Abstract
The paper is a concise review of the module on new venture creation. Almost every aspect that is required of an entrepreneur is covered in this module and also mentioned in the paper. Diverse subject areas like new venture start-up risk, funding and financing of new ventures, business plans for a new venture, concepts like harvest goal and models that help in decision making have been covered here. Many small and medium ventures are started by individual or families. In such a scenario, the problems found in family owned ventures and the ways in which they can be solved have also been covered. The mindsets and methods model of entrepreneurship is an example of such a model. The concept of franchising and its backbone, the service delivery system is also a part of this paper. The layout of this paper has been done on the same model as the topics were learnt, week by week. This is only a brief description and review of the whole module, since what has been learnt in the past several weeks is very large for a full depiction. This module is ideal for businessmen, prospective and current managers and those who are planning to start new ventures.
Introduction
The past seven weeks of the module on entrepreneurship and starting new ventures has been an extremely useful session. It has been doubly advantageous because I am a reasonably successful entrepreneur myself (as the owner and managing director of Thai Lay Fashion Company). The information and education gained from this module will help to improve my business and help me in fine-tuning many aspects and processes in the business. This paper is an attempt to present all that has been learnt in the module in a concise and coherent form. All the main topics that have been covered will be briefly mentioned in the introduction before moving on to the main body of the work. The usual housekeeping details as mentioned in the assignment will be given at the end of the paper just before the conclusion. The initial chapters were concerned with the concept of economic and personal freedom which is one of the main reasons why people become entrepreneurs. A case study of a person called Kurt Bauer was also reviewed. A marketing plan for an organization with regard to the issues of starting a venture was also done. The difference between an idea and an opportunity, and how entrepreneurs use the business plan process to identify the best team members, director, and value-added investors was also studied. The importance of factors other than finance was also discussed. Another interesting section was the difference between and entrepreneur and an administrator. The concept of employee motivation, and rewards was also very informative and useful.
Next section was about the role of the top management and mangers with regard to employee recruitment and retention. Proper care and effort should be taken by a new entrepreneur while in the act of a new venture creation. The topic related to that was the due diligence and evaluation process required by potential investors. The different sources of finance that is available to an entrepreneur in the process of venture creation came next. Financing was studied in depth in the next chapter with regard to debt and equity financing. Franchising is an import and popular way of doing business. The most important part of the franchise process is the creation of a service delivery system. This was what was studied next. The concept of harvest goad was studied as the second last chapter in the module. The last module was in fact in the form of an interview. It was with regard to problems faced by family owned businesses and an analysis of the interviewee’s business with the Mindset and Methods model was done. The whole module will be given in a concise form in the coming sections. Real life examples with references to the topics covered will be given wherever possible. It is to be noted that the examples will focus mostly on small and medium businesses since the topic is related to that concept.
Week 1
The Entrepreneurial Mind & Process
The following definition though long clearly states what entrepreneurship is all about. “It is the dynamic process of creating incremental wealth. The wealth is created by individuals who assume the major risks in terms of equity, time and/or career commitment or provide value for some product or service. The product or service may or may not be new or unique, but value must somehow be infused by the entrepreneur by receiving and locating the necessary skills and resources.” (Hisrich, Peters and Shepherd 2004, p.8). This will replace the need for a long winded explanation about the concept. A person who engages in the above activities is an entrepreneur.
Steps to lessen failure and increase chance of success
Even though failure rates of new businesses are quite high, the following steps can be followed so that chances of success will be increased.
Adequate capital: One of the most important things that a start-up should ensure is to have adequate capital (including working capital). Capital can be obtained though financial institutions like banks, angel investors or though the concept of venture capital (VC). Each financial institution will have their own policies on providing loans depending on the type of business, the reputation of the businessman, the security he can provide etc. “Angel investors are individuals who invest in businesses looking for a higher return than they would see from more traditional investments.” (Angel Investors. 2008). Most have their own criteria for providing finance and will usually insist on a board position and the right to provide consultancy to the start-up venture. Venture capital is the least risky way to start a business.
Match between Capital and the Opportunity: Every idea and opportunity needs a certain amount of capital to be successful. So, plan according to your capital available. The opportunity itself should be studied thoroughly for its feasibility.
Other factors: Other factors that contribute towards the success of a new venture include understanding the competition, competent employees, and the ability to conduct the day to day running of the business.
Normative Case Method
Decision making is an important and often crucial function of an entrepreneur. He or she will be faced with situations that may seem difficult to understand and come to conclusion. One of the methods to overcome this is to use what is known as the normative method of analysing given situations. A graphical representation of the analysis process is given below. This section will be the analysis of a given case study using the normative analysis method.
