Introduction
Online educational tools such as Google Classroom have gained a massive following over the past years due to their reliability in assisting teachers in sharing content with students, irrespective of geographical limitations. As a result, many institutions worldwide have shifted all their education initiatives online or adopted a mix of digital and in-house teaching and learning. Although extensive research describes the effectiveness of technological solutions in enhancing education, limited studies focus on the applicability of assessment solutions such as online quizzes on students’ learning development. Hence, the following research addresses this topic and makes assumptions that online quizzes have benefits and disadvantages that educators should acknowledge in spearheading positive advancements.
Background
Rigorous assessment and evaluation methodologies are critical for high-quality education because they inform teachers of students’ weaknesses and areas that require more attention for better outcomes. However, the benefits of periodic examinations extend to learners by enlightening them about their strengths and giving them an idea of the topics they should study more to obtain desirable results. Nevertheless, the techniques used in the process are critical in facilitating development because different assessment approaches target specific learning indicators and solicit various reactions from students (Sotola and Crede, 2021).
Online quizzes are commonly adopted to assimilate students’ ability to memorize information and understand concepts. However, more research on the reliability of these methods is needed to ensure educators maximize their benefits. Hence, the following study investigates whether using online quizzes to assess learners’ development is valid and reliable in improving learning outcomes and offers recommendations to enhance the value of online assessments.
Research Methodology
The study adopted a qualitative research design, allowing it to draw data from various resources. Qualitative studies describe approaches to obtaining non-numerical data and theoretical concepts to investigate phenomena. Subsequently, the study received information by conducting a literature review of past scholarly resources focusing on the effectiveness of online quizzes in evaluating educational advancement. The data sources selected for the research included books, journals, and authoritative websites. As a result, the study searched for information in journals such as the Educational Research Review and search engines including Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar, and Google Books. The initiatives singled out seven scholarly journals published less than five years ago that addressed the topic of concern and analyzed these resources for correlations.
Literature Review
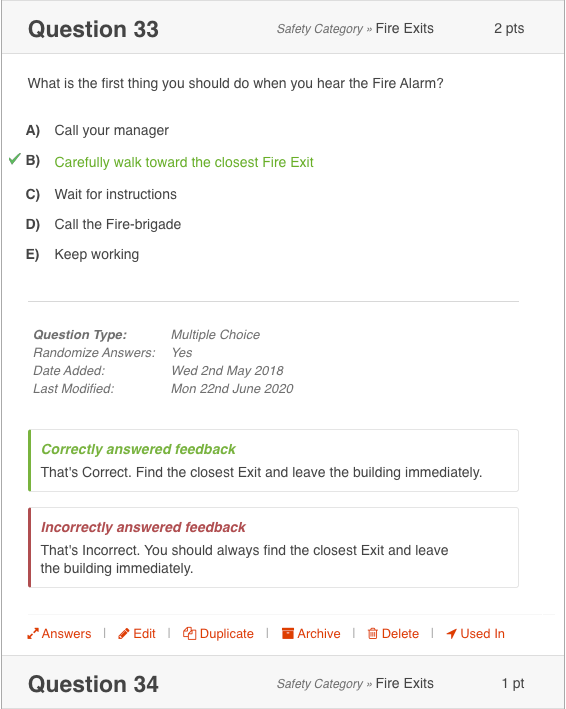
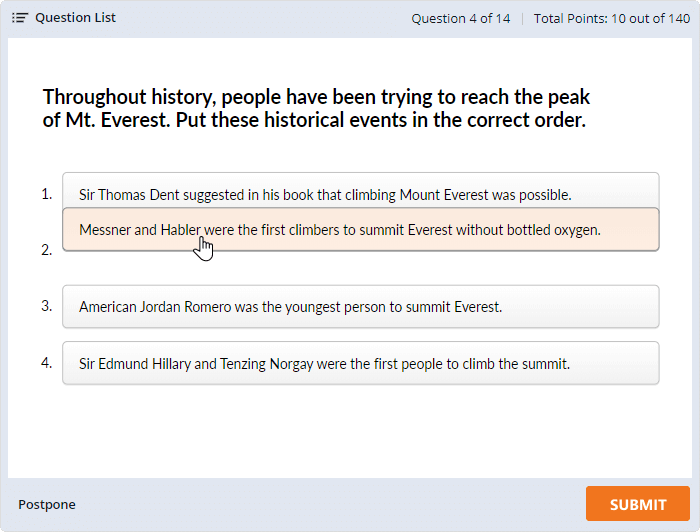
Online education solutions place significant responsibility on the student as they necessitate being self-disciplined, self-motivated, ambitious, and curious to enhance continuous learning through discovery. As a result, evaluation provides critical information on whether students meet specific targets and their levels of understanding (Ogange et al., 2018). Online quizzes commonly test learners’ ability to grasp concepts, knowledge of various ideas, and long and short-term memory. The various types include multiple-choice tests, simulations, tutorials, short answer questions, performance evaluation tests, presentations, flashcards, and case studies, as shown in Figure 1 (Sabrina et al., 2022).
