Executive Summary
The study tends to determine the relationship between employees’ satisfaction and empowerment, compensation, and career development, taking ADNOC as the case. Both qualitative and quantitative methods of data collection were applied. Besides, the literature review, a survey was conducted among thirty participants to determine the correlation between the variables.
The findings from both the literature review and the survey indicated positive correlations between employees’ satisfaction and empowerment, compensation, and career development. According to content analysis based on the reviewed literature, compensation plays a critical role in employee satisfaction. Besides enhancing performance, employees are mostly motivated by a better remuneration system of the firm.
Factors such as pay rate system and compensation reviews were found to have a critical role in enhancing satisfaction, motivation, and performance. Besides compensation, employee empowerment was also cited as significant in enhancing satisfaction. Besides, factors including involvement in decision-making, participation in goal setting, increased access to information, increased latitude in the work, and increased opportunities to suggest improvements are the indicators of employee empowerment.
The results indicated that the firm is somewhat effective in ensuring that the indicators are attained. In terms of opportunity for growth, the survey indicated fair performance by the firm. The majority of the respondents were not satisfied with the level of interest the firm show for professional growth. However, as indicated in the literature, the survey results show a positive correlation between these variables and the satisfaction of employees. The conclusion is that employee empowerment, compensation, and career development have a positive influence on the job satisfaction and motivation of the workforce.
Introduction
Employee satisfaction is critical in the attainment of the organization’s goals. In fact, there is a positive correlation between employee satisfaction and reduced turnover rates. Therefore, firms should pursue actions that ensure increased employee satisfaction within the workplace. Various factors determine the level of satisfaction among employees within the organization.
Some of these factors include employee empowerment, compensation, and career development. While the level of employee satisfaction within the organization can be determined by several variables, the paper will concentrate on how empowerment, compensation, and career development influence employees’ satisfaction within the organization in particular ADNOC.
However, the research paper is organized as follows. First, the paper will discuss the purpose of the research study. The paper will then provide the company overview and study problems. Second, the paper will discuss the research methodology, including both primary and secondary data collection methods. Third, the paper will discuss the literature review in which independent variables are highlighted in detail with the support of examples and how they can affect the organization. After that, the questionnaire analysis will be discussed. Finally, recommendations will be addressed and a conclusion drawn on the study findings.
The Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to investigate the correlation existing between employee satisfaction and empowerment, compensation, and career development. The objectives of the study include
- To determine the relationship between an employee’s satisfaction and the independent variables
- To determine the effects of each of the independent variables on the employee’s satisfaction
- To determine the best guidelines approach to implementing the independent variables
The research objectives were particularly determined to answer the following questions
- What is the relationship between employee satisfaction and empowerment, compensation, and career development?
- What are the effects of empowerment, compensation, and career development on employee satisfaction?
- What are the best approaches and guidelines to implement empowerment, compensation, and career development?
The Company Overview
Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) is one of the leading oil and gas companies in UAE. Since its establishment in 1971, the firm has experienced steady growth, particularly its activities within the oil and gas industry. Besides, the firm has been successful in establishing its subsidiaries within the UAE and the Middle East, resulting in the integration of all activities within the oil and gas industry.
In fact, since its inception, the firm has increased its business operations and attained a competitive edge to become one of the leading global oil producers. Currently, the firm has over fourteen subsidiaries working in various areas within the oil and gas industry around the Middle East. Besides, the firm has numerous business interests in both upstream and downstream business activities. The subsidiaries of the firm range from ADCO to ADNATCO.
Problem Definition and Symptoms
The number of new firms in the Middle East, particularly in UAE has tremendously increased over the past decade. Among the industries that have attracted firms is the oil and gas. As a result, there is intense competition leading to restructuring and realignment to attract highly skilled and talented employees.
The continuous scramble for highly skilled personnel has resulted in an increased percentage of workforce turnovers, which further caused a decrease in the general productivity and efficiency. As a result, human resources management within ADNOC decided to conduct an extensive research that would enable it to understand the variables that contributes to increased satisfaction of workers. The understanding of the relationship between the variables and the worker’s satisfaction would enable the firm put in place strategies that guarantees increased competitiveness.