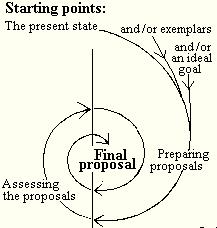
“Normative approach aims at finding out not only how things are, but above all how they should be, which means that it will be necessary to define the subjective point of view that shall be used, in other words to select the people who shall evaluate the proposals which aim at improving the object of study.” (Routioo 2007).
Kurt Bauer case study
Kurt Bauer is a young business graduate who has two options, one becoming a businessman partnering with his brother and a few other associates and the other to work under a businessman called Ludwig (salary, commission and a possible future partnership). The mindset of the man presented in the picture is that he has dreams of becoming a big businessman. The problem for Kurt is which option to choose here. He can go and work under Ludwig in the future hope of getting a full partnership and he can start a venture on his own. The problem (defined) is that both cannot be done simultaneously without negatively affecting the outcome of the two options. This is not a major issue and Kurt will most probably opt for the second option. The main problem is that nearly half of new business ventures fail to succeed and Kurt is about to start one on his own. The solution is that Kurt should go into business on his own with financial help from his venture capitalist uncle and his brother. Alternative solutions include availing the services of a professional venture capitalist, taking a loan, or getting capital from angel investors. As for the decision on the issue, Kurt should get collateral from his uncle (instead of a loan) and use it to get capital from a bank or similar institution. He can release the collateral once the loan has been repaid or he has enough assets on his own.
Venture Capital and angel investors in Hong Kong
Hong Kong has a vibrant international trade and business history and its venture capital industry is very strong. “Hong Kong is the largest venture capital centre in Asia, having the second largest concentration of venture capital professionals in the region and managing 32% of the total capital pool in the region.” (Hong Kong Venture Capital Sector. 2009). The region has a strong association for the protection of venture capitalists called the Hong Kong Venture Capital and Private Equity Association (HKVCA). It was formed in 1987 with the primary objective of having an organized body to provide such capital and also for protecting the interests of venture capitalists and private equity financing companies in the country. The region also has an organization for connecting potential new venture entrepreneurs to angel investors and funds under the name of Hong Kong Angel Capital Network (HKACN).
Week 2
Difference between an Idea and an Opportunity
An opportunity is differentiated from an idea in terms of its marketing possibilities. All opportunities are exploitable for business growth and customer acceptance. Opportunity is profitable for business. But all business ideas are not marketable or profitable for the business firm. Before undertaking an opportunity as a business, the needs and demands of targeted customer group has to be identified properly. For modifying the opportunity as a business way, the personal skills of entrepreneurs have to be applied on it. (What is the Difference Between a Business Idea and an Opportunity. 2009). “An idea is a thought that lacks action and potential for profit. An opportunity, on the other hand, is an idea that can be executed, at a profit, within an undetermined period of time (a window of opportunity).” (Steward 2008).
For converting an idea in to an opportunity, judgment of the created ideas have to be done quickly by using the Venture opportunity screening Exercises (VOSE). The concept is explained below. An idea occupying money making characteristics are considered as opportunity. Only few of the ideas are advantages for business through customer attraction and profitability. After undertaking an idea as an opportunity for the business, entrepreneurs has to take steps to shape the opportunity. For this the needs and objectives of the business concern have to be analyzed. The cost effectiveness of particular idea comparing with its alternatives also has to be considered. The selection criteria for an opportunity must be in terms of major benefits, market possibility and potential business strengths supplied by each opportunity. (Chapter 5: The Opportunity, p.3). (Chapter 5: The Opportunity, p.2). For shaping an idea into an opportunity, a thorough research on the market characteristics has o be carried out by the entrepreneurs. Analysis of competitors will provide an overview about the potential strength and competency of the firm with regard to its competitors. (Chapter 4: Shaping your Opportunity, The opportunity, Creating shaping, recognizing, Seizing, p.139).
How Can the Entrepreneurs Use the Business Plan Process to Identify the Best Team Members, Director and Value Added Investors?
A business plan is the written description of the future of a business. It is a tool for entrepreneurs to realise their business goals. Entrepreneurs can use the business plan for coordinating the human resource personnel towards the business goals. Managers can be directed properly through well prepared business plans. Investment seeking entrepreneurs can use the business plan for transmission of their vision to potential investors. Potential investors can be attracted to the business with proper business plan. “A Business Plan is the foundation, or rather a springboard, towards the establishment and growth of a new business, particularly in the later stages of growth. A business plan is an essential tool for companies raising capital.” (The Importance of a Business Plan. 2008).
