Introduction
Dubai metro is a project that has been commissioned in Dubai to serve a population of 1.5million people and it’s forecasted that it will serve a population of 5.5 million people by the year 2020. The project is developed and operated by roads and transport authority and the red line is planned to be completed by September 2009. This project began because the government felt that there was a need to improve the transport system of Dubai municipality and the railway system was identified as a better way of easing the traffic congestion. This is because there was a huge growth of the population and there was a severe traffic congestion problem in the town. The growth of the town has not only been due to the people but also the tourists who visit the town were projected to be 15,000 people P.A in 2010. With such people as travelers plus the resident people, Dubai metro project became an important aspect for the Dubai municipality.
The project was initiated through the directive from the ruler who saw the need to cater to the growing population to ease congestion on the road system. The provision of funds to construct the modern urban railway system was meant to improve railway capacity and modernize Dubai and be able to compete with other stations in the world. The Dubai metro is said to have 57 stations with four lines. Some of the lines that will be operated will be electrical.
Stakeholders
Dubai Metro will have many stakeholders and the selection of the city to have this railway system that serves its citizens will promote the economic development of the country including promotion of the culture of the people of United Arab Emirates. A wonderful business community and world-class business community and a free duty center that is well known worldwide have made Dubai a town with many stakeholders. The world-famous trading center of Dubai has enabled the city to enter into the world heritage site for people from Africa and other parts of the world. The Dubai Sevens (Rugby), Golf and horse racing have made the town have sportsmen as stakeholders of the transport system in Dubai. A relatively high asset base is reported to be a major boost to the Dubai municipality to raise capital funding for the project. However, the city is badly in need of a new strategy of attracting extra external funding for the project. The private business stakeholder in Dubai will be delighted with the ability of the city administration in handling this new economic development activity which will boost the growth of the city. The fragmentation of economic development activity will be confusing if Dubai municipality will be unable to raise these projects. The business community stakeholder will be very much confused if the municipality looks for several partners to deliver the railway line that will serve the city adequately.
Despite the improved economic activity of the Dubai municipality, there is a need for the inclusion of all stakeholders in the project. These stakeholders who are among them the government the public and the society, private sector, environmentalists, human resources and travelers are very important to the success of the project. Various sections of the project should be given priority by various stakeholders.
The private sector stakeholders will give priority to the section that will reduce congestion in the city while the public and the society at large will be interested in the reduction of congestion, proper accounting of public funds that will be used In the project and many other aspects.
A traveler who comes in a form of tourists forms a greater stakeholder since 15 million of them are expected to be visiting the city annually. These people are interested in quick services as they visit the city. They will also be interested in the modification and standardization of the tourism attracting sites to enable them quickly get what they want and travel back home. Therefore the organization and the project as the implementation will be of paramount importance to the organization.
The active participation of shops owners, hotels and other businesses in ensuring that the project succeeds will boost their lives because it is an economic activity. All this will lead to the sustainable economic development of the town.
Supplier issues
The Global Supply Chain Forum (GSCF) describes Supply Chain Management as:
“Supply Chain Management is the integration of key business processes from end-user through original suppliers that provide product, services and information that add value for the customer and other stakeholders.”
To gauge the effectiveness and efficiency of key business processes it is important to measure their performance (Shepherd and Gunter, 2005). Measuring performance may provide an in-depth understanding of the supply chain, its characteristics and improve its overall performance (Chen and Paulraj, 2004). Performance measurement is defined as a process of quantifying the effectiveness and efficiency of action (Neely et al., 1995). Measuring performance is translating the complex reality of performance into a sequence of limited symbols that can be communicated and reproduced under similar circumstances (Lebas, 1995).
Beamon (1996) proposes a few inherent characteristics for an effective performance measurement system. These are inclusiveness, universality, measurability, and consistency. To measure the efficacy of a process, it is important to benchmark the same. Benchmarking serves as an ideal tool for identifying improvement (Camp, 1989). There are a large number of performance metrics available ranging from 13 to 60 (Huang and Keskar, 2006).
