Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to prepare a comprehensive strategic plan for ‘new’ GM Company. However, this report will discuss the vision, mission, objectives of GM, Porter’s 5 Forces, the position of GM in the BCG matrix, the grand strategy matrix, generic strategies, and so on.
Background of the company
General Motors the world’s mega automotive manufacturer that was established in 1908 and it was seriously affected by the credit crush in September 2008. Under SOA (Sarbanes Oxley Act) chapter 11, General Motors has been treated as bankrupt. To protect against the financial crisis, the US government extended its hands with bailout bills, and rescue package, and now owned 60% shares of GM. With the change of lion shares, the government criticized the business model of GM and urged to implement a comprehensive strategic plan for new shaped GM Company.
Vision
GM’s vision is to be the market leader in the global automobile industry by providing superior quality products
Mission
- One of the main aims of GM is to regain lost market share;
- Its present mission is to introduce more fuel-efficient 24 new vehicles within 2012;
- Applying Divestiture strategy in order to emphasize more on core business;
- Restructuring the company via temporary Federal assistance;
- Extraordinary customer care, constant development, and diversified product line (Thomas, 2009).
Objectives
The ultimate goal of GM is to hold a market leader position by developing product range, increasing profits, eliminating major challenges, lessening operating expenses, applying strategic plans, and restructuring the entire organization.
Porter’s five forces model analysis
To evaluate the competitive environment of GM, this report will concentrate on Porter’s five forces model –
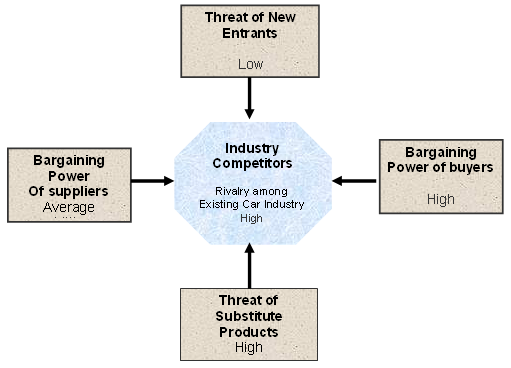
- Threats from new entrants: GM Corporation (2009, p.11) reported that GM and other automobile companies had faced intense competition in the global market for the financial crisis, unstable oil prices and reduction in the employment rate. Generally, it is difficult for a new company to capture the market of GM but there is a risk of competitive stress from newer domestic carmakers of China and India as these new companies are popular to middle-class target customers.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: According to the annual report 2009 of GM Corporation, the major suppliers are generally raw materials companies, which supply steel, aluminum, fuel, rubber, motor engine, resins, copper, lead, systems, components, and other parts of the car, etc. However, the power of these suppliers varies from area to area considering the availability of the suppliers, for example, GM clears the payment in the second month of the delivery.
- Bargaining power of buyers: Before the economic meltdown, purchasers were a relatively less influential factor in the car industry as most of the customers of GM concentrated on quality rather than price though it differed from one market area to area. However, the bargaining power of purchasers is escalating due to the current pressure of recession as many customers now consider the price of the cars.
- Threats of substitute products: GM also faced hard competition from some other alternative transportation besides direct competitors, for instance, the demand for public transports like buses, railways, and trams have increased because of recession;
- Rivalry among existing firms: GM has to compete with many direct and indirect competitors at both domestic and international stages, such as the main competitors of GM are Honda, Ford motors, Mitsubishi, Land Rover, Toyota, BMW, etc. However, all major companies of this industry had adversely affected by the recession, for instance, in 2009, GM’s sales had lowered by 30% than 2008 and cut a huge number of jobs with limited payments (GM Corporation, 2009). The following table no 1 demonstrates the global market share of the players of the automotive industry –
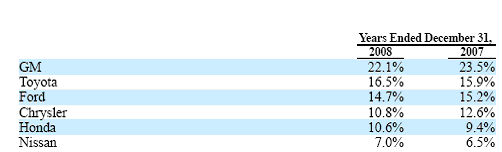
Position of GM in BCG Matrix
The BCG matrix is a portfolio planning process to measure GM’s market situation in terms of relative market growth rate as well as relative market share –
- Star: Due to high- growth and high- share, GM occupied this segment before the global financial crisis but it failed to hold its reputation;
- Cash cow: GM is not in this segment as this area point out the low growth with high-share business;
- Dog: Unfortunately, GM occupies this segment now as it demonstrates low- growth with a low share of its business and it requires large investment for further development. However, the US government owned 60% of its share, so it can assume that it will capture the position of Star very soon by properly utilizing its capital and investment funds;
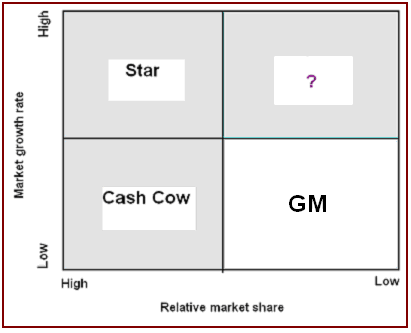
- Question mark: the competitors of GM hold the position of Question mark in a global economic downturn as they experienced a favorable growth rate in a few countries of the world.