Research Methodology
Secondary data collection
Secondary research is a process where the required information is collected through existing literature or studies that have been conducted. In this study, the secondary data will primarily be obtained through the literature review of peer reviewed academic journals regarding the proposed topic. Similarly, the secondary research data and information will accrue from the organization’s records particularly on the relationship between employees’ satisfaction and empowerment, compensation and career development as well as any other document that has been filed by the organization in relation to the human resources practice under study.
Primary Data Collection (Surveys)
In this study, though all the employees of the firm were deemed viable, only 30 selected through appropriate sampling strategy participated in the survey concerning the research topic. Essentially, only twenty employees out of 2800 participated in the survey. Among the 30 employees that participated in the survey, 17 were males while 13 were females. Besides, the age of the participants ranged between 28-40 years and the majority had extensive experience with the firm.
In addition, the questions on the survey questionnaire concentrated on the study variables that included empowerment, compensation and psychological contract and their relationship with motivation. Moreover, the study was conducted at ADNOC HQ Company without considering its subsidiaries. The data from the survey was aimed at assisting in devising sound and rational study conclusions amid offering feasible recommendations for the research being conducted.
Employee Job Satisfaction
Employee’s satisfaction is one of the major determinants of the organization’s success. In fact, increased rate of satisfaction among employees in their jobs are directly linked to increased performance and attainment of the firm’s objectives (Mushipe, 2011). As such, organizations have greater responsibility of ensuring that their employees are satisfied.
Employee Empowerment
Overview
Employee empowerment is considered one of the factors that contribute to increased job satisfaction. In fact, an empowered employee feels highly motivated which in turn leads to increased job satisfaction (Maria & Militaru, 2013). However, Lawson, Savery and Alan 2001 argue that the concept has often been misunderstood within the workplace. Majority of the organization’s managers often misses the concept in their practices.
While most organizations believe that employee empowerment is the total submission of responsibilities and control, empowerment involves is a culmination of various ideals and tenets that increases employees’ satisfaction (Lawson et al., 2001). In fact, communications play a significant role in employee empowerment. Essentially, all aspects of the organization have to be communicated freely and understood by employees. The businesses processes are ranging from the strategic plan to key performance indicators and daily decision-making procedures.
The concept of employee empowerment is often described as the processes that enable an employee to autonomously contemplate, perform, conduct, respond and regulate their work processes (Ismail, 2007). In fact, effective employee empowerment has constructive insinuations not only on increased employee’s satisfaction but also on various organizational features including retention of the workforce (Pelit, Öztürk & Arslantürk, 2011).
Elements of Employee Empowerments
Delegation of Authority in Decision-Making
The delegation of authority in decision-making is the process through which employees are given the opportunity to decide and act on their individual work processes. Employees always feel empowered when given an opportunity to make independent decisions and act on various factors affecting their work processes (Lawson et al., 2001). Allowing workers to make personal decisions is a critical element in employee empowerment and often leads to increased job satisfaction. Essentially, the ability to make independent and persona
l decisions make employees feel motivated which in turn leads to increased job satisfaction.
In ADNOC, employees are organized into teams that have greater autonomy in making personal decisions. In other words, there is increased flexibility of decision-making processes within teams compared with individuals. However, workers feel comfortable with the flexibility in team’s decision-making processes due to the nature of their work processes. Essentially, workers would feel empowered when given greater autonomy in decision-making, which in turn increases their motivation and job satisfaction (Maria & Militaru, 2013).
Encouragement and Support
An organization can provide support to the employees through various ways. In fact, employees would always feel empowered when the organization supports its decisions and work processes. The organization can encourage increased performance, being innovative as well as good behaviors within the organization (Mushipe, 2011). Besides, the organization can support workers through the provision of technical knowhow and finances required in the completion of tasks. An employee that are supported and encouraged would always be motivated towards the completion of the assigned tasks, which in turn increases performances and job satisfaction.
In ADNOC, employees are always being supported and encouraged in order to complete their tasks. ADNOC is one of the organizations that have employees’ empowerment practices that encourage increased performance. However, such practices are executed through teams and not individually. Generally, encouragement and support provide employees with the increased capability of accomplishing a given task. In other words, encouragement and support are one of the critical elements of employee empowerment.