Given such large numbers of performance measures, it is important to categorize them. Categorization helps the measures to be compared and analyzed so that performance measurement selection within a category can be easier (Beamon, 1999). Neely, et al., (1995) proposes 4 categories in their paper, including quality, time, flexibility and cost. Holmberg, (2000) argued that there should be synchronization between a measurement system and the overall objectives of the firm. Van Amstel and D’hert (1996) indicated that the performance measures depend on the level at which the measurement is done e.g. activity level, functional area level.
The company has a specific corporate mission. This mission has to remain clear to all those in management and especially all employees asking the questions what is our business? Who is our customer? What is value to customers? What will our business be? What should our business be? Are questions that the company has raised in creating the strategic plan.
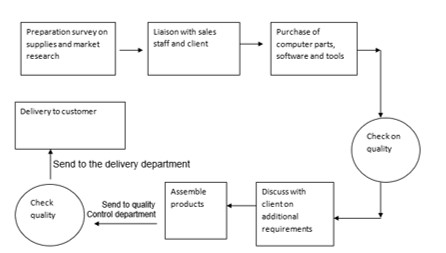
The company will examine the external environment and the internal environment before deciding on the best process to achieve its mission objectives. Metro’s business objectives and goals are to provide a good product at the best prices and to expand its market share while checking any unwanted expenses. This is then tied into the development and supervisors prepare program plans and finally gather feedback while exercising control.
The process will be tested and analyzed with regard to the time taken to complete the process, the efficiency of each member of the team, the understanding of the job by both supervisors and workers and other criteria. Control is exercised on each step of the process by setting up targets, providing a checklist and identifying weak points along the process. The feedback will be the basis of making any changes to the business objectives or personnel. Information will also be shared with all other departments such as human resources marketing, accounting and delivery. The internal customer is the employee of the workshop. He plays a role in making the process work. With training on his role in relation to the entire process and overall company objectives he will be able to do a better job.
The external customer is the buyer of the product or services. A well-defined process will guarantee that he gets the right product. The company sales and workshop staff have to liaise so that he gets what he exactly asked for.
The fishbone or cause and effect diagram is a technique used to organize the ideas about potential causes into a logical structure that can be used to identify when there’s a variation from a planned outcome and isolate and identify potential causes of that variation.
- A short form of definition of the problem- the high number of computers returned for repair by customers are placed in the box at the head of the fishbone thus focusing on the problem at hand.
- The staff will brainstorm and the resulting list is used as the source of information. At this time we eliminate ridiculous impossible and insignificant ideas. We now have zeroed in on what the group thinks may be the problem.
- Generic headings are chosen by examining the brainstormed lists these being the four M’s: manpower, method, material, and machines and also environment and policies that affect the company.
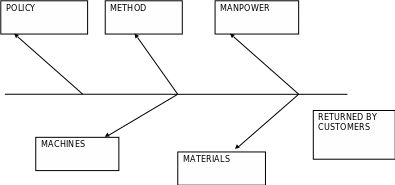
- Each cause idea that is accepted by all. It must be carefully and recorded and understood by all the team.
- The fishbone now has a lot of information about the problem but we need to further analyze the root cause one alternative will be to take one of the bones of the fish and break it down further. For example under manpower, we may include lack of training as one of its bones and add on cause ideas such as no training policy and no method of assessment of fitness in the fishbone diagram.
Having identified the problem by way of the fishbone diagram, the leadership will have a clear idea of their mission and be able to organize policy and strategize to manage all resources which include financial, information, material and technological resources. Management will be able to identify the skills and capabilities of its people in the workshop which was the main source of the problem. Skills will be developed through recruitment, training and career progression, how people and team agree with targets and a continuous review of performance involving everyone in the company in the continuous improvement with people being empowered to take appropriate action.