However, Usagawa (2018) suggests that educators can design these quizzes to aim at specific factors, such as increasing student engagement and promoting learning by enhancing motivation. The researchers explain that online quizzes challenge learners’ perceptions and allow them to tackle problems from various perspectives (Usagawa, 2018). In addition, they encourage students to become more curious by stirring up their interests to identify where they went wrong.

Most online quizzes are different from other forms of digital assessments because they do not contribute to graded results. As a result, they allow better self-expression and encourage students to respond according to their comprehension (Sotola and Crede, 2021). That being said, online quizzes are a more reliable way to gauge students’ understanding of concepts because they factor out limitations such as the pressure associated with getting everything correct and the reparations of failing. In addition, online quizzes are beneficial in creating a competitive learning environment because results can be tabulated and ranked to inform students of their performance (Ogange et al., 2018).
Hence, they help students determine whether they are failing their classwork and push them toward more effort. Similarly, the transparency associated with online quizzes enables teachers to note unusual changes in performance and take action (Sotola and Crede, 2021). Therefore, online quizzes are dependable measurement tools because they create a competitive education environment and provide a more accurate evaluation of results.
Similarly, online quizzes are appraised for their ability to enhance students’ engagement by establishing a learning community with valuable experiences. Teachers can issue online quizzes before introducing a topic in class to judge students’ general knowledge or after completing a course to evaluate their understanding (Elzainy, El Sadik and Al Abdulmonem, 2020). Regardless, these techniques engage learners in brainstorming and sharing ideas associated with their studies. As a result, students develop a positive attitude toward learning due to continuous engagement with various concepts and exposure to others’ opinions. Subsequently, online quizzes can help establish online communities by inspiring students to engage in discussions and develop relevant solutions to problems (Gamage et al., 2019). Similarly, online quizzes enable teachers to actively participate in these discussions and comment on the student’s ideas. Hence, they facilitate learning by encouraging interactions between peers and educators.
Although online quizzes are reliable in soliciting a positive response from students and encouraging higher levels of teacher participation in online class discussions, they might fall short of expectations if not designed to meet educational standards. According to Sotola and Crede (2021), mastery and occasional completion of online quizzes strongly predict students’ performance in summative examinations. However, educators need help to achieve desired outcomes due to their inability to design online quizzes that investigate specific indicators depending on learning needs (Gamage et al., 2019). In addition, some teachers need a plan of action or routine to guide their assessment using online quizzes. As a result, they may need help finding helpful information or learning how to use the data for learning improvement. Therefore, instructors should pay more attention to their role in designing reliable online quizzes and facilitating learner engagement.
Discussion
The literature analysis reveals that adopting online quizzes in students’ evaluation and assessment bears significant benefits that surpass testing students’ knowledge and understanding of concepts. Depending on their designs, online quizzes can encourage knowledge-seeking habits in students and facilitate self-learning (Sabrina et al., 2022). In addition, they contribute to a supportive learning environment where students can share their ideas, learn from each other, and interact with one another, thus making digital education more exciting and interactive (Elzainy, El Sadik and Al Abdulmonem, 2020).
Better yet, online quizzes enhance the value of the teaching experience for teachers as it puts them in a better position to tell whether their students are familiar with learned concepts accurately. Online quizzes maximize students’ engagement by facilitating continuous interaction with class materials and including their instructors in class discussions. Therefore, educators can use these quizzes to improve their educational initiatives and obtain better results.
Despite numerous benefits to teachers and students, online quizzes have disadvantages that prevent educators from reaping their benefits. For example, these quizzes take various forms and are applicable in different situations. Therefore, failure to acknowledge these variations can limit the relevance of online quizzes and erode their effectiveness in evaluating students’ advancement and guiding learning instruction (Gamage et al., 2019).
In addition, designing online quizzes to assess specific learning outcomes is a complicated process that can inhibit teachers from occasionally adopting these mechanisms to foster continuous improvements (Sotola and Crede, 2021). As a result, they may need to see the benefits of using online quizzes in assessments compared to other evaluation methods, thus discouraging their application. Hence, informing teachers of the stages and mechanics involved in designing, issuing, and obtaining data from online quizzes can guide them to improve gradually.
Recommendations
Online quizzes are a unique type of assessment due to their transparency and range of applications. However, most students have yet to master how to tackle these quizzes, thus introducing limitations to their effectiveness. According to Usagawa (2018), continuous assessment and formative feedback processes are critical to ensuring the reliability and validity of online evaluations. Therefore, educators should lead their students in responding to these quizzes and establish a culture that applies the technique to improve learners’ engagement and outcomes (Sotola and Crede, 2021). Although giving out quizzes after every lesson might be strenuous, there are several tools that teachers can leverage to design appropriate quizzes and teach students how to use them to improve their performance. Therefore, ensuring the continuous application of this assessment method can help educators gradually improve learning and achieve educational goals.
Assessing the validity and reliability of online quizzes requires a comprehensive understanding of the mechanics involved in their designs and how to use information obtained from these evaluations to promote learning. Therefore, educational institutions should organize teacher training to equip educators with the skills to design and use online quizzes to enhance learning development (Gamage et al., 2019).
