Correlation Test
To establish the nature of correlation that exists between mindfulness and two forms of happiness, namely, subjective happiness and Oxford happiness, Spearman’s correlation test was used. According to Coolican (2014), Spearman’s correlation test is suitable in the analysis of ordinal data because it is a nonparametric test, which assesses the extent of dependence between two variables. Since Spearman’s correlation test ranks measurements before analysing their dependence, it gives an accurate correlation of nonparametric data. As scales, such as subjective happiness scale, mindfulness scale, and Oxford happiness scale, collect data in ordinal form, Spearman’s correlation test is appropriate in analysing their dependence. The Spearman’s correlation test gives a correlation coefficient, which is a value that ranges from -1 to +1. The correlation coefficient gives the nature of dependence or relationship that exists between two variables.
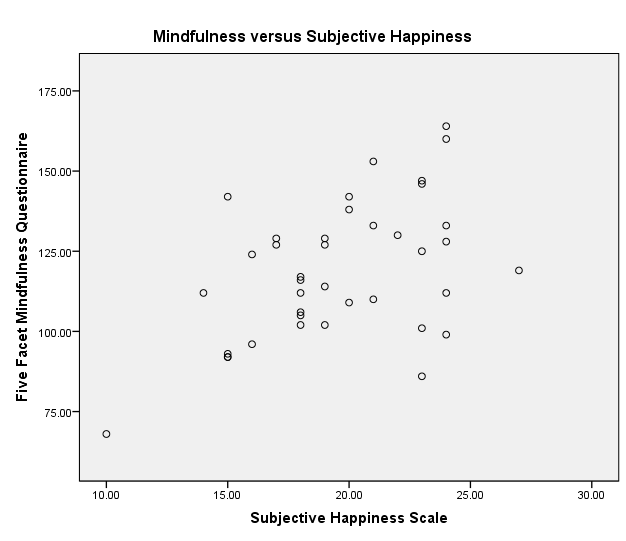
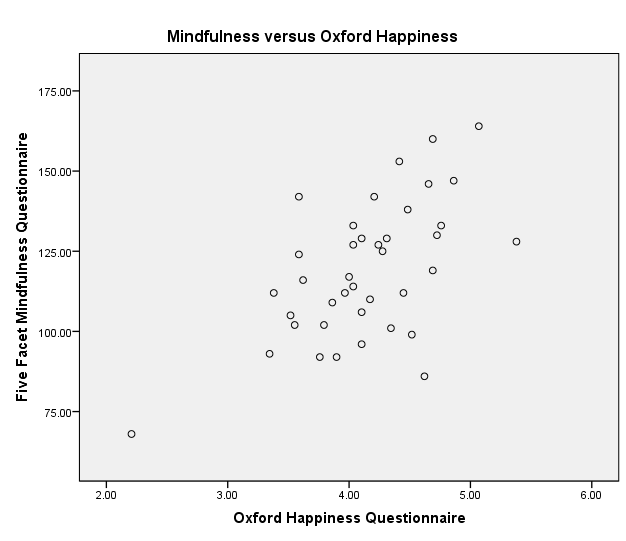
The hypothesis of the study is that mindfulness has significant positive correlation with subjective happiness and Oxford happiness. The test of the hypothesis using Spearman’s correlation, one-tailed test, indicates that mindfulness has significant positive correlation with subjective happiness, (rs = 0.472, p = 0.001) and Oxford happiness, (rs = 0.590, p = 0.000). The positive correlation between mindfulness and subjective happiness is moderate, whereas the positive correlation between mindfulness and Oxford happiness is very strong. Analysis of correlation coefficients reveals that mindfulness correlates more with Oxford happiness than subjective happiness. However, since the p-values are less than 0.05, the correlation tests show that mindfulness has significant positive correlation with subjective happiness and Oxford happiness.
Data Analysis: Spearman’s Correlation
Correlation between Mindfulness and Subjective Happiness
Correlation between Mindfulness and Oxford Happiness
Scatter Diagrams
Descriptive Statistics
T Tests Repeated Measure Design. Analyse Comparing Means, Head Samples as Same People Generated
Given that the blindness study consists of four related measurements, the appropriate form of test statistic, which can analyse collected data, is paired-samples t-test. The four related measurements provide different pairs of data, which paired-samples t-test can analyse by comparing means. Weinberg and Abramowitz (2008) state that paired-samples t-test is suitable in comparing the means of two related groups. The related groups in this case are the three pairs of measurements, namely, Q1 and Q2, Q2 and Q3, and Q3 and Q4, which are obtained from the four related measurements in the blind study.
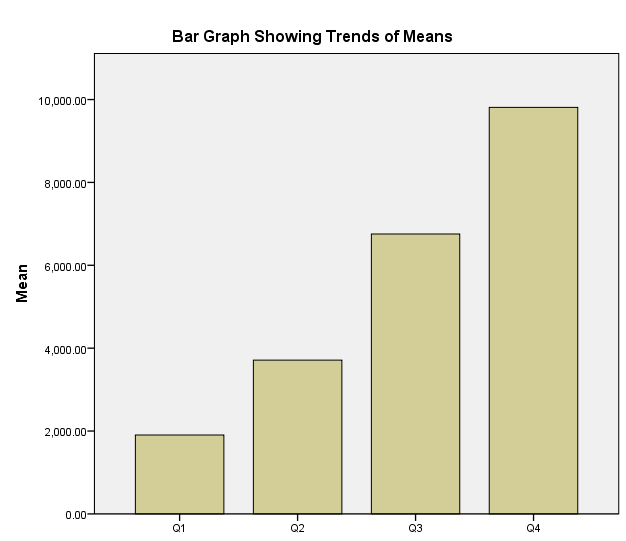
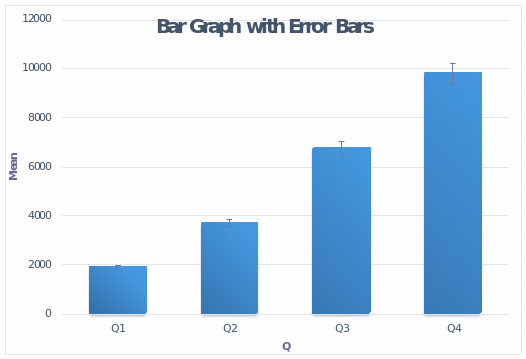
The hypothesis of the blind study is that there are significant differences between means of Q1 and Q2, Q2 and Q3, and Q3 and Q4. The paired-samples t-test indicated that there were significant differences between means of Q1 and Q4 (t(64) = -22.688, p = 0.000), Q2 and Q3 (t(64) = -15.355, p = 0.000), and Q3 and Q4 (t(64) = -13.817, p = 0.000).
Pairs of Measurements
Pair 1: Q1 and Q4
Pair 2: Q2 and Q3
Pair 3: Q3 and Q4
Data Analysis
References
Coolican, H. (2014). Research Methods and Statistics in Psychology. New York: Psychology Press.
Weinberg, S., & Abramowitz, S. (2008). Statistics using SPSS: an integrative approach. New York: Cambridge University Press.