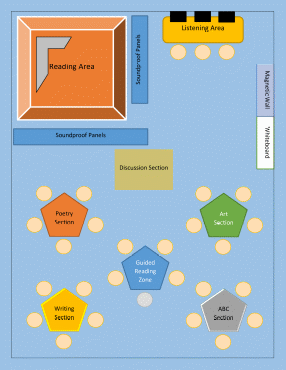
It is important to note that literacy centers seek to promote literacy in a comprehensive manner by developing essential skills in a multifaceted way. The sketch with labels for the literacy center can be accessed in Figure 1 below the text. The key areas of focus of the literacy center for the given classroom will focus on vocabulary, fluency, comprehension, writing, reading, listening, communication, and alphabet puzzles.
When it comes to the list of supplies, the most important elements include basic educational resources. These include age-appropriate books, alphabet puzzles, poems, headphones, computers, tables, seats, soundproof panels, colored pens and pencils, a sofa, a whiteboard, brushes, paint, carpets, pins, TV, CD, and magnetic letters (Solis, 2022). These core items are needed for the literacy centers in order to provide children with the tools and instruments needed to facilitate literacy, learning, and development. The key areas of the literacy center will include a poetry section, art section, ABC section, writing section, reading area, listening area, guided reading zone, magnetic wall site, whiteboard area, and discussion area.
The key rules will be centered around independent work in order to minimize the reliance on the literacy center educator. The underlying rules of conduct and behavior include self-sufficiency, independence, collaboration, self-regulation, organization, and responsibility (The Balanced Literacy Diet, 2011). The reasoning is that children should be able to learn individually as well as collaboratively to develop the skills needed in their future.
By creating a learning environment where the learners actively engage with resources and tools to improve their literacy, they will simultaneously become more competent at navigating and directing the process at their own pace. This essentially constitutes an activity-based and student-centered learning concept (Solis, 2022). Children are curious and eager to become more literate by nature, but they need to be provided with access to the materials, social circle, tools, and learning environment. In other words, the literacy center will heavily focus on enabling self-sufficiency, independence, collaboration, self-regulation, organization, and responsibility.
The children will be introduced to the literacy center by conducting a physical tour of the space. The purpose of each site or table will be labeled visibly, which will prevent confusion and rule violations. The first step will involve introducing the fundamental six rules of the literacy center, which are self-sufficiency, independence, collaboration, self-regulation, organization, and responsibility. The second step is to help a child to meet and greet other children if they do not particularly know each other. In other words, social cohesion is critical for the success of learners as well as the center. The third step will focus on dividing children into groups and allocating their corresponding sites of literacy development to jumpstart the process, but they will be allowed to visit any area they prefer.
During the year, the books, CDs, puzzles, and poems will be updated in accordance with their development to ensure that the resources match their age and literacy levels. The consumables will be constantly replaced, such as paints, brushes, pens, and pencils. The soundproof panels will be subsequently replaced by walls to ensure that the reading area is quieter. The interior will additionally be changed with decorations depending on holidays, seasons, or other events at the center.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the literacy center will develop children’s vocabulary, fluency, comprehension, writing, reading, listening, communication, and alphabet puzzle-solving skills. The key areas are the poetry section, art section, ABC section, writing section, reading area, listening area, guided reading zone, magnetic wall site, whiteboard area, and discussion area. The six rules of independent work include self-sufficiency, independence, collaboration, self-regulation, organization, and responsibility.
References
Solis, K. T. (2022). What are literacy centers? Language Humanities. Web.
The Balanced Literacy Diet. (2011). Literacy centers: Developing skills in reading and writing (virtual tour) [Video]. YouTube. Web.