Autonomy and Freedom
Autonomy and freedom is the ability of employees to autonomously contemplate, perform, conduct, respond and regulate their work processes (Maria & Militaru, 2013). In other words, the ability of employees to perform all the work processes without tight regulations forms the supervisors. In addition, employees that enjoy such autonomy in the work processes feel highly empowered.
In ADNOC, autonomy and freedom are provided to the employees but with limited procedures. Autonomy and freedom do not necessarily apply to the work processes particularly to the employees at the lowest cadre. However, employees in senior management positions have increased autonomy in decision-making and other work processes.
Financial Empowerment
Financial empowerment is directly linked to motivation and job satisfaction. From the perspective of employees, financial rewards are a major determinant of motivation and increased performance (Pelit et al., 2011). On the other hand, financial empowerment involves freedom to allocate the financial resources in line with the goals of the organizations. The freedom in the determination of financial spending within the departments enables such employees to prioritize their needs, which in turn increases the employee’s motivation and job satisfaction.
In ADNOC, the departmental heads and teams are empowered to have their own budgets that would enable them attain the desired goals and accomplish the assigned tasks. The financial freedom in budgetary allocations and prioritization of needs has led to increased motivation among teams and various departments within the organization. Essentially, financial empowerment both in terms of compensations and in terms of freedom in budgetary allocations is critical in enhancing the employees’ motivation and job satisfaction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Employee Empowerment
Employee empowerment is directly linked to increased motivation and satisfaction. Essentially, employee empowerment contributes hugely towards the motivation of employees, which in turn leads to increased performance. Essentially, employee empowerment is considered one of the significant factors that contribute to increased job satisfaction. Maria and Militaru 2013 argue that empowered employee feels highly motivated, which in turn leads to increased job satisfaction and performance. Further, Pelit, Öztürk and Arslantürk 2011 asserts that employee empowerment contributes to increased innovativeness and enable employees to make decisions and take actions as well as control of their own work processes. The freedom to make decisions, act and take control of individual work processes is leading to increased motivations, which translates into greater efforts geared towards attainment of the organizational goals. In essence, empowered employees have a sense of control of personal efforts towards success, which in turn benefits the entire organization (Ismail, 2007).
Guidelines to Apply Employee Empowerment
The implementation of employee empowerment is critical in ensuring an environment where employees work as a team and reliability among the workforce.as such it is critical to have a guideline through which such processes could be implemented. The first step involves adopting the characteristics of a good leader. In fact, the organization leadership should continue promoting employee empowerment programs and leadership capabilities.
The second step involves clear and concise delegation of tasks. All employees have to understand their roles and responsibilities on the assigned tasks. The third step is acknowledging the achievements of the employees. In fact, all success should be appraised and rewarded. Fourth step involves opening the doors to the employees. In other words all the opinions and views of the employees should be valued and being involved in the decision-making. The fifth step involves coaching of employees on new skills and the developments the firm has undertaken. Sixth step is the promotion of employees’ education.
Managers should provide an environment through which employees can advance in terms of training and development in order to optimize their performances. The seventh step is the delegation of power. As employees increase their skills and competencies, more freedom is necessary particularly in determining the level of responsibility in accomplishing a given task. The eighth step involves acquiring feedback from the employees. In this step employees opinion on how best they can be empowered is considered. Finally, the manager should be willing to perform tasks they assign to their employees. In this case, leadership roles remain critical.
Opportunities for Growth and Job Satisfaction
Overview
One of the critical elements of employees’ satisfaction is the availability of opportunity for personal growth. Studies indicate that employees are more satisfied in an environment where they have increased opportunity for personal growth and development (Wanous & Lawler, 2012). As such, employees would prefer working in an organization that provides increased opportunities for personal advancements in terms of skills acquisitions. Opportunities for growth involve the capability of the organization to provide programs that ensure increased skills acquisitions by the employees. In most cases, organizations provide career development, skills enhancement as well as educational programs for their employees as part of this endeavor.