The process from start to finish has been identified along with all other value-adding activities such as how the company systematically manages its processes. We are also able to measure performance and review processes and set improvement targets as per company specifications.
Customer satisfaction is the goal of the company. The perception of external customers to the organization’s products and services is important to the future well-being of the company. The fishbone diagram has highlighted the need to update tools and machinery in the workshop and improve the layout and lighting of the workplace. Having identified this situation the management will liaise with the accounts department and research and development departments to decide on the best way to implement the findings. A positive outcome will have a direct impact on the quality of services and quantity of products as well as the morale of staff.
We have also identified improving the quality of personnel as well as motivating shop front workers. Training regularly will eliminate mistakes while assembling computers while making the process take a shorter time to be completed. Regular updates on new trends will assist employees to keep up with the needs of customers. Having an on-call line with customers has been regarded as the most important result of the exercise. The flow chart of the process shows limited communication with customers as one reason the end-product does not satisfy some customers. The company is aware of the daily changes of computer software products and has set up a telephone and email system that updates the customer on how the product is being assembled.
Leadership has an unstructured approach to training and no process of bench making. There was no evidence of any formal quality management and a lack of information on training. Finally, there was no formal evidence of customer requirements.
The company’s values, visions and strategies were not attained and there was no evidence of a medium or long-term plan. There was also a need to integrate total quality activities with the needs of the business. There was no written method of evaluating effectiveness, the irrelevance of policies about customer requirements and competitor’s analysis.
Purchase
Dubai Metro will purchase various goods and services that will be used for their activities. These goods and services range from train, railways, vending machines, ticket machines, mainframe systems, hard and software, electronic devices, furniture, monitoring equipment, metal and glass, escalators, elevators, conveyors, buses, security systems, access control and many others.
These items that will be purchased by Dubai metro will be intended to provide services to the people by ensuring that the product of the company is in constant supply to the members of the public. The work for Dubai metro, which covers a computer corridor with green and red lines of 318 kilometers, is to use various construction materials. The construction material that will be used in this project includes spare parts railway, metals, electrical system, alarm system, and many other systems that are needed for the project. In the purchase of the required items for the project, billions of money have been used
Corporate social responsibility
With the changing trends of business in the world context, the concept of responsibility of the business organizations towards community development has gained immense importance. The combination of the concepts of taking responsibility for the development of the community and the profit-making business development is the challenge the present business organizations are striving to achieve (Price, 2007). The corporate sectors doing business in the modern market scenario are expected to be accountable for their actions impacting all their stakeholders including consumers, employees, suppliers, investors and shareholders, communities as well as the environment rather than just concentrating on profit-making purposes (Price, 2007).
With the growing concern for community development more and more corporate sectors are seen to engage in corporate social responsibility not only because of legal bindings but also due to their internal voluntary policies. With this increase in efforts related to employee and community development the debate related to the applicability and utility of the concept of corporate social responsibility in the business scenario has also become important. The supporters of the concept find a huge amount of business benefits from the implementation of corporate social responsibilities whereas the opponents having a more conservative attitude do not find any benefit of the same and think it to be over-hyped. But in spite of these debates and doubts about the applicability of corporate social responsibilities it can be stated to provide benefits both to the organizations and the society in a larger context attracting the organizations to take action in favor of the same.
Several types of research have been conducted in this regard to determine the applicability and acceptance of the concept of corporate social responsibility at the corporate levels and also at the government and community levels. In this regard the articles about the results and the concept generally target the opponents of the concept as well as the corporate sectors in order to convince them about the benefits of the concept. As a whole all the researches and articles in relation to corporate social responsibility are targeted at the corporate sectors which are generally expected to act in favor of or opposition to the concept as per the stance taken in the articles or researches. Thus the target audience for these discussions is mainly the corporate sector. The investors also play a very important role as the target audience the researches and articles aim to convince them to invest in companies supporting or opposing corporate social responsibilities. This targeting is very clear from the article “Corporate social responsibility: Is good citizenship good for the bottom line?” by Tom price (2007) discussing almost all the issues and arguments placed in support or opposition of the concept of corporate social responsibility.
