Key Aspects of Economic Interdependence
The modern world is a complex mechanism, as it consists of numerous actors engaged in the division of labor and resource exchange. Even the countries with high political and economic influence have always experienced a need to trade 1. This matter can be explained by the economic interdependence theory, as all nations are the parts of the trading network and exchange the resources and products, which they cannot manufacture on their territories. The primary goal of the paper is to address the economic interdependence theory while discovering its critical tenets and highlighting the variables.
The economic interdependence suggests the enhancement of the economies of scale, a constant increase in the utilization of the raw materials, and decreasing marginal returns2. The overall level of economic growth (GNP) is linked to the dynamics of the economic interdependence, as the state gains can occur through trade3. The presence of GNP establishes the equilibrium in demand and supply of the nations, as the required goods are delivered to the nations in need. Nonetheless, presented aspects create the possibility for the opportunity costs, as the countries exchange the commodities4. The mentioned features are the core tenets of the theory and help determine the assumptions and the influence on the variables.
Economic Interdependence Theory: Assumptions
As was mentioned earlier, the economic interdependence theory requires the counties to engage in economic relationships. In this case, the exchange rate is one of the aspects of the economic interdependency, as the exports of one nation are dependent on the currency exchange in another country5. It defines interdependency and makes the sufficient exchange of resources a possibility. It determines the country’s GNP and assures the presence of the opportunity cost.
The political aspect has to be considered, as the impact of policies and sanctions cannot be underestimated due to its ability to be considered as a cause of limitations of the product’s exchange6. The development of a favorable political environment is essential as it defines the capabilities of the country to trade with the other nations. Lastly, the presence of peace assures the well-being of the nations and allows governmental budgeting and planning to maintain the flow of imports and exports7.
Expectations of Future Trade and Conflict
Based on the information above, the primary variables selected for the analysis are future trade expectation, which is an independent variable, and conflict (dependent variable). The presence of interdependence tends to exist due to the dependency of the GNP of the nations on the exchange and diversity of labor. In general, future trade expectations can be referred to as the development of the particular trends and expectations about the potential areas of the behavioral patterns of the nations engaged in the trading relationships8.
The conflict implies the nations have different viewpoints while determining the necessity of the distribution of the particular resources9. In this instance, the conflict is considered as a political, economic, and social phenomenon, as it has a vehement influence on the well-being of the country and causes instability in the world. In turn, it contributes to the understanding of the precise economic expectations of other actors due to the existence of the conflict’s rationale.
Variables in the Context of the Theory
The economic interdependence theory has a vehement influence on the selected variables. The expectations of future trade might be considered as a potential reason for the development of the conflict in the context of the economic interdependence theory since the lack of compliance with the anticipations might be a cause of the increased level of aggression10. In this case, the expectation of future trade is the matter, which tends to affect the growth of the conflict and define the assumption regarding the actions of other actors. In turn, the conflict is a response to the actions of the other participants of the economic exchange due to the absence of agreement in future opportunities.
Operationalization of Each Variable
Additionally, the variables are discovered in more detail. Expectations of the future trade are divided into the positive and aggressive attitudes towards the actions of the other nations while referring to the ability of the country A to fulfill the expectations of the state B. A negative attitude are determined by the lack of economic growth and rise in the development of the trade policies in the country B. As for the conflict, it will have two gradations as war and peace. On the contrary, peace will be characterized by the sufficient wellbeing of the nation and the economic enhancement. Trading relationships will be developed in a sophisticated manner while aiming at the increase in GDP and division of the resources.
Casual Logic
The interdependence of the selected variables can be described with the assistance of the graph presented in Figure 1. In this case, it remains evident that the lack of agreement with the future trade expectations can be considered as the primary reason for the conflict, as it drives the cultivation of the negative attitudes of the political leaders. In turn, it leads to the increasing necessity of the interventions in the functioning of the other countries to assure the delivery of required resources11. In turn, peace is associated with the ability of the countries to find compromises and contribute to the understanding of the substantial nature of the exchange and development of economies of scale for economic growth. The peaceful environment is the primary cause of the economic, social, and political stability and definer of the establishment of the trusting trade relationships12
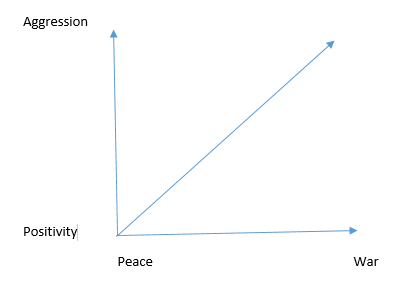
Generic Hypothesis
The findings contribute that the generic hypothesis can be formulated as if state A does not comply with the expectations of state B to deliver the required resources, state B may change its attitudes to aggression, and a lack of the compromise may lead to the conflict. On the contrary, the trusting relationships and compliance with the trade expectations are core definer of the absence of conflict. Figure 2 depicts the flow of events related to the presented hypothesis.
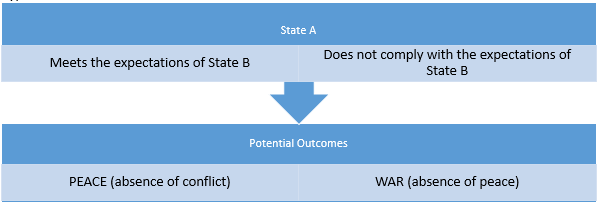
Conclusion
The economic interdependence theory is the core component in the modern world, as it defines the division of labor and exchange of the resources. Its critical tenants affect the global economy by influencing GNP, opportunity costs, exchange rates, and division of labor. The future trade expectations affect the presence of conflict, and the development of the policies can help introduce new approaches for the optimization of exchange and the ability to find equilibrium between supply and demand.
Bibliography
Copeland, Dale. Economic Interdependence and War. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2015.
Gartzke, Erik, Li, Quan, and Boehmer, Charles. “Investing in the Peace: Economic Interdependence and International Conflict,” International Organization 55, no. 2 (2001): 391-438.
Humphreys, Macartan. “Natural Resources, Conflict, and Conflict Resolution: Uncovering the Mechanisms,” Journal of Conflict Resolution 49, no. 4 (2005): 508-537.
Footnotes
- Dale Copeland, Economic Interdependence and War (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2015), 29.
- Ibid, 30.
- Ibid, 45.
- Ibid, 47.
- Ibid, 160.
- Ibid, 161.
- Erik Gartzke, Quan Li, and Charles Boehmer, “Investing in the Peace: Economic Interdependence and International Conflict,” International Organization 55, no. 2 (2001): 391.
- Copeland, Economic Interdependence and War, 38-39.
- Macartan Humphreys, “Natural Resources, Conflict, and Conflict Resolution: Uncovering the Mechanisms,” Journal of Conflict Resolution 49, no. 4 (2005): 508.
- Copeland, Economic Interdependence and War, 48.
- Ibid, 161.
- Gartzke, Li, and Boehmer, “Investing in the Peace”, 399.