The acquisition of skills is critical for job security and confidence in the accomplishment of a given task. Besides, some employees may need to change their careers depending on the current needs of the organization. In any way, the opportunity for growth is aimed at enabling employees to acquire increased skills and competencies that result in increased performance and satisfaction.
Elements of Career Development
Career Development
Employees have become more conscious of their career development. In fact, current employees’ demands for personal growth and development have increased tremendously. As such, most organizations are now engaged in programs that are geared towards meeting the individual needs of employees (Wanous & Lawler, 2012). Essentially, career development opportunities to employees are more beneficial to the organization. Career development would ensure that the best talents are developed and retained within the organization. As such, organizations always tend to offer training as well as other programs that ensure improvement of the employees’ skills.
Development Programs for Junior Employees
Most organizations offer various development programs for their junior employees in order to attract and retain the best talents. ADNOC have come up with new programs for skills development aimed at attracting young graduates into the organization. The program provides increased benefits particularly in the career progress that is based on performance. The reason for the program is to provide opportunities for young and talented graduates to participate in the development of the economy.
Career Paths
Career paths are the line in which an individual is specializes. Most employees within the organization have their areas of specialization. For instance, some employees are specialized in accounting and engineering while others specialize in management. In most cases, employees would want to improve their skills in these specialized areas. Besides, employees would pursue new developments in these areas while others may want to change their career paths. In ADNOC, employees are given an opportunity to pursue their career paths. In fact, two opportunities are offered at managerial levels for employees that would want to change their careers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Career Development
One of the advantages of career development is the acquisition of skills. The acquisition of skills is critical for job security and confidence in the accomplishment of a given task (Wanous & Lawler, 2012). Besides, some employees may need to change their careers depending on the current needs of the job market and work environment. Essentially, career development is aimed at enabling employees to acquire increased skills and competencies that result in increased performance and satisfaction.
Guidelines to apply Career Development
Career developments are often undertaken through various training and development programs. Training and development should be aimed at improving the skills and competencies of the workforce. Training and development programs should also enhance specialized skills required to accomplish a particular job. Training and development should be broad enough to encompass the need of individual employees’ career growth.
Compensation and Job Satisfactions
Overview
Compensation systems are defined as any type of pay and incentives that an employee receives from the employer for the services rendered by the employees. In essence, compensation systems can be classified into either direct or indirect (Dinkin, 2009). Direct compensation includes wages and salaries, incentives and bonuses while indirect compensation includes benefits and non- fiscal rewards such as employee recognition programs and bendable working hours provided by the employer. Generally, compensation is vital in management since it rewards employees for their services and gives a source of livelihood (Dinkin, 2009).
Job satisfaction is comprised of several work friendly activities such as challenging work, exciting assignments, proficient management, good compensations and rewarding career. However, research has indicated that good compensation systems are the core component of any job satisfaction (Martocchio, 2011). In fact, most employees need adequate and equitable compensation systems that are fair and effectively correspond to their respective competencies skills and abilities. In addition, good compensation programs are very important in motivating employees hence increasing their productivity.
Elements of Compensation
Compensation and Benefits
One of the major effects of compensation is that employees are motivated to attain increased output. Good remunerations increase the worker’s motivation and job commitment that is translated into high performances (Richards, 2006). The forms of compensation also enhance the performance culture among the employees. However, these forms of compensation can hardly be determined without appropriate measurement procedures on job performance and output. Besides, increased efficiency cannot be divorced from employees’ high performance and attainment of the organizational goals. In ADNOC, employees are provided with better remunerations and benefits in order to retain the best talent and skills.
High Pay Strategy
Well-developed firms in the industry normally apply the high pay strategy. The high pay strategy involves providing employees with pay rates higher than the industry average (Shields, 2009). Studies indicate that high pay strategy leads to increased employees motivation and satisfaction. However, the best compensation strategy involves offering the pay rates depending on the prevailing current market rates (Locke, 2008). In ADNOC, the compensations are based on the prevailing market rates. In fact, the compensations are based on the employees’ performances, which are evaluated after a given period.
