profitability in 2016, which suggested strategic and operational problems in the company. The company reported in its annual report that the supply of new homes was limited that increased transactional costs and prices. Furthermore, the number of mortgages approved was also affected by the Brexit referendum. These factors affected the company’s sales and ability to achieve profitability growth. The changes in the profitability trend are also depicted in Figure 1, which illustrates that although there was an increase in the company’s revenue in 2016, its net profit declined as compared to 2015.
Table 2: Profitability ratios. Source: Source: (Morning Star, 2018; Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
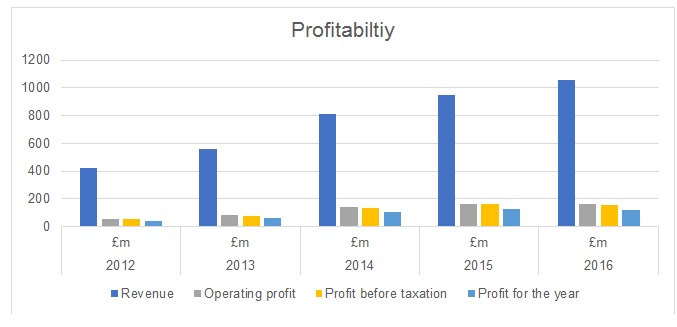
In order to sustain or improve the company’s profitability, its management needs to work on strategies that could release funds held in its inventory. Furthermore, the company should focus on overcoming quality issues, which could also affect its brand reputation. It is identified that the UK home market is expected to shrink after Brexit and UK companies could experience financial difficulties as they have a high number of construction projects in progress and the demand for new homes is expected to fall (Bovis Homes Group, 2017). A slowdown in the economy could lower the profitability of Bovis Homes. Therefore, it should speed up its projects and try to sell them quickly before a major price correction comes into play.
Dividend Analysis
The dividend policy of a company is indicative of its current financial position. If a company generates a high profit, then it is likely to distribute it to shareholders. On the other hand, if there is a loss or additional funding requirement, then the company would not distribute retained earnings to its shareholders. In the case of Bovis Homes, it could be indicated that the company generated a profit and paid dividends to its shareholders every year during 2012-2016. However, it could be indicated that the growth in the value of dividend per share (DPS) was related to the profitability (EPS) of the company. Figure 2 depicts the trend observed in the values of DPS and EPS, and it could be indicated that there was a positive relationship between these two variables till 2015. The company paid a higher dividend, although its EPS declined in 2016.
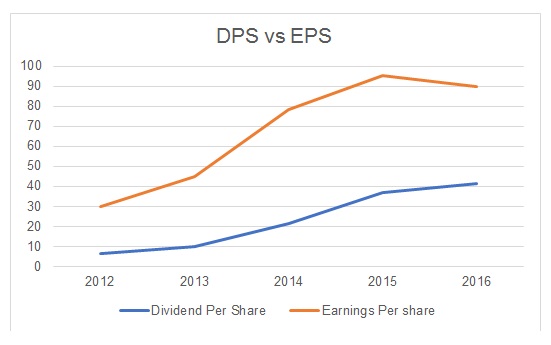
During 2013-2015, the company reported substantial growth in the value of dividends paid to its shareholders, which then slowed in 2016 to just 12.53%. However, if the values of dividend pay-out ratio in Table 3 are analysed, then it could be indicated that the company had a higher pay-out in 2016 than other years. Furthermore, the dividend yield of the company was increased to 5.04% in 2016 as compared to 3.59% in 2015, which indicated that the company distributed more funds to shareholders in the last year than before. The strategy was aimed at maintaining the confidence of shareholders in the company, although it did not achieve its profit target in 2016. The company’s strategy could be explained by using Dividend Signalling Theory, which states that companies use their dividend policy to demonstrate their strategic stance (Ross, 2016). If the company fails to sustain its profitability in 2017, then the equity market could observe a major withdrawal of investment from its shares, which would create further problems for the troubled company.
Table 3: Dividend and ratios. Sources: (Yahoo! Finance, 2018; Morning Star, 2018; Bloomberg, 2018).
Financial Stability and Liquidity
The financial stability of Bovis Homes is assessed by calculating values of different ratios given in Table 4. The values of the two ratios including debt to equity ratio and debt to assets ratio indicate that the company had low debt in the last five years. In fact, the company paid off the entire loan in 2016 and its capital structure comprised of equity only. The capital structure preference theory states that companies should use their equity first for investing in their business before borrowing from financial institutions. However, it could also mean that the company incurred a high tax on its operating profit. The tax-shield advantage was foregone by the company as it paid off all of its debt (Brigham and Ehrhardt, 2016). The value of assets to equity ratio was more one in the last five years, which was a positive sign as the company had a significantly large value of total assets. However, the analysis also indicates that the company had a large inventory and investment in land, which means that a significant proportion of the company’s funds were held up, and it could be difficult for it to sell them off immediately to release cash. The time interest earned shows that the company had generated a sufficient operating profit to pay interest charges. The company is unlikely to face any solvency issues in the coming periods, which also means that its business is viable.