A Business plan is the guideline for managing the business in profitable ways. The business plan should explore business goals and strategies to all persons engaged in the business operations and the ways for achieving them. This will provide competitive strength for the firm. (An Introduction To Business Plans. 2009). At the time of selection process of staff personnel, business plan will act as a basis for setting up of selection criteria. Thus best team members suitable to the business objectives can be selected. It explains the purpose of the organization. By establishing vision in the business plan it can persuade others to contribute for achieving the vision. Business plan can be used as yardstick for measuring the operational performance of employees and managers.
Real life examples
There are many examples of success storied that started from and idea which became an opportunity and eventually a business success. Such corporations have now become multinational companies. But the example given here is not very well known outside of Hong Kong. It also shows that any person can succeed in the region and need not be born here. The founder of the Lan Kwai Group is actually a German by the name of Allan Zeman. He had an idea to start a western style restaurant in a relatively small street called Lan Kwai Fong (the name adopted by his company as well). The ideas became a success and eventually he bought the whole street which became a cultural hotspot for tourists and locals alike. His idea developed into real estate and is now known in Hong Kong as Mr. Lan Kwai Fong. “Later, in 2004, Zeman became chairman of Ocean Park, an amusement park which is now out performing and thriving against the struggling Hong Kong Disneyland.” (Cole 2008).
Week 3
Money is the Least Important Part of the Resource Equation
Even though finance is an important part of the business process and new venture creation, there are other factors, that are equally or more important. The potential value of a business unit can be analysed using the Timmons model
The Timmons Model
“The Timmons model of the entrepreneurship process provides a framework for identifying and evaluating venture potential. It helps determine the viability of new business model and emphasizes rigor in opportunity assessment.” (Minniti 2007, p.12).
Entrepreneur requires various resources such as human resources including top professionals, finance, physical assets, and a business plan. Money is the least important part of the resource equation because starting of a new business requires entrepreneur’s ability to take risks as well as abilities to overcome all challenges towards objective of the business. Financial factor comes only as the least important factor for the entrepreneur. “Mill (1984) suggested that Risk taking is a key factor in distinguishing entrepreneurs from managers. It is believed that entrepreneurs take greater degree of risk especially in areas where they have control or competencies in realizing the profit.” (Che, Naresh and Li 2006, p.1).
Utilization of professionals is a crucial decision process. Entrepreneur needs to look into whether the services of professionals and other important factors such as technical know-how, expertise in the field etc. are essential or not. Alternative solution can be used without appointing professionals which will help to reduce much cost and effort. “Competency is one of most crucial factors to ensure the success of new business ventures.” (Che, Naresh and Li 2006, p.5).
Week 4
Difference between an entrepreneurial manager and an administrator?
Even though it may sound similar, the manager and entrepreneur are two different characters and needs different skills and capabilities in each case.
Differences
The primary difference between an entrepreneur and administrator is with regard to risk bearing and conflict management, both inside and outside the organisation. While an entrepreneur manager has material stakes and investments in the business, an administrator is staff personnel who delegates work to employees and supervises their performance. “Entrepreneurs are always thinking of ways to make money for themselves and create a successful business, while managers only consider working for others.” (McSnackins 2008, p.4).
A manager is concerned with day–to-day activities of the business enterprise, and is accountable for persons working under him. Thus, the main difference between entrepreneurial managers is that there is need to assess what needs to be done for the corporate, and the manager determines how this could be performed, or achieved. Thus the main area would be policy making and procedural for entrepreneurial, while for administrators, it would be practically executing them. The main areas in which there are perceived differences between entrepreneurial managers and administrators could be seen in terms of the following. An entrepreneur has to be competitively oriented while an administrator had to be an expert in day to day administration.
The former should always look for opportunities, whereas as for an administrator, this will be considered to be a quality rather than a necessity. An entrepreneur is an investor and employer while an administrator is an employee. An administrator is only responsible for the area in which he controls whereas an entrepreneur has to have full control and responsibility of the entire organization. It is seen that ethical values also play an important role in entrepreneurship and sometimes short term gains have to be foregone for long term profits and objectives. “What is ethical is not always obvious; rather situations involving ethical issues are often ambiguous.” (Timmons and Spinelli, p. 326). However, administrators are not under such kind of pressures or stresses, and only needs to perform assigned tasks determined by the management.