Periodic Compensation Review and Adjustment
Organizations often review their compensation systems after a particular period. In most cases, the rewards are reviewed on a yearly basis taking into consideration the employees’ performances and other external factors such as inflation and government regulations. Periodic review is critical in maintaining the pay rate that is commensurate with the needs of employees, which in turn motivates and ensure increased performance and satisfaction (Schoeffler, 2005).
Advantages & Disadvantages of Compensation
Most contemporary organizations are recognizing the employees’ compensation as one of the significant human resources practices that enhance organization competitive advantage and success. In essence, proper compensation ensures continuous flow of qualified staff with the required skills and technical competence to keep the organization at the competitive edge (Amuedo-Dorantes & Mach, 2013). The organizations have to recognize the fact that the qualified staff with the required skills and technical competence is the key driver for their growth and development. With the existing competitive environment, organizations find it necessary to keep such qualified staff within their workforce (Andrews & Rose, 2010). In addition, organizations must remain flexible when it comes to the management of employees’ compensations and benefits.
Guidelines to apply Compensation
The firm is to apply the reward system based on the job design and the level of performance. Besides, the firm is to apply the reward system based on other factors including the level of competencies, education, experience and positions in order to increase job satisfaction among employees.
Questionnaire Analysis
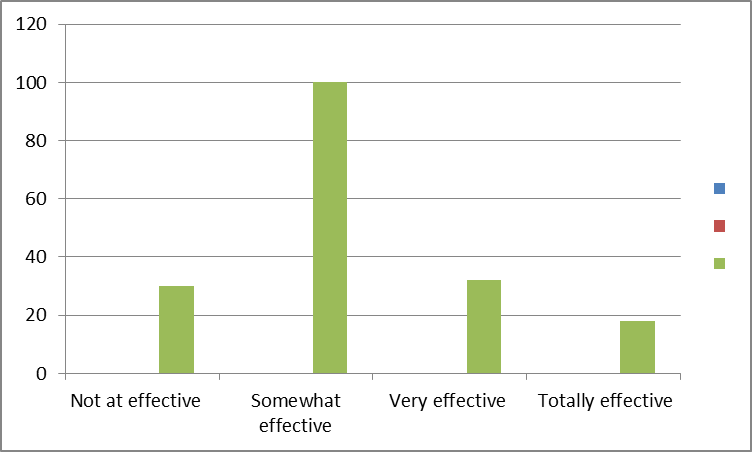
According to the survey that was conducted, the respondents were satisfied with the compensation systems of the firm compared with other variables. However, in terms of opportunity for growth and employee empowerment, the firm was found to be average. Considering the employee empowerment variable, the majority of the respondents rated the firm somewhat effective in their methods of empowering employees.
In fact, about 54% agreed that the firm is somewhat effective in allowing employees to make independent decisions on issues affecting their work processes. Besides, only 26% agreed that the firm is very effective while 10% gave the firm ineffective rating. Similarly, 43% argued that the firm is somewhat effective in providing opportunities for employees to suggest improvements while about 29% suggested that the firm is very effective. However, about 67% of the respondents agreed that they somewhat participate in setting goals and objectives relating to their job processes.
Moreover, according to the findings, the firm’s decisions are still made at the top. In fact, the majority of the respondents agreed that the firm is not effective in allowing employees at the lowest ranks to propose decisions affecting the organization and their job processes. In addition, the respondents are equally dived over the availability of information required for decision-making processes. About 52% felt that the organization is somewhat effective in providing such information. Similarly, about 54% of the respondents felt that the organization is somewhat effective in providing greater latitude for job processes as they gain experience.