In spite of increased inclination towards implementation of corporate social responsibilities, some people argue against the utility of corporate social responsibilities. According to the opponents like Friedman, the benefits of corporate social responsibilities are overstated and the proponents of the concept are actually willing to impose increased government supervision on the organizations. Moreover they state that the primary aim of a business organization should be to increase profit taking into account the interest of the shareholders (“Rethinking the social responsibility of business”, 2005).
In general the corporate executives are seen to believe in the benefits of the corporate social responsibilities overwhelmingly and more and more of them are incorporating issues like ethics policies, stakeholder engagement, and transparency about the risks of products or processes in their business strategies (“The McKinsey global survey of business executives: Business and society”, n.d.) About the legalities, the proponents and the organizations understand their responsibilities for meeting the requirements of the regulations permitting them to take certain activities for the betterment of their business and show voluntary approaches to meet the requirements (Price, 2007). According to the big corporate organizations, they should try to ensure benefit for all their stakeholders through socially responsible and legally abiding business practices and this approach only can be helpful to ensure increased return for the stockholders of the organizations (“Rethinking the social responsibility of business”, 2005).
With this approach integrating private and social needs through the business strategy of “people, planet, profit” the concept of corporate social responsibilities are integrated with the big business deals also.
These market trends supporting the implementation of corporate social responsibility are found not only due to the increased concern of the corporate sectors to have a healthier business environment but also due to the changing investment trend in the global market. It is seen that the investors are now more concerned with the social performance of the companies before making decisions about investment in those companies. Studies reported more than a quarter of the shareholder US population makes investment decisions keeping in mind the social performance levels. Consumers are expecting more socially responsible acts from the companies and pressurizing them in this regard. As a result the general global trend for the companies is to take more socially responsible actions to please the consumers as well as the investors (“Corporate Social Responsibility Monitor”, 2007).
The United Arab Emirates for a very long time has depended continuously on its transport industry. Transport has thus not only been a passion for young and old over the years, but is the most valuable source of national income as well. Uniquely related to their motor vehicles, most communities solely depend upon the transport system to do their most basic of everyday activities in mail, newspaper, groceries and other edible goods, emergency services, and most vitally in coping to keep pace with a very competitive world outside.
Motor vehicles and locomotives are the most valuable of assets that contribute substantially towards national property and income. In the past too, motor vehicles have been the most vital of constituents of the United Arab Emirates Transport system. Dubai Metro project made ultimate bush deliveries to business and mining communities and canneries almost in the whole of Dubai Sound in the past. The tourism industry also heavily depends upon transport in Dubai, both directly and otherwise.
Perhaps the best example to illustrate the doctrines and values of social responsibility is the transport industry and the social responsibilities of individuals involved in it.
An employee in the transport industry requires flexibility of thoughts and believes that success depends largely on the ability to adapt—proactively shape-changing events to its advantage as well as to react quickly to constantly changing conditions. He sees a chance as an important perspective and believes that chance must be viewed not only as a threat but also as an opportunity which he must be ever ready to exploit.
The employees in the Industry regard improvisation and presence of mind as important traits of social responsibility in continuously changing situations. Rather, the best they can hope for is to impose a general framework of order on the disorder, to influence the general flow of action. The group sees each element as part of a larger whole that must cooperate with other elements for the accomplishment of the common goal. At the same time, each has its own mission and must adapt to its own situation. Each must deal with friction, uncertainty and disorder at its own level. The force regards it as a great challenge to understand the changing aspects of social responsibility and believes that ignorance may take them to a lesser position.