SWOT analysis of GM
The strength, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats would discuss to evaluate the position of GM in recession –
Strengths
- Large Market Share in the global car manufacturing industry;
- Brand awareness is the key factor to creating a positive image in customer’s minds;
- It has long experience to protect the company from any risks;
- It has strong global supply chain management and positioning strategy.
Weaknesses
- GM’s market share in the US has dropped due to fluctuated economic and political situations;
- Fluctuated market share, poor organizational structure, and lower profit margin.
Opportunities
- It has the opportunity to develop its hybrid technology, new vehicle styles and models;
- It has innovative power to increase market share;
Threats
- Competitors and global financial crisis are the main problems for its operation.
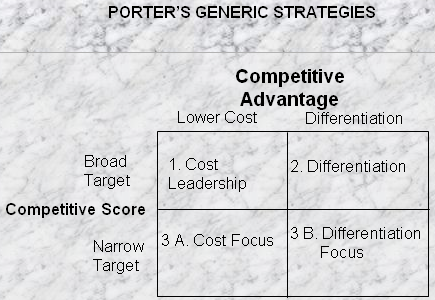
Porter’s Generic Strategy
Cost Leadership: As the automobile market is too competitive, the new GM Corporation should supply the products at low prices in order to boost its profit margin and carry on its business as a market leader in such economic circumstances.
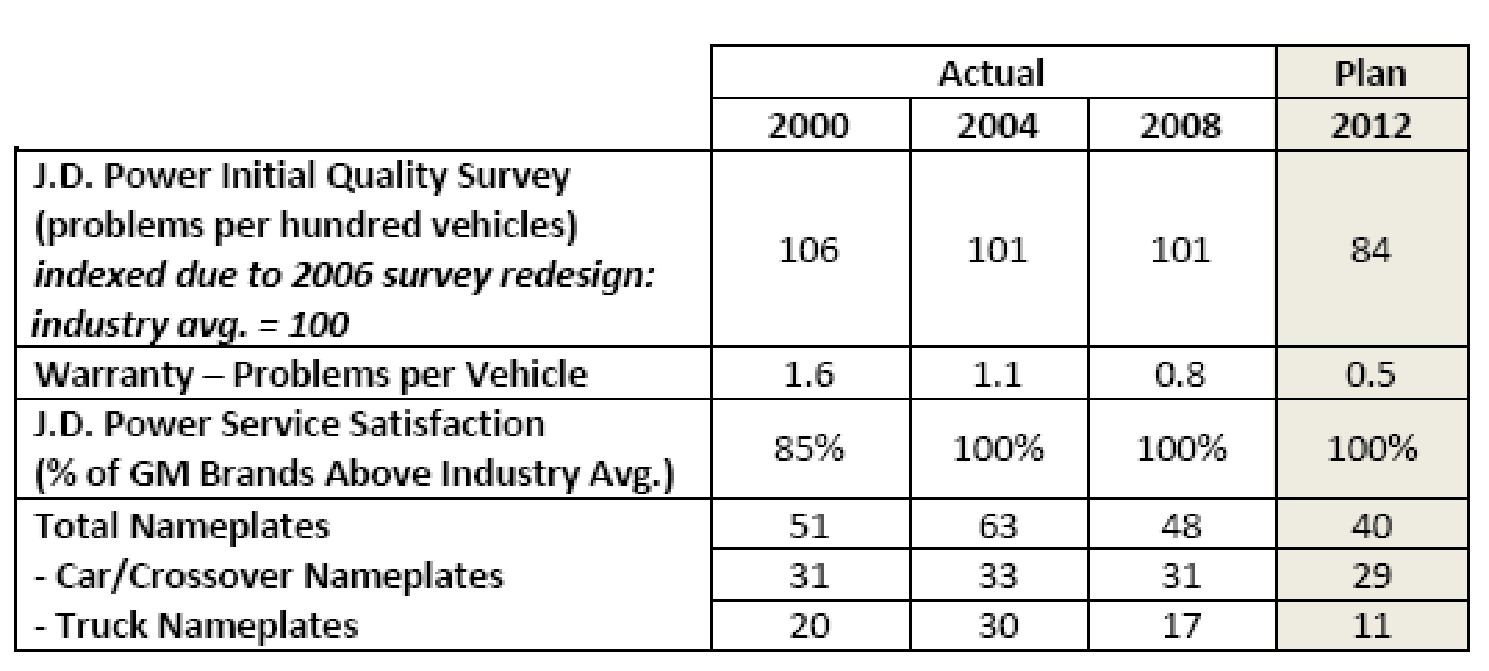
Focus: GM Corporation (2008, p.4) pointed out in its restructuring plan that GM would concentrate on new product development for further expansion besides its core business. However, it will develop the quality of its products in order to lessen the market risks and the following figure shows the action plan –
Differentiation strategy: From the beginning of its operation, General Motors considered very low levels of a diversification strategy, so it manufactured cars and related products with sharing the raw materials and earned more than 70% from single sectors. In this context, it should diversify its product range to come back as a market leader in this industry
Implementation
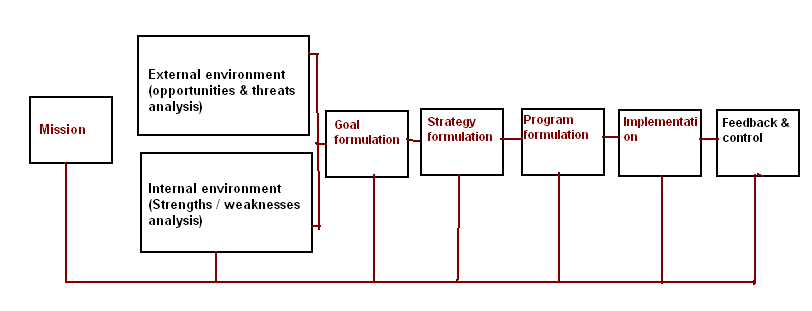