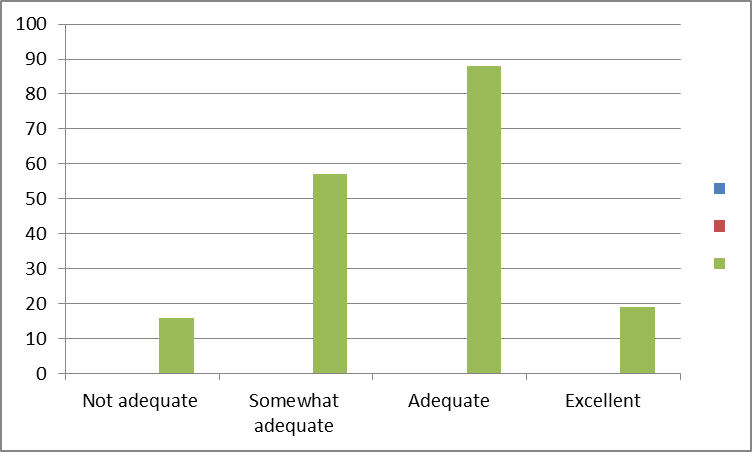
In terms of opportunity for growth, the majority of the respondents agreed that the organization has provided employees with adequate prospect for career development. In fact, about 70% of the respondents agreed that the firm provides adequate opportunity for professional growth. On the contrary, about 20% of the respondents felt that the firm somewhat give employees opportunity to professionally grow. Similarly, the majority of the respondents agreed that the organization provides adequate training needed to complete the required tasks. In fact, about 60% rated the organization adequate and excellent in terms of the availability of training for particular tasks.
Contrary to the expectations, most of the respondents are somewhat satisfied with the level of interest the organization has on their professional growth. Besides, about 52% felt that the organization does not support or show inadequate interest on professional growth and development. Similar sentiments are also expressed on the organizational support for personal career development. In fact, about 63% of the respondents were dissatisfied with the organization’s behavior towards the variable.
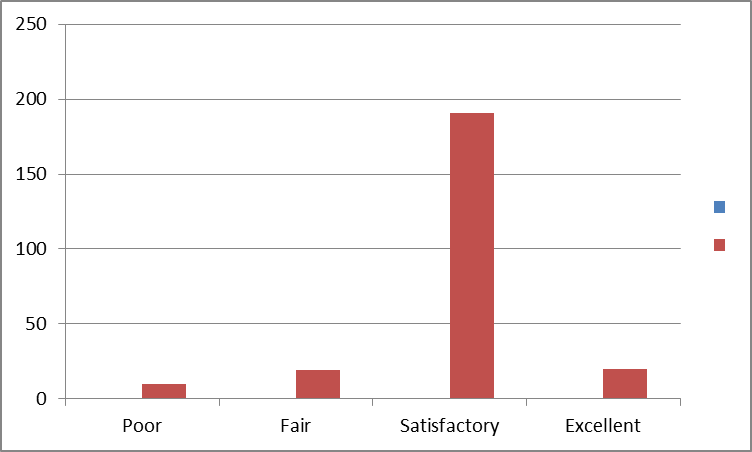
The contrasting results are not observed in the compensation variable. In fact, the results confirmed the claim of better compensation packages the organization offer to the employees. About 83% of the respondents rated the compensation package as satisfactory. Similarly, about the same rating is given the firm’s compensation package compared with other firms. Besides, about 73% of the respondents agreed that the compensation package offered by the firm is highly competitive. The question on benefits offered by the firm received almost the same response. In fact, about 74% of the respondents agreed that the benefits the firm offer is highly competitive compared with other firms in the industry. Moreover, the respondents were satisfied with the manner in which the firm conducts their compensation reviews. While only 10% disagreed with the reviews conducted by the firm, about 83% of the respondents agree that the compensation reviews are satisfactory and excellent. Generally, about 85% of the respondents agreed with the compensation strategy of the firm as being satisfactory.
Recommendations
- The following need to be enhanced to increase job satisfaction
- Providing employees with an opportunity to make individual decision concerning their work processes. Therefore, in relation to this variable
- Workers should be to suggest improvement in relation to their work processes
- Employees at the lowest ranks should be allowed to participate in the decision-making processes
- Employees should be allowed to set their own goals and objectives concerning their assigned tasks.