Table 4: Financial stability ratios. Source: (Morning Star, 2018; Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
The liquidity ratios including current ratio and quick ratio are calculated and their values are provided in Table 5.
Table 5: Liquidity ratios. Source: (Morning Star, 2018; Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
It could be noted that the value of the current ratio remained significantly higher than the benchmark value of one in the last five years. It indicated that the company had current assets more than its current liabilities. It also implied that the company did not have any liquidity issues in those years. However, it is important to analyse the composition of the current assets to assess the liquidity of assets owned by the company. The analysis indicated that the company had a large inventory in the last five years. The quick ratio value, which is determined after deducting the value of inventory from current assets, was much less than the current ratio value in all five years. It means that the company did not have sufficient liquid assets, which could create financial difficulties for it in the situation of a major economic shift. The company should try to build up cash by selling off its properties and land. Moreover, it should improve its inventory management to lower its inventory value.
News
In early 2017, the company’s board of directors was involved in a merger negotiation with Galliford Try that would have generated £2.5 billion. However, the largest investor in Bovis Homes forced the board to call off these negotiations and go ahead with making a deal with Redrow, which is also a competitor of the company (The Telegraph, 2017). As a result, the company called off its negotiation with Guilford but at the same time hired the former CEO of Galliford and appointed him to the CEO’s position in the company (Martin, 2017). The board expected the new CEO to help the troubled company as it stated, “During his time as Chief Executive, he oversaw the transformation of Galliford, increasing the scale of the housebuilding business and improving profitability” (Martin, 2017).
Under the leadership of Greg Fitzgerald, the company has turnaround its business to a great extent. It is reported that the company will achieve its profit target for 2017 (Reuters Staff, 2017b). One of the key strategies that the company is currently following is to sell its land assets (Reuters Staff, 2017a).
The company came under heavy criticism because of the low quality of construction reported by its clients (White, 2017). It is reported that the company ignored the quality standards because of the increased number of projects that it carried out in the last few years. The clients also complained that the company’s warranty did not cover all repairs, which caused a lot of trouble. Another report by Evans (2017b) indicates that the company is experiencing poor reputation due to the unfinished properties or low quality of finishing.
Analysis
There is a possibility of a merger with Redrow (Reuters, 2017), which could help the company in the long-term. This merger would generate funds for its shareholders and overcome its business-related problems. Based on the reports regarding quality issues, it could be stated that this situation should be addressed by the company’s management on an urgent basis. With the industry slowdown, this issue could pile up problems for the company. The company could lose its reputation as one of the leading home developers, which would affect its revenue and profit in the coming periods. The company’s management should re-evaluate internal controls and procedures to ensure that operation managers control the cost and quality of its finished properties. The company’s decision to sell its land assets could help the company to release its funds and invest in technologies and training of its workers to improve the construction quality. It is understood that if the UK is going through a transition phase after Brexit, which could affect the demand for houses and also the availability of labour. It means that the company would need to re-evaluate its strategy and focus on customer retention and loyalty. The analysts are of the view that investors should wait for the company’s financial results for the year-ended 2017 (Financial Times, 2018).
Corporate Governance
The Financial Reporting Council (FRC) revised the UK Corporate Governance Code in 2016, which set out the responsibilities and requirements for ensuring that all UK publicly listed companies comply with and report in their annual report (ICAEW, 2018). It could be noted from the annual report of Bovis Homes that there is a separate disclosure of corporate governance that includes details of directors, non-executive directors, committees, and directors’ responsibilities and remuneration. It can be stated that the company complies with the UK governance code. The company’s board of directors include five non-executive directors and one executive director. The company recently appointed Greg Fitzgerald as the company’s CEO (Megaw et al., 2017). However, there is a lack of diversity based on gender as there is only one female director. Moreover, the small size board could imply a high concentration of decision making among the six directors. It is also noted that only one director has been on the board for more than five years. The resignation of the ex-CEO also raised doubts about the effectiveness of the company’s board and its decisions (Evans, 2017a).