Real life examples
A job opening (in Hong Kong) for an administrator describes the responsibilities (or duties) for that post. They include general accounting duties and charge of general office administration. (Japanese Speaking Accountant and Admin. 2008). The person also has to have three years experience in the above mentioned duties. This is in agreement with what has been said above. Entrepreneurial characteristics are common everywhere whether it is in Hong Kong or any other part of the world. The case of Mr Thomas Tso, is an ideal example of a businessman who had ideas, saw an opportunity, and was willing to take the risk. “One of the keys to business success for Thomas Tso is to never look back. When he arrived in Canada from Hong Kong in June of 1990 he had a business plan. There were challenges ahead, but Mr. Tso was determined to succeed. As a result, he runs a successful automobile sales and service dealership with plans for significant expansion.” (Tso).
Employee Motivation and reward
Employee motivation can be defined as the “the level of energy, commitment, and creativity that a company’s workers bring to their jobs.” (Legal Definition: Employee Motivation Law and Legal Definition. 2009). In order to maintain and increase the above factors, the employee will have to be motivated and rewarded. The first reaction about what motivates an employee would be that it is the monetary compensation received in exchange of work performed. Many theories and studies have proved that monetary compensation is only one of the factors that motivate employees. According to the book ‘Employee Reward’, the following factors will have to be taken into consideration when trying to motivate and reward employees. They include satisfaction of individual (employee) needs, specific and challenging goals to work for, and the individual expectations of reward by the employee. Other important factors are fairness, equity, and consistency. “Motivation strategies should incorporate all the elements referred to above.” (Armstrong 2002, p.66).
The different theories and studies on motivation is testimony to this fact. They include “Douglas McGregor (theory y), Frederick Herzberg (two factor motivation hygiene theory,) Abraham Maslow (theory z, hierarchy of needs), Elton Mayo (Hawthorne Experiments) Chris Argyris Rensis Likert and David McClelland (achievement motivation).” (Employee Motivation: Theory and Practice. 2008).
Motivation can be extrinsic (tangible) and intrinsic (intangible).
Motivation is a challenging task. Setting a reward system is equally challenging and efforts to make it perfect by providing proper job descriptions, setting up performance standards and benchmarks, proper monitoring and periodic reviews and changes (to the reward system) when needed is required.
Recruiting and retaining of employees
It is often said that employees are the most important assets of an organization. It is the quality and ability of the employee, along with the capability and leadership shown by the top management of the company that ultimately results in its growth and success. The employee factor is especially true in the case of a new or start-up business. The employees, in close association with the management have to play a crucial role to attracting, retaining and growing its customer base. The top management of the company has to play an extremely crucial role at this juncture of entry. They have the huge responsibility of recruiting the senior, middle, lower level managers, supervisors and entry level employees of the firm. They can resort to many established and accepted ways of doing this. The most common ways are advertising in the print and visual media, taking employees from other companies, using networking or availing the services of a professional staffing agency. In the case of senior level management it would be ideal to use networking contacts established from sources like friends, business associates, auditors, venture capitalists, and other associates. An advantage is that the costs involved in paying fees of a staffing agency or paying for advertising space can be saved. Advertising for jobs is useful for attracting a large number of applicants and it can benefit the company by having a large pool of talent to select from. (Recruitment Methods. 2002).
Advertising can be done in classifieds and trade journals which will less costly and more effective. But this form of attracting talent can be quite expensive and wasteful. Cost of advertising will depend on the media and the publication in which the advertisement is given. It can be wasteful because the ad might not be visible or it might attract the wrong types of potential employees. Another effective but costly option would be to use the services of a professional staffing agency. The recruitment process involves sending interview dates, preliminary interview, short-listing, second and final interview and sending letter of acceptance. A contract along with a job description will have to be prepared for signing.
Real life examples
Intel is a very well known, respected and probably the largest processor manufacturer in the world. The Hong Kong division has implemented a lot of employee benefits to motivate and retain their employees. According to the company website, “Intel’s benefits plans are designed to keep employees—our most important asset—healthy and productive. Our benefits are generous and personalized, in many cases letting employees choose the options that are right for themselves and their family.” (Our Greatest Investment is Our People: Hong Kong). They include medical benefits, maternity benefits, pension programs, life and accident insurance, paid leave, professional counseling for employees and their dependents etc.
Week 5
This section deals with the actual creation of a new venture and includes topics like due diligence and funding of an enterprise.
Due diligence
Diligence can be defined as “conscientiousness in paying proper attention to a task; giving the degree of care required in a given situation.” (Diligence (noun). The word due is added to reinforce the amount of care that should be taken while starting a new venture. “The entrepreneur, as earliest investor, should pursue due diligence on their idea early and often. This due diligence precedes the decision to invest more time and money in their venture and involves attempting to identify and resolve the most critical uncertainties (unknowns) surrounding the new venture.” (Due Diligence).