Today the world has become a difficult place to live in, very much due to the competitiveness and rivalry that has crept into the society. Apart from the personal responsibility that every individual has, social responsibility is one critical element that is becoming extremely necessary for every individual to adapt to these fluctuating social and political environments.
Protecting and nurturing personal health and emotional well-being by communicating the necessities and requirements assertively in all relationships is an important part of taking self-responsibility for one’s actions. When we take personal responsibility, we admit we are the only ones responsible for the choices we make and that we, not other people or events, are responsible for the way we think, feel or react. We believe that it is our life and we are in complete charge of it. We are free to enjoy or disdain it. Even though we are not responsible for all that happens to us, we are responsible for the way we think, feel, and act when they happen. Personal responsibility is different from other responsibilities.
Taking the initiative or reacting in response to the opponent is critical for all individuals in the Transport industry, as defined by the doctrine. An employee in the Transport Industry defines focus as the convergence of effects in time and space on some objective and believes that devoting means to unnecessary efforts or excessive means to necessary secondary efforts violates the principle of focus that is counterproductive to the original goal. Focus can be achieved through cooperation towards the accomplishment of a goal that applies to all elements of the force, involving every marine of the force. The group also regards boldness to be a prime quality, based on strong situational awareness, to first weigh the situation, and then act.
The Dubai map depicts numerous little motor vehicles symbols embedded all over the town and the Dubai metro project will add another pollutant to the system. These symbols indicate Bus-stations and the metro project will create a railway station that will be used by the transport system that will be used by this project. Dubai is one of the biggest sources of income for the transport industry. Its terrain is such that only rail can prove to be an effective model for proper communication of men and goods. Thus Dubai offers tremendous scope for the business of transport. Today, if light is thrown on the history of Dubai transport, one surely finds that the state depends heavily on its transport industry. Transport has thus not only been the primary passion for most young and old Dubai over the years but is the most valuable source of national income as well.
Transport was never as easy and fun-filled as one may find today. Early Dubai drivers indeed have had several difficult and sometimes even fatal experiences on the road and soaring high traffic jams in Dubai. Unlike today, it was then incredible for a driver to even imagine calling and ahead and determining the exact scenario of the road ahead of the community he would glide into. The driver would rather drive in blindfolded and look for and look for a space ahead to avoid the traffic jam which often resulted in greasy accidents. However, history reveals a few exceptions too. By the time transport enhanced and industrialized, these road systems were polished and refined and today our drivers barely ever think twice while driving on the roads in Dubai.
Although a productively rich and self-sufficient town in terms of the abundance of resources or Dubai not only in the past but even today depends heavily on the business of transport. Today Dubai draws a major part of its overall income from transport and business which remains the most important prospect in the long years to come.
Uniquely related to their transport system, most communities in and out of Dubai solely depend upon the Dubai rail system to do their most basic of everyday activities in the mail, newspaper, groceries and other edible goods, emergency services, and most vitally in coping to keep pace with a very competitive world outside. Strangely though, the history of United Arab Emirates transport begins slowly on a long boat ride for a motor vehicle. An era of growth for the transport industry, the 1960s was the period when motor vehicles were left as the sole means to reach isolated and remote places.
Dubai is the home for several brave and skillful businessmen who have today, become an indispensable institution in this part of the world. Dubai’s geographical scenario explicitly opposes other forms and modes of communication and transport, this certainly being the greatest advantage to the transport industry in the region. The Dubai terrain entertains no other communication techniques other than through air. People residing in areas as remote and distant as these are left out with bare any other choices when it comes to the commonest of daily requirements and needs. Mail, groceries, supplies and transportation are only very few of the basic needs of the people of Dubai living in far away, unreachable places.
In spite of increased inclination towards responsibility, some people argue against corporate social responsibility but Dubai metro has taken necessary steps to ensure the emission of carbon which is likely to destroy make society a good place to live. as part of corporate social responsibility the project has undertaken necessary steps to implement human rights to ensure that employees rights are taken care of such as their security during work hours. Dubai metro is a rail system that will serve a population of 5.2 million people by 2020 the environmental security as well as sustainability has been taken care of by identifying activity that will be used to ensure employees are not affected.