After discussing the overall condition, this report identifies the following prospective strategic- planning process of GM:
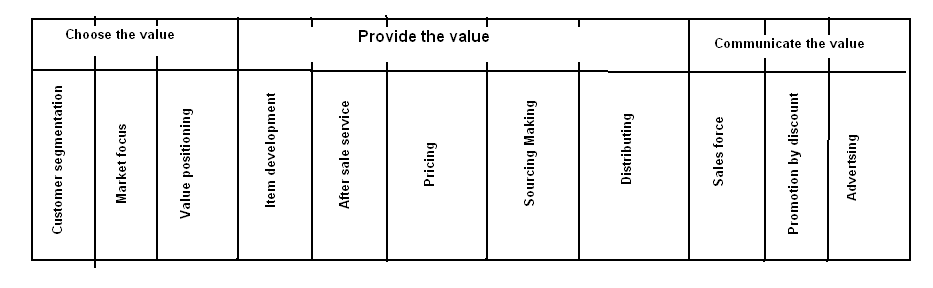
However, new GM Corporation should also implement the value-delivery process and 4 P’s of the marketing mix –
Recommendations
- GM should implement the cost-effective strategy in order to avoid further economic loss;
- It should strictly follow SOA to reduce internal conflict and litigation costs;
- It ought to combine the financial and creative communication plan;
- New GM Corporation should be more attentive to meet customer demands because the market is too competitive in terms of product, price, service, innovation, technology, loyalty, safety, price, fuel economy, style and so on;
- It should restructure dividend and pricing policies;
- It should target middle-class people and introduce products considering their earning level;
- Introduction of flexible production and utilization of modern technology;
- Besides customers, it should maintain a good relationship with overseas suppliers, making a connection or mutual co-ordination with foreign policymakers by using the latest technologies;
- It should formulate a better incentive plan in order to motivate its employees;
- In addition, it should increase the budget for R&D and provide special offers for loyal customers;
- It should more concentrate on Asian and Middle- East markets.
Conclusion
It would be difficult for GM to regain its glorious position in terms of more vehicle sales in the high level of competition but GM has some competitive advantages to recover its position. In addition, federal assistance and the recommendation of a new restructuring plan will help GM to save the company from the adverse impact of the financial crisis.
Reference List
GM Corporation. (2008) Restructuring Plan for Long-Term Viability.
GM Corporation. (2009) Form 10-K General Motors Corp – GM.
Thomas, C. (2009) General Motor’s Strategic Analysis.