They include factors like whether the project will work out, whether the entrepreneur can manage it, whether there will be a market for the products, and whether the team is capable. Three components for the basis of a new venture and several questions should be raised and answered for each of the components. The components are the market, the technology and the new venture (business).
Venture evaluation
It is not surprising that potential customers will conduct an evaluation process before investing in the business. “A VC’s decision to invest in a specific venture is more than an evaluation of a given venture’s business model; it also takes into account the NVT members and numerous other criteria.” (Busenitz, Fiet and Moesel 2005).
VC stands for venture capitalists and NVT stands for new venture team. A study about venture evaluation processes “confirms that relatively consistent evaluation criteria are applied across the industry and corroborates previous models which suggest that the venture capitalist’s decision-making consists of several stages.” (Boocock and Woods, 1997).
The criteria include factors like level of innovation, need (demand) for the product and value to the customer, the profit margin of the product, production capability, product life cycle, and the level of capital needed to satisfy the above criteria. The most important criteria probably will be the perception of the investors in the ability of the entrepreneur in successfully developing the business.
Sources of finance for the new venture
There are many ways in which a new venture can be funded. They include, debt and equity financing, venture capital funding, funds from friends and relatives, and angel investors. In the paper related to the week (submitted earlier as a part of weekly assignments) the choice of funding was a balance between debt and equity funding. However, for the purpose of this study, it is proposed to confine to mezzanine financing requirement for software industry that deals high end customized software solutions on a global level.
This option is believed to provide access to large equity base that could sustain the company in future years and also provide impetus to further investment proposals in future for demanding software business needs and future diversification plans
Pros and cons of equity funding
The main advantages, or benefits of equity funding are as follows. There is non dependence on loan or debt capital that is more risky in terms of mandatory interest payments and other costs. This is because “as debt, the interest is payable on regular basis and the payment must be repaid, if not converted into equity. “ (Timmons and Spinelli 2007, p. 425).
Dividend payments to shareholders would be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and, in the event of deferred payments, could be a source of corporate savings for future use. A broader and diversified capital base is ensured, providing motility and spread to fund movements. The public image of the company is build, especially in a competitive market, and third parties have greater confidence in dealing with them. There are certain disadvantages also. There is greater degree of legal and financial accountability is forthcoming in public limited companies. Strict Companies Registration Office compliances and tighter regulatory framework would be in force. This could prove very cumbersome for newly started companies with little professional experience or expertise in these areas of public accountability.
Real Life examples
The concept of due diligence was practiced in the case of a new start-up dotcom company called HarQen LLC. In this case due diligence was taken by one of the cofounders Lauren Flanagan, as well as venture capitalists. Both of them found the venture very promising after inspection and agreed to fund the venture. “That due diligence got Flanagan interested in the technology. She told the company she was interested in investing if it would agree to move beyond comedy.” (Gallagher 2008).
Week 6
Franchising
Franchising is one of the most sought after ways of doing business in the world today. It has become so popular that this concept is being tried out in many avenues of business. The most crucial component in franchising is the service delivery system which practically forms the backbone of the concept.
Service delivery system in franchising: According to Francorp, a leading franchise consulting and development firm, “the key is that you start with an exceptionally sound baseline service delivery system.” (Conner 2008).
There is more literature written about the importance of an SDS. According to the book ‘Franchising’, an SDS is the fundamental means by which the customer satisfaction in a franchising business is assured and also created a competitive advantage for the franchisees. “Every franchise has a well defined SDS, however overt or transparent it may seem to an outside observer.” (Spinelli, Rosenberg and Birley 2004, p.20). A well laid our service delivery system has the following advantages. It “Encapsulates the intellectual knowledge of the franchise as a business asset. Written instructions which add value to a business process are leased to third parties to generate a profit.” (Preparing the Franchise Package: Understanding the Business System, p.6).
Evaluation of an SDS
The importance of the SDS has been established and now the review of a sound system is being done here. This can be done on the basis of procedures followed in the evaluation of a general service delivery system and its quality. This will be done on the basis of a study conducted on the effectiveness of fast food franchise outlets in the USA and Korea. The study included the following variables commonly referred to as SERVQUAL, which is a common yardstick to measure service quality. The variables are tangibleness, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. An SDS should assure that tangible factors like “physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication materials.” (Chang, Lim and Kim, p.1230).