Thus to conclude the entire discussion it can be said that the corporate sectors in the worldwide context have identified the benefits of implementing corporate social responsibility in terms of social growth, cost-effectiveness, profitability and increased investment and thus are getting increasingly attracted towards the implementation of the same in their own business strategies in order to ensure their viability and stability in the changing global context.
The process
The financial magnitude of these issues convinced Dubai municipality to organize a working capital. The task force included three managers one from data processing system group, the second a chief engineer and the third a profit center controller. The task force was asked to:-
- Diagnose the inventory reduction opportunity
- develop a comprehensive program for reducing inventory and
- Implement the program.
Diagnosing the problem
The first assignment was to assess what opportunity existed for inventory reduction and investigate how inventory could be reduced without curtailing service. The scientific inventory planning computer simulation model showed the top management a quantum opportunity existed. The size of the opportunity confirmed the task force next investigated how to achieve the reduction. First, it examined in depth the current production planning and inventory control operation and through interviews the task force identified two key analytic talks that would lead to inventory reduction.
- The first task was to determine a better approach for managing and allocating measured by labor hours
- The second task was to find a better balance of cost of carrying inventory against the risk of shortages. Data analysis by the task force showed that inventory had not been well balanced at the school level.
- The team constructed seven scientific models that addressed the two tasks.
E-processing
E processing has provided many benefits to businesses in the world. E-process has redefined the purchasing department and improved stock management in the organization. Dubai metro project will benefit greatly by implementing E processing to enable them to improve purchasing. All the data that will be used by the project will be saved in the E processor and the data that will be included will be E electrical data, purchasing data, procurement data. This will enable the organization to efficiently manage the procurement and inventory of the organization. The procurement department will be able to access materials in-store and understand when the materials should be purchased. Being a transport system ticketing will be done on E process where all the stock are installed for use in a central system.
To make E-processing more secure for the company, I will ensure there is internet security in order to make the information that is begin shared in departments to be more reliable. Internet security in the organization is of paramount importance as all organization departments are assured of the secure information.The steps to be undertaken to make E processing for purchasing electrical data and procurement will be as follows:
There are types of information that require confidentiality such as the research data, insurance and medical records, new product or service specifications, and some corporate investment strategies. Most banks and loan companies have their legal obligations to protect the privacy of their clients. Even hospitals and testing laboratories need to protect the records, drug treatment, and medical test results of their clients (Cha, 2008).
Any information can be corrupted when made available to a non-secure network. All the information can be modified by intruders in the most unexpected manner, and its entire content might lose its integrity. There can always be unauthorized changes made to information that alter the integrity of the file. Integrity is an essential factor in securing financial data and other related activities such as electronic funds transfers, financial accounting, and air traffic control. There are always possibilities that information or files in the computers be erased, become inaccessible that results in loss of its availability. Through this incident, the authorized person cannot get the information they need. In the concept of Internet Security, securing the availability of files is one of the important attributes particularly n service-oriented businesses that relied on information like the airline schedules. Among the important attributes of Internet Security is the maintenance of network availability that relies on its network connection. There are computer users who experience denial of certain services and this incident prohibits them to get an access to the network or specific services being provided through computers. Relative to the concept of Internet security, any information that goes through the computers needs to have authentication that can prove the claims of the users. Authentication includes the use of passwords that can prove the person’s identity. There must also be “authorization” to every file that will act in determining whether the particular user has the right to carry out certain activities like reading a file or running certain programs. Authorization and authentication work hand in hand and the strength of its provided security is effective if the authentication cannot later be refuted (Avolio, 2008).