These directors are members of the governance board, and they participated in 11 board meetings held in 2016. These directors review business trading, strategies, and compliance with the code of conduct. There are three committees including audit, remuneration, and nomination committees that perform different duties to ensure that there is complete transparency in business activities at the management level. The governance board is also responsible for making sure that the company has an effective risk management and control framework to identify risks facing its business and develop effective strategies to reduce or mitigate these risks in accordance with the guidelines provided by the FRC (Financial Reporting Council, 2014). The remuneration details of each director are provided in the annual report. However, there is no estimation of the present value of shareholdings of each director allocated to them under the company’s employee share scheme. The remuneration report indicates that the board did not approve bonuses for the company’s directors in 2016 because business and customer targets were not achieved. It was a positive step taken by the board, but it also raised concerns regarding the effectiveness of the company’s board that was not able devise and implement appropriate strategies to avoid business problems. The company also disclosed total voting rights of shareholders according to the FSA disclosure and transparency requirement (Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
Net Asset Value
The company’s Net Asset Value (NAV) is determined as “total assets minus total liabilities” (Tucci, 2015). In other words, it is the value of the company’s equity at the year-end. Table 6 provides the NAV of Bovis Homes PLC.
Table 6: Net Asset Value. Source: (Bovis Homes Group, 2017).
It could be indicated that the net asset value of Bovis Homes Group PLC was much less than the current share price. It could imply that there were financial problems faced by the company that could affect its share price in the next few weeks or months. If the NAV of a company is less than its share price, then it is expected that the stock price would adjust itself downward to close this gap (Krantz and Johnson, 2014). In this case, the preferred investment strategy would be to sell the company’s shares. Figure 3 shows the stock price trend of Bovis Homes, and it could be indicated that there is a top-down situation, which implies that the stock price can fall from its current level.
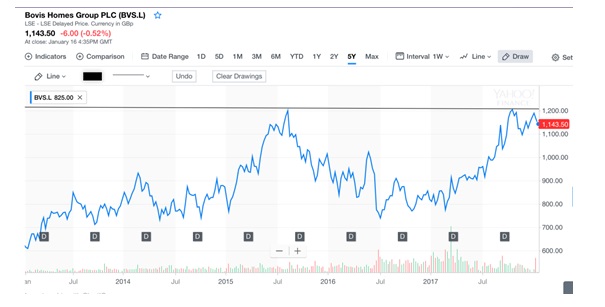
It could be stated that the home building market is likely to shrink due to the overall slowdown of the UK economy after Brexit (Partington, 2017). However, it is also indicated that the company will achieve its profit target in 2017 based on its business restructuring strategies, which is a positive sign. Therefore, it is recommended that there is no investment opportunity at present to buy the company’s shares.
References
Bloomberg. (2018) Bovis Homes Group PLC. Bloomberg. Web.
Bovis Homes Group PLC. (2018) Vision and values. Bovis Homes Group. Web.
Bovis Homes Group. (2017) Annual report and accounts 2016 – Bovis Homes Group Plc. eDocument View. Web.
Brigham, E. F. and Ehrhardt, M. C., 2016. Financial management: theory and practice. Boston: Cengage Learning.
Evans, J. (2017a) Bovis Homes chief executive departs after profit warning. FT. Web.
Evans, J. (2017b) UK rush to build homes compromises quality – Financial Times. FT. Web.
Financial Reporting Council. (2014). Guidance on risk management, internal control and related financial and business reporting. FRC. Web.
Financial Times. (2018) Bovis Homes Group PLC. FT. Web.
ICAEW. (2018) UK corporate governance code. Web.
Kelly, M. and Williams, C. (2014) BUSN – Introduction to business. Stamford: Cengage Learning.
Krantz, M. and Johnson, R.R. (2014). Investment banking for dummies. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Martin, K. (2017). Bovis says no to Galliford, but yes to its former CEO. FT. Web.
Megaw, N., Martin, K. and Thompson, J. (2017). Bovis rejects bid approach from Galliford Try as it recruits new CEO. FT. Web.
Morning Star. (2018). Bovis Homes Group PLC – BVS. Morning Star. Web.
Partington, R. (2017). UK construction ‘flirting with recession’ as Brexit uncertainty bites. The Guardian. Web.
Ralph, A. (2017). Troubled Bovis gives ex-chief executive £500,000 payoff. The Times. Web.
Reuters Staff (2017a). UK builder Bovis to reduce land bank as part of turnaround. Reuters. Web.
Reuters Staff (2017b). Update 1 – UK builder Bovis on track to meet 2017 profit expectations. Reuters. Web.
Reuters. (2017). Redrow sees “compelling” value in merger with Bovis after bid was rebuffed. Reuters. Web.
Ross, S. (2016). Essentials of corporate finance. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
The Telegraph. (2017). Bovis investor urges bid talks with Redrow. The Telegraph. Web.
Tucci, P.A. (2015). The handy investing answer book. Canton: Visible Ink Press.
White, A. (2017). Our new Bovis home is falling apart and our warranty is worthless. The Telegraph. Web.
Yahoo! Finance. (2018). Bovis Homes Group PLC (BVS.L). Yahoo! Finance. Web.