Reliability of tasks and operations should be there to ensure quality. Responsiveness or the willingness of the staff to be of service to customers and to meet their requirements is another important factor. Employee should be made knowledgeable, courteous and should be able to impart a feeling of trust and confidence in customers. Also an element of empathy rather than sympathy should be taught to the employees in dealing with customers. The above mentioned study also adds that these factors were not adequate in fully evaluating the service delivery systems and added the following components to the study. They include sanitation (hygiene), location of the franchise, the parking facilities available, the quality of the service (in this case food), the environment in which the franchisee is situated and the image or perception of customers about the franchising company. All the elements if properly ensured can give a high evaluation rating to a service delivery system in any franchise business.
Real life examples
Franchising is a concept that is gaining in popularity in the region. But a problem that occurs to international franchisors is the difference in culture, beliefs, and work/management practices in an alien country. The service delivery system may have to be adjusted to suit the above mentioned factors. “For the franchisor, the problem of incomplete information regarding their franchisee-agent’s behaviour is aggravated by this decentralised service delivery system whose geographical scope extends beyond national boundaries.” (Distance Management). The above sentence was taken from a study on franchising success by international franchisors in East Asia. The study claims that companies with well laid out and adaptable service delivery systems have managed to find success in Areas like Hong Kong and Singapore. Examples of successful franchisors include McDonalds’, Burgher King and Kentucky Fried Chicken.
Week 7
The harvest goal
The term has an agricultural connotation because of the word harvest. In fact the concept is similar to the activity done by a farmer. Like the latter, the entrepreneur also nourishes his business by putting in money, effort, and risk in order to create a profitable operation. This is like the farmer who puts in seeds, fertilizers, water, pesticides, and effort in order to harvest his crops. In business harvest goal hence refers to exiting the well-built business (an exit strategy) at a huge profit in order to find capital for new ventures, to retire, to do philanthropy or for any other worthwhile goal. A harvest goal can be summed up by the following sentence. “The professional entrepreneurs and investors know that harvesting an entrepreneurial venture is the approach taken by owners and investors to realize after-tax cash flows on their investment. It defines how they will extract some or all of the economic values from their investment.” (Price 2002, p.212).
This denotes that it is possible and even accepted that an entrepreneur can start a business with and exit strategy in mind as the first option itself and not when the business is seemingly unsuccessful or difficult to manage.
Harvest goal options
A harvest goal can be achieved through many ways and the important ones are given below. One option is the employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). Another option would be the management buyout, whereby the existing top management or partners will buy out the entrepreneur’s share. Mergers and acquisition is also another method to realize the harvest goal. Strategic alliances and an outright sale to interested parties can also be considered harvest goal options. By offering shares to the public thorough a IPO can also be pursued which will result in the shares of the entrepreneur sold of completely or becoming a minority shareholder in the company. The company can then be handed over to a professionally formed board of directors with the former owner playing a small part like the chairman of the board. The day to day affairs will be handled by the CEO and the board of directors. (Harvest Options. 2004).
The founder of Parenting Magazine was a person called Robin Wolaner, Gary and George Muller who started and made successful a company called Securities Online, Ewing Marion Kauffman started the successful pharmaceutical company called Marion Labs are all excellent examples of entrepreneurs who harvested their start-up ventures for various reasons. These reasons include, retirement, philanthropy, starting other new ventures
Week 8
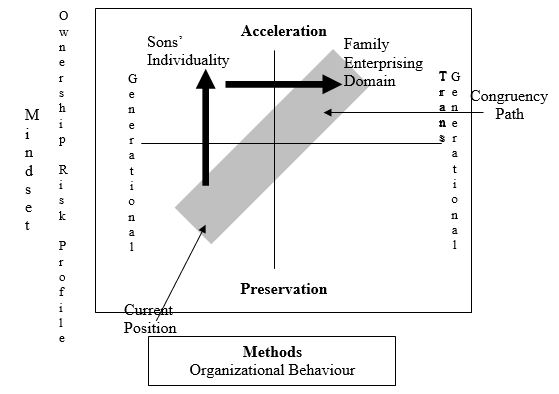
Analysis of a family business using the Mindsets and Methods Enterprising Model
It can be said that many of the large corporations of today have been started in a small way by individuals and their families. Due to hard work and vision, they have now grown to the status and size that one sees today. There are still many family owned firms that are profitable, and still classified as small and medium enterprises (SME). Many of them remain small or medium either because their owners choose to remain as such or due to a plethora of problems that plague such units. There is a saying that the father started the business, the son became rich, and the grandson ended up being poor. There are several reasons for this and includes bringing personal emotions into business, informality, tunnel vision, confusion in roles, favouritism, nepotism, problems in succession, problems in communication, etc. (20 Challenges Faced by a Family Owned Business. 2007). Even though an exaggeration in most cases, there some truth in this saying. This section is an attempt to understand a typical family run unit and the circumstances by which they remain as such. This will be done through a review of literature (briefly) and mainly through an actual interview of a business family in Hong Kong. The family in question runs a successful furnishing company in Hong Kong. The owner, his two sons and nephews are the main persons involved in running the show. The owner has a soft corner for his nephews. The latter are not very smart even though they are honest. One of the sons want to expand the business but lack of enthusiasm in his father and cousins frustrates him.