There are several aspects of controls and procedures that are applied to support the business needs and their Internet connections. There are elements of policy that are derived from the security controls such as the software encryption, import control, and system architecture. Security policies are carried out in managing the Internet connections. Authentication is the process used in verifying the valid users or processes that will be allowed to have an access. There are Internet-accessible systems such as firewalls and routers. Internet connections usually show various problems and authentication is applied to impersonate a user. Authentications are made available in various types such as robust, static, and continuous. In static authentication, passwords can be compromised due to replay attacks. Static authentication provides protection against attacks in which an imposter cannot alter the information during an exchange and subsequent session. Robust authentication applies cryptography and other techniques in creating one-time passwords that are used to create sessions and consequently, robust authentication can be compromised by session hijacking. Robust authentication cannot protect the connection against attacks in which the imposter can alter the flow of information. One-time passwords and digital signatures can be used in the level of its protection. Continuous authentication provides protection against impostors who actively influenced the connection. It provides form of authentication through the use of a digital signature algorithm that applies to every bit of data. There are combinations of cryptography that provide form of authentication. Data on computers are considered rarely static and each modification applied to the computer runs the risk of introducing viruses that could damage the computer configuration. Software controls provide security against the existing challenges such as viruses. Some organizations allow downloading of software through the Internet and they commonly used virus scanning at the firewall; however, it does not eliminate the need for server-based virus scanning. A virus is a self-replicating program and it can modify a program. Viruses can damage and delete all the data on a disk and there are different levels of sophistication needed to detect certain viruses. There is a security service policy that prevents introduction of viruses. It can detect if the boot record or data file is contaminated with a virus. It includes removal tasks that delete viruses from infected systems and may require reinstallation of the operating system from the infected file. There is virus scanning software that can detect viruses that are previously identified; however, sophisticated viruses are being developed continuously. The software can be installed only from approved internal servers and file transfers from external sources are not permitted. Anti-virus software limits the spread of viruses within the network, most often, anti-virus software is configured and installed on computers (Arnold, 2008).
Time Basic Issues
The project will take several years to complete however the following is the time chart of how the project will be implemented.
Implementing other supporting recommendations:
An organizational task force was formed to consider four remaining organizational issues:
- training and development
- organizational structure
- staffing
- Top management role.
The organizational task force worked for 10 weeks to analyze, resolve, and recommend a program. They presented their report to the management committee at the end of the 12TH-week charter.
Methodology
This provides the fundamental analysis of the research formulation and framework. It includes the basic summary of literature review, work in accordance with the findings with the help of a conceptual framework of quantitative measures along with measures taken during data collection and sample designing. It would also justify the collection procedure and provide an insight into measures taken during primary and secondary data collection.
As it was discussed in the previous section, the literature review of previous studies was limited in a sense that it does not establish purchasing system required. As it was mentioned this could be a result of undefined objectives and accordingly different points of emphasis. This section will make an attempt to connect the conclusions presented in the literature review, related to the topic of this research, through data collection and analysis.
The framework of this study will be of a quantitative design. The reason for this selection is mainly because of the causal relation approach in establishing the aim of this study and its hypothesis. Additionally, as survey was chosen as the tool for data collection, where it could be considered as the traditional technique in quantitative techniques, this choice could be seen as appropriate. Another argument in favor of quantitative design is the fact that the purpose is seen in achieving generalization and prediction through established hypotheses and theories, rather than interpreting the data and having a theory as a final result. The main assumption is that general internet skills showed through internet usage and online shopping, positively affect their privacy awareness. In that sense two variables were established, where the independent variable was assigned to the internet and online shopping skills to control different variations of that value, and the customers’ privacy awareness is the observed value and thus the dependant value. The main process will imply aside from the background information measuring the customers’ retention within the online shopping activities based on the various behavioral marketing changes.
The secondary data was gathered through conducting a series of personal interviews, where the interviewees were selected randomly and asked questions similar to the survey with an exception of providing a brief description of the literature review findings in the context of privacy. Implementing such an approach, was intended to eliminate the factor of ignorance in case of privacy issues when used as supportive data.