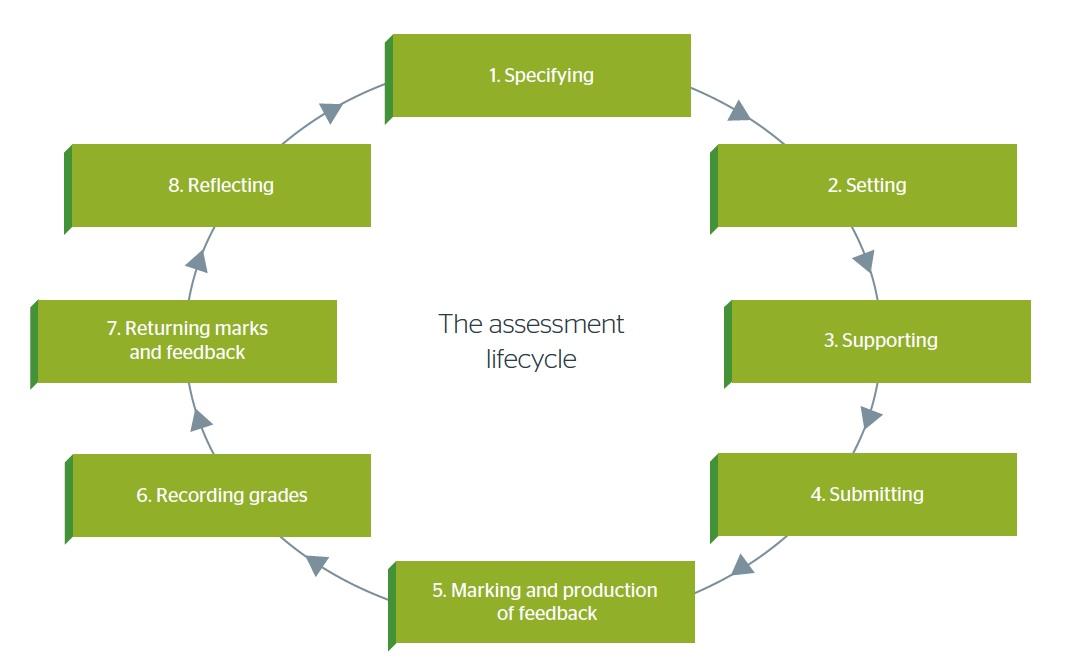
Paying attention to all the components of the assessment life-cycle can guide educators on where to begin. Figure two highlights the life cycle’s main factors, including specifying, setting, supporting, submission, narking, recording grades, providing feedback, and reflecting (Enders, Gaschler, and Kubik, 2021). In addition, teachers should have access to resources that guide them in maximizing the benefits of online quizzes and inform them of the latest techniques and commonly used designs to obtain comprehensive results(See appendix). With time, more teachers will learn of the value of online quizzes and familiarize themselves with the strategies to improve teaching and learning using these solutions.
Conclusion
Evaluation and assessment are integral in delivering instruction because they assist educators in determining whether their methods achieve the intended outcomes. In addition, the results obtained from evaluations affect decision-making as they inform instructional needs and aid in curriculum design. Notably, adopting online quizzes in assessment and evaluation is beneficial for progressive learning because it assures transparency and allows teachers to note their students’ understanding.
Moreover, they create a supportive environment that will enable students to contribute openly to discussions. Furthermore, online quizzes encourage engagement through continuous interactions and include educators in the forum. However, most educators fail to experience these benefits because of unreliable designs and a need for more information on how to use online quizzes to improve learning outcomes. Thus, institutions should train teachers on how to apply these solutions and encourage their occasional use so that students can gain a mastery of how to tackle these quizzes and maximize their benefits.
Reference List
Enders, N., Gaschler, R. and Kubik, V. (2021) ‘Online quizzes with closed questions in formal assessment: How elaborate feedback can promote learning’, Psychology Learning & Teaching, 20(1), pp.91-106. Web.
Elzeiny, A., El Sadik, A. and Al Abdulmonem, W. (2020) ‘Experience in e-learning and online assessment during the COVID-19 pandemic at the College of Medicine, Qassim University’, Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, 15(6), pp.456-462. Web.
Gamage, S.H. et al. (2019) ‘Optimising Moodle quizzes for online assessments’, International Journal of STEM Education, 6(1), pp.1-14. Web.
Orange, B.O. et al. (2018) ‘Student perceptions of the effectiveness of formative assessment in an online learning environment’, Open Praxis, 10(1), pp.29-39. Web.
Sabrina, F. et al. (2022) ‘Ensuring academic integrity in online assessments: a literature review and recommendations, International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 12(1). Web.
Sotola, L.K. and Crede, M. (2021) ‘Regarding class quizzes: a meta-analytic synthesis of studies on the relationship between frequent low-stakes testing and class performance’, Educational Psychology Review, 33(2), pp.407-426. Web.
Usagawa, T. (2018) ‘Effectiveness of e-learning experience through online quizzes: a case study of Myanmar students’, International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 13(12). Web.
Appendix
Examples of commonly used online quiz layouts