Solution using the mindsets and methods enterprising model
The most important step is to create communication through dialogue without going into arguments. It is difficult to have effective business communication between family members. The initiative should be taken by the son who holds the MBA degree since he is technically sound with regard to areas like HRM. He should either convince them or remove them from the scene, even at the cost of family displeasure. The issue of the business and its employees is more important at this juncture. Moreover the nephews might come around once a strong threat is voiced from their uncle. Timing is of essence and the sons want to start diversification immediately while the father is more complacent about it. Both parties should adjust their comfort zones and come to a mutual time schedule. Creativity should be encouraged in the dialogue. Many pleasantly surprising suggestions and ideas may come up even from the father and the nephews (if they come around). Sixthly, a passion for the business should be developed among all the family members.
Practical applications of the above module
Each section in our modules required a practical application with regard to what has been learnt in the module. This is a brief recap of the business plans, market strategy, funding options and other aspects with regard to the module in relation to an existing organization. As an owner and managing director of a real organization, my focus was on the Thai Lay Fashion Company Ltd and the new venture that is planned in the UK namely, Thai Lay garments.
With regard to a new venture like the concept of a retail unit in the UK, the following aspects have to be mentioned here. The first part relates to the Changing Business Environment with regard to the Marketing Plan for the Thai-Lay company. In such a situation any company will have to focus on issues like Cost leadership marketing strategy, Product Differentiation strategy, Focus strategy, Pricing strategy, Promotional strategies, Product distribution, Human resources strategy, Financing strategy, and growth plans. In the individual module papers, I had prepared a detailed plan for equity financing and funding and hence not elaborated here. We also have well laid out plans for employee recruitment, retention and rewards. The concept of having well laid out job descriptions will now be seriously looked into also. The interviewing of a business family was a new experience for me and gave me insight and knowledge of potential problems (and solutions) that exist in small and medium family businesses.
Normal housekeeping for the week
The last week of this module was as useful as the rest of the week plans. It was more of a recap of what has been learnt in the module rather than explaining the benefits that I got from a particular weekly session. On the whole, this module was and excellent one both personally and as an entrepreneur. As for this particular final week, my tutors were as helpful as usual. If ever there was an issue, the fault was mine and not due to any other persons. I have been able to attend STUDENT TO INSERT ACTUAL NUMBER number of classes out of the total required. On the whole, the module has been exceptionally useful. I have been able to strengthen my existing knowledge about certain chapters like financing while new concepts like franchising (service delivery system), harvest goal, mindset and methods model etc have been leant. This course module will definitely help in my life and career as an entrepreneur. I can also say that in case of starting of a new venture, I will be more efficient and will plan my endeavour with due diligence and care.
Conclusion
The module on new venture start-ups has been concluded in an eventful eight weeks of intense study. Diverse topics have been covered in the module. They include risks that a new entrepreneur will face during the start-up and eventual building up and growth of the enterprise. Diverse funding options available and the ideal choice in a given situation was also studied. In the case of my company, the choice at this stage would be debt and equity financing with additional funds (if required) from friends and personal savings. Recruitment, reward, and retention of employees is an important factor in the success of any venture and this is especially true in the case of start-ups. Entrepreneurs will have to make decisions that may have far reaching effect in the business, and the Normative method to assist in this task has also been studied. The mindset and methodology model for assessing family owned businesses was also very useful and informative. The concept of franchising (and service delivery systems), angel investors, difference between an entrepreneur and administrator etc were relatively new topics, but were extremely important in understanding the many aspects of running business and starting new ventures. In the case of the retail shop planned, these can be implemented if needed,
Practically every aspect that is required in the case of a new venture start-up was covered in the module. It can be said that any person interested in starting a new venture as well as developing his existing one can benefit from the contents given in the module.