Limitations
Limitations to the research would include many different considerations. Those considerations are inclusive of the number of respondents along with the number of users and officials in the general vicinity. Other things that limit this research would in fact be the concerns of other levels of awareness including professionals of various genres. Certainly, another limitation includes the ready acceptance to answer the questionnaires provided regarding this research project. The numbers of students willing to volunteer this information even with assured anonymity provided several limitations toward tabulation and calculation accuracy regarding percentages.
References
- Beamon, B.M (1996) ‘Performance Measures in Supply Chain Management’, Proceedings of the 1996 Conference on Agile and Intelligent Manufacturing Systems, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, 2-3, New York
- Beamon, B.M (1998) ‘Supply Chain Design and Analysis: Models and Methods’, International Journal of Production Economics, 55, 281-294
- Benbasat, I, Goldstein, K.D and Mead, M (1987) ‘The Case Study Research Strategy in Studies of Information System’, MIS Quarterly, 11:3, 369-384
- Camp, R.C (1989) Benchmarking- The Search for Industry Best Practices that Lead to Superior Performance, ASQS Quality Press, Milwaukee, WI
- Chan, F.T.S (2003) ‘Performance Measurement in a Supply Chain’, International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 21, 534-548
- Chen, I.J and Paulraj, A (2004) ‘Towards a Theory of Supply Chain Management: The Constructs and Measurements, Journal of Operations Management, 22, 119-150
- Chopra, S and Meindl, P (2001) Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
- Christopher, M (1992) Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Strategies for Reducing Cost and Improving Services, Pitman, London
- Ellinger, A.E (2000) ‘Improving Marketing Logistics Cross Functional Collaboration in the Supply Chain’, Industrial Marketing Management, 29, 85-96
- Gunasekaran, A and Ngai, E.W.T (2003) ‘The Successful Management of A Small Logistics Company’, International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 33:9, 825-835
- Gunasekaran, A, Patel,C and Tirtiroglu, E (2001) ‘Performance Measurement and Metrics In A Supply Chain Environment’, International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21:102, 71-87
- Gunasekaran, A., Williams, H.J and Mcgaughey, R.E (2003) ’Performance Measurement and Costing System in New Enterprise’, Technovation, 25:5, 523-533
- Huang, S.H, Sheoran, S.K and Keskar, H (2005) ‘Computer-Assisted Supply Chain Configuration Based on Supply Chain Operations Reference Model (SCOR) Model’, Computers & Industrial Engineering, 48, 377-394
- Knemeyer, A.M and Murphy, P.R (2004) ‘Evaluating The Performance of Third-Party Logistics Arrangements: A Relationship Marketing Perspective’, Journal of Supply Chain Management, 40:1, 35-5
- Lebas, M.J (1995) ‘Performance Measurement and Performance Management’, International Journal of Production Economics, 41:1/3, 23-35
- Mcginnis, M.A (1978) ‘Shipper Attitude towards Transportation Choice: A Factor Analytic Study’, International Journal of Physical Distribution & Material Management, 10:1, 25-34
- Neely, A, Gregory, M and Platts, K (1995) ‘Performance Measurement Systems Design: A Literature Review and Research Agenda’, International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 15:4, 80-116
- Rao, K, Young, R.R (1994) ‘Global Supply Chains: Factors Influencing Outsourcing of Logistics Functions’, International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 24:6, 11-19
- Shepherd, C and Gunter, H (2005) ‘Measuring Supply Chain Performance: Current Research and Future Directions’, International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 55: ¾, 242-258
- Lambert, D.M and Pohlen, T.L (2001) ‘ Supply Chain Metrics’, International Journal of Logistics Management, 12:1, 1-19
- Toni, A.D and Tonchia, S (2001) ‘Performance Measurement Systems: Models, Characteristics and Measures’, International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21:1/2, 46-70