Strategic Role of Corporate Strengths/Weaknesses in the Internal Strategy Analysis
Partial SWOT
The Ford company is an American international automobile producer with a strong reputation among its users. The partial SWOT shows whether the company can survive in the market concerning its performance and competitive advantage. The business entity can understand its strengths and weaknesses, which motivates them to design feasible strategic thinking. The institution’s executive managers can effectively concentrate on its prowess to build opportunities to curb external threats.
Table 1. Partial SWOT Table (created by the author)
SW Analysis
Swot analysis assists the entity know where to start and achieving long-haul goals. Concerning the strengths, Ford operates in 125 nations indicating an excellent brand reputation, which has been essential in developing consumers’ goodwill, thus improving its revenue collection. In addition, the strong business supply chain network, which is high across nations, enables the firm to acquire raw materials and procure inventory cheaper (Ford, n.d). The outstanding management team serves as the reason behind venture prosperity, ensuring the quality is maintained across all the retail stores. Lastly, the entity has strongly adapted to the dynamic business environment, making them undertake business activities sustainably.
The first weakness experienced by Ford is that most of its vehicles are recalled as they have oil leaks, indicating ineffective research and development. The low financial ratios have made existing and current investors withdraw, engendering deteriorated economic performance (Ford, 2021). The lack of a strong presence in emerging markets has made Ford not have a solid audience to purchase their commodities. Finally, its higher automobile production costs have led to declining financial performance compared to its competitors.
Strategic Inferences/Implications
From the SW analysis, there are several suggestions that Ford can embrace to continue thriving in the automobile industry. The company’s main challenges are extensive business rivalry and a lack of invention (Hitt et al., 2020). Significantly, the company must employ strategies including research and development and advancing innovation capabilities to match the new and existing car manufacturing companies and escalate its production network to elevate economies of gauge.
Strategies to Capitalize Strengths and Improve Weaknesses
Ford needs to utilize corporate-level strategies to enhance its weaknesses and capitalize on its strengths. One such technique involves using market development by the company to assist them in enchanting prevailing products, such as cars, and selling them in new markets (Ford, 2021). In addition, the product development strategy will enable Ford to generate new products to capitalize on strengths by sustaining the market and meeting customer demands.
IFE Matrix and Analysis
The internal factor evaluation matrix is a strategic instrument deployed to examine Ford’s internal environment to showcase its weaknesses and strengths in the venture’s functional areas. The IFE matrix is essential in offering the ground for pinpointing and examining relationships among such business areas. The company uses it to pinpoint potential market threats and opportunities to enable it to survive. Ford’s IFE matrix is as follows:
Table 2. Ford IFE Matrix (created by the author)
The IFE matrix was developed by first allocating the weight percentage of each of the listed strengths and weaknesses and giving them the corresponding rating from 1 (not essential) to 4 (most superior) from the responses obtained from the research survey. After that, the weight and the ratings are multiplied to obtain the total weight scores from all eight components (Salo et al., 2021). The IFE matrix has some strategic inferences and implications. The weight scores are cumulated, and the outcome exceeds 2.5 since the value is 2.85. The phenomenon insinuates that Ford has a stronger internal position foundation at the corporate level.
Grand Strategy Matrix
A grand strategy matrix is a crucial tool that assists in generating alternatives and diverse techniques for the firm. The tool is used to assess Ford’s strategic implications at the corporate level. A company can deploy market development, market penetration, retrenchment, strategic alliances, acquisition, joint ventures, and horizontal integration strategies. For the Ford company to survive competitively in the external environment, it falls under quadrant I. Ford’s grand strategy matrix is as follows:
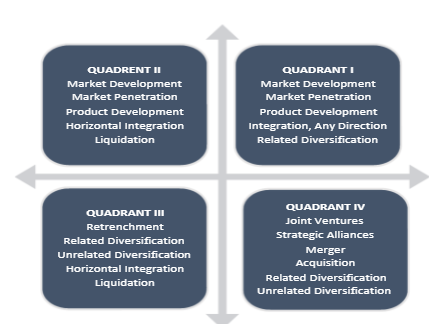
Matrix Development and Implications
The grand strategy matrix was developed by breaking the four quadrants, y-and x-axis, whereby each manifests a combination of Ford’s market growth and competitive position. The plot in the x-axis represents the business rivalry rank, with the right side showcasing strong competitiveness and the left weak strifes (Salo et al., 2021). There are implications and strategic inferences that can be retrieved from the grand strategy matrix. At first, the Ford company belongs to quadrant I as it owes to rapid market growth and strong competition. The firm must embrace market penetration in emerging economies and development integration to design current commodities to continue being sustainable, as these strategies align with its existing weaknesses.