- Accessibility to information should also be enhanced within the organization particularly the information needed for the completion of the job processes
- Trainings for completion of particular jobs
- Training programs that provide opportunity for professional growth
- Provision of professional development support programs including educational vacations and incentives
- Compensations based on performance
- Review of compensation systems particularly on a yearly basis
- The following recommendations should be introduced to increase job satisfaction
- Talent management
- Compensation system based on performance
Conclusion
Employee’s satisfaction has been found to be critical in the attainment of the organizational goals. In fact, the study indicates positive correlation between employees’ satisfaction and empowerment, compensation and career development. Therefore, firms should pursue actions that ensure increased employee satisfaction within the workplace. As indicated in the study, empowerment, compensation and career development determine the level of satisfaction among employees within the organization. The factors interact with each other to influence the level of satisfaction employees have with the organization. Essentially, these variables remain critical for organizations to remain competitive within the current global marketplace. As recommended, ADNOC must implement these factors in order to remain relevant in a highly competitive industry.
Appendices
Appendix 1: The Questionnaire
Employee Empowerment – Response scale
(1) not at effective, (3) somewhat effective, (5) very effective, (7) totally effective
- I am involved in making decisions that affect my work
- I am given an opportunity to suggest improvements
- Proposed decisions are made at the lowest appropriate level
- I participate in setting goals and objectives for my job
- I have access to the information I need to make good decisions
- As I gain expertise, I am allowed more latitude on the job
Opportunity for growth – Response scale
(1) not adequate, (3) somewhat adequate, (5) adequate, (7) Excellent
- How could you rate opportunity for professional growth available to you
- How could you rate available training needed to complete your tasks
- Rate the level of interest the organization show for your professional growth
- How challenging is your job
- How could you rate opportunities available for career growth and development
- How could you rate organization support for personal career development
Compensation – Response scale
(1) Poor, (3) fair, (5) satisfactory, (7) Excellent
- Kindly rate your compensation package
- How could you rate your compensation package with similar rewards other firms offer
- How competitive is your benefits with similar jobs in other companies
- How could you compare you benefit plans with various levels within the organization
- How could you rate your compensation reviews
- How could you rate the competitiveness of your remunerations with other firms
- How satisfied are you with the organization compensation strategy
- How motivated/satisfied are you with the compensation package
Appendix 2: Questionnaire Results
Appendix 3: Variability
References
Amuedo-Dorantes, C & Mach, T 2013, “Performance pay and fringe benefits.Work incentives or compensating wage differentials?” International Journal of Manpower, vol.24 no.6, 673-698.
Andrews, A & Rose, J 2010, “A Preliminary investigation of factors affecting employment motivation”, Journal of Policy and Practice, vol.7 no.4, 239-244.
Dinkin, E 2009, “5 point plan: Five steps to developing a long- term total compensation plan”, Employee Benefit News, vol.23 no.6, pp.32-33.
Ismail, A 2007, “Relationship between performances features and job satisfaction: does interactional justice act as a mediating role?” Academy of Management Journal, vol.35 no.5, pp.921-955.
Lawson, K, Savery, J & Alan L, 2001, “The relationship between empowerment, job satisfaction and reported stress levels: some Australian evidence”, Leadership & Organization Development Journal, Vol.22 no.3, pp.97 – 104.
Locke, E 2008, “Toward a theory of task motivation and incentives.” Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, vol.3 no.2, 30-76.
Maria, O & Militaru, E 2013, “The relationship between employee empowerment and employee professional satisfaction”, Quality – Access to Success, Vol.14 no.132, pp.90-99.
Martocchio, J 2011, Strategic compensation: a human resource management approach, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Mushipe, ZJ 2011, “Employee empowerment and job satisfaction: a study of the employees in the food manufacturing sector in Zimbabwe”, Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, vol.3 no.8, pp.18-41.
Pelit, E, Öztürk, Y & Arslantürk, Y 2011, “The effects of employee empowerment on employee job satisfaction: A study on hotels in Turkey“, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, Vol.23 no.6, pp.784-802.
Richards, DA 2006, “High-involvement firms: compensation strategies and underlying values”, Compensation and Benefits Review, vol.38 no.3, pp.36-49.
Schoeffler, B 2005, “Employee incentive plans: Make them worthwhile”, Insurance Journal, vol.4 no.2, 345-357.
Shields, J 2009, Managing employee performance and reward: concepts, practices, strategies, Melbourne, Cambridge University Press.
Wanous, J & Lawler, E 2012, “Measurement and meaning of job satisfaction”, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol.56 no.2, 95-105.