Bibliography
An Introduction To Business Plans. (2009). Entrepreneur. Web.
Angel Investors. (2008). Small Business Notes.
ARMSTRONG, Michael. (2002). Fairness Equity and Consistency. Employee Reward. 66. Web.
BOOCOCK, Grahame., and WOODS, Margaret. (1997). The Evaluation Criteria used by Venture Capitalists: Evidence from a UK Venture Fund. International Small Business Journal, 16 (1), 36-57.
BUSENITZ, Lowell W., FIET, James O., and MOESEL, Douglas D. (2005). Signalling in Venture Capitalist-new Venture Team Funding Decisions: Does it Indicate Long-Term Venture Outcomes? Entreprenuer.
CHANG, Daesung., LIM, Seongbae., and KIM, Hwanyong. A Comparative Study on the Service Quality of Global Fast Food in USA and Korea: Evaluation of Service Quality. 1230.
Chapter 4: Shaping your Opportunity, The opportunity, Creating shaping, recognizing, Seizing, p.139. (Provided by the Student).
Chapter 5: The Opportunity, p.2. (Provided by the Student).
Chapter 5: The Opportunity, p.3. (Provided by the Student).
CHE, Rose Raduan., NARESH, Kumar., and LI, Yen Lim. (2006). Dynamics of Entrepreneurs’ Success Factors in Influencing Venture Growth. The Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability.
CHE, Rose Raduan., NARESH, Kumar., and LI, Yen Lim. (2006). The Dynamics of Entrepreneurs’ Success Factors in Influencing Venture Growth: Abstract. Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability, 2 (2), 5. Web.
COLE, Lesley. (2008). Hong Kong Success Story: Allen Zeman, AKA “Mr. Lan Kwai Fong”, AKA Hong Kong’s “Mouse Killer”. Ventures.
Diligence (noun). AudioEnglish.Net.
Distance Management. 23.
Due Diligence.
Employee Motivation: Theory and Practice. (2008). Accel: Team Development.
GALLAGHER, Kathleen. (2008). Laughing All the Way To New Ventures. Physorg.
Harvest Options. (2004).
HISRICH, Robert D., PETERS, Michael P., and SHEPERD, Dean A. (2004). Definition of Entrepreneur Today. Entrepreneurship. 8.
Hong Kong Venture Capital Sector. (2009). LowTax.net.
Japanese Speaking Accountant and Admin. (2008). Tempstaff Hong Kong Limited.
Legal Definition: Employee Motivation Law and Legal Definition. (2009). USLegal Definitions.
MCSNACKINS, Clacky. (2009). Manager vs. Entrepreneur: Major Personal Differences. Helium. 4.
MINNITI, Maria., et al. (2007). Summary with Implications for Practicing and Teaching. Entrepreneurship. 12.
Our Greatest Investment is Our People: Hong Kong. Intel. Web.
PRICE, Robert W. (2004). Creating Your Exit Strategy and Exit Goals: Harvesting from Your Venture’s Value. Roadmap to Entrepreneurial Structure. 212. Web.
Preparing the Franchise Package: Understanding the Business System. 6.
Pentti. (2007). Normative Analysis and Preparing the Proposal: Starting Points.
Recruitment Methods. (2002). Business Bureau-UK: Small Business Information Resource.
ROUTIOO, Pentti. (2007). Normative Analysis and Preparing the Proposal: Logic of Normative Analysis.
SPINELLI, Stephen., ROSENBERG, Robert., and BIRLEY, Sue. (2004). Establishing the Service Delivery System(SDS): How Does the FRM Provide a Framework for Marshaling Resources. Franchising. 20.
STEWARD, Scott. (2008). The Difference Between an Idea and Opportunity. Miles Media and Marketing.
The Importance of a Business Plan. (2008). VCGate: Powerful Venture Capital and Private Equity Software Directory. Web.
TIMMONS, J., and SPINELLI S. Chapter 9: New Venture Creations: Entrepreneurship for the 21st Century: Personal Ethics and the Entrepreneur: Overview of Ethics, P. 326. (Provided by student).
TIMMONS, J., and SPINELLI, S. 2007. Ch.13: Obtaining venture and growth Capital: New Venture Creation: Entrepreneurship for the 21st Century, 7th ed. (International 2007), McGraw-Hill. P. 425. (Provided by customer).
TSO, Thomas. Success Stories: Kingscross Motor Sports. Ontario.
What is the Difference Between a Business Idea and an Opportunity. (2009). Business on Squidoo.
20 Challenges Faced by a Family Owned Business. (2007). Lee Ivan Accumulated Experience.