Strategic Role of Internal Resources/Departments/Processes
Business-Level Strategies
Primarily, the organization’s business-level strategy concentrates on its regulations, objectives, and actions to deliver the anticipated value to the target audience while sustaining a competitive edge. The functions and structure at Ford play crucial responsibility in shaping its automobile strategic approach (Hitt et al., 2020). The company utilizes the intensive growth strategy to grow its available dealership and escalate its international market sales turnover. The phenomenon enables the entity to safeguard its dominant market position while advancing its profitability.
Company’s Product Line and Target Market
Ford motor company provide several items, but some of its main product lines include vehicle leasing, buses, trucks, tractors, automobiles, accessories, and financial services. Therefore, Ford’s product line is manufacturing automobiles and financial services delivery to their customers (Ford, n.d). The target market for the business entity includes women and young people who have a relative income and can purchase their cars at affordable prices.
Explaining Business-Level Strategies
At first, the business-level strategies enable a company to query itself and how effectively it can compete in a particular industry. Ford company uses focused cost leadership to offer cars cheaper to its target market than its competitors. In addition, the business organization deploys focused differentiation to continue offering its customers unique financial and automobile services (Hitt et al., 2020). The techniques make the company acquire tremendous operational scope and competitive advantage.
Functional-Level Strategies
These approaches support the business-level and corporate-level strategies by allocating different entity divisions with responsibilities per established goals and actions. The objectives and undertakings at Ford have shifted within departments as a result of Covid-19 to determine financial stability (Hitt et al., 2020). The company focuses on deploying and escalating operations efficiency and maintaining personnel safety as the key functional-level strategies to continue executing its objectives.
Company Assessment
The company uses a vertical organizational structure for the top three offices, including the president, chairman, and executive deputy president. All the personnel works integratively to ensure the firm’s success (Ford, n.d). In addition, Ford has a decentralized culture grounded on fostering technical and functional excellence, working together, and acting as a role model in implementing core values and delivering results. The company’s marketing production involves manufacturing vehicles, such as sedans, which have made them record high profits. Ford utilizes an activity-based accounting system to remain viable and competitive in the market. In 2021, the company invested approximately $7 billion in research and development (Ford, 2021). Lastly, the firm has multiple operational activities, including designing, developing, producing, selling, and servicing the Ford and Lincoln cars, providing customer service accessories and parts, and credit.
How the Strategies Align with the Company’s Vision and Mission Statements
At first, Ford’s vision statement is to assist in constructing a better globe, while its mission involves improving people’s lives by making mobility accessible and affordable. The statements direct each Ford’s functional unit to contribute toward venture objectives (Ford, 2021). All departmental teams concentrate on the vision and mission to assist Ford in generating world-class automobile solutions to attain the target market demands by ensuring ethical growth, innovation, and sustainability.
Strategic Financial Analysis for the Last Reported Fiscal Year
Four Specific Financial Ratios
Table 3. Financial Ratios (Created by the author)
In 2021, Ford’s long-term debt ratio stood at 0.22, while that of the automobile sector was 0.32, indicating that the available assets could effectively liquidate the debt. Its current ratio was 12.6, while the industry average was 1.08, indicating the entity can pay short-haul obligations and cover debts sufficiently. The industry inventory turnover ratio was at 1.69, with the company’s ratio of 2.09, indicating a strength for Ford. Lastly, the firm can use its assets and generate profit as the return of assets is at 0.41 and the sector’s relative is 3.13 (Ford, n.d). There is a weak correlation between the industry average of 0.32 and the long-term debt ratio for Ford. The relationship between the industry average of 1.08 and the current ratio is strong. At the same time, there is a strong correlation between the industry average and the inventory turnover ratio. The relationship between the return on assets and the sector financial average shows a strong correlation.
Summary
The analysis’s significance is to determine Ford’s weaknesses and strengths and establish its strategic direction and performance. The company’s main business-level strategies include focused differentiation and cost leadership, while the corporate approaches are market penetration, product, and market development. The functional-level techniques include maintaining business sustainability, ensuring safety, and enabling operations efficiency. The findings indicate Ford has strong financial prowess in the market compared to the average industry, and the strengths outweigh the weaknesses. The findings of the external environment indicate that Ford company can expand as it faces the opportunity of technological advancement for innovating new products. Nevertheless, it may face threats of facing intense competition from rivals manufacturing similar products.
References
Ford. (n.d). 2021 annual report: Ford motor company. Web.
Ford. (2021). Helping build a better world: Making life electric.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2020). Strategic management: Concepts and cases: Competitiveness and globalization. Cengage Learning.
Salo, M., Ondracek, J., Saeed, M., & Bertsch, A. (2021). Crocs, inc.: Managing corporate resources (strategic perspectives). Delhi Business Review, 22(2), 105-123.