Singapore’s Economy and FDI Potential
Singapore is the country chosen as a recipient of foreign direct investments (FDIs) in the present paper. Singapore has a population of 5.454 million people, and its GDP reached approximately 397 billion dollars, according to World Bank statistics from 2021 (The World Bank, 2021). The biggest manufacturing industry in Singapore is electronics, whose revenue equaled 1.68 billion dollars in 2021 and is expected to reach 2 billion dollars by 2024 (Statista, 2023). The inflow of FDIs to Singapore in 2022 constituted 140 billion dollars, demonstrating that the country is a highly popular FDI destination (The World Bank, 2022).
The most prosperous manufacturing sector in the country is electronics engineering, which was mentioned earlier as the biggest manufacturing industry. Electronics engineering as a manufacturing sector has grown significantly in recent years, amounting to only 0.35 billion dollars in 2017, and the revenue grew to 1.68 billion in 2021 (Statista, 2023). However, the software and IT services industry is the number one industry in general, with a lot of potential for investment growth.
Trends in FDI
Singapore has become one of the most attractive recipients of FDIs in recent decades. The total FDI received by the country in 2000 was 15.52 billion dollars, which equaled 16.15% of the country’s GDP in that year (Macrotrends, 2023). In the following years, however, the inflow of FDIs started growing exponentially as the country was industrializing. In 2004, the GDP inflows reached 24.39 billion dollars; in 2007, the number rose to 47.34 billion, 26% of the country’s GDP. After two years of a drop in FDI due to the world financial crisis, the FDI inflows returned to the previous numbers and reached 55.32 billion in 2010 (Macrotrends, 2023).
In the following years, the levels of FDI fluctuated, but a new leap happened in 2016, when the sum of FDI reached 99 billion dollars, comprising almost a third of the country’s GDP. In the year of the pandemic, the FDI dropped, but it started growing again in 2021 and is continuously growing at the present moment (Macrotrends, 2023). The following graph demonstrates the low FDI in Singapore and its percentage in the country’s GDP over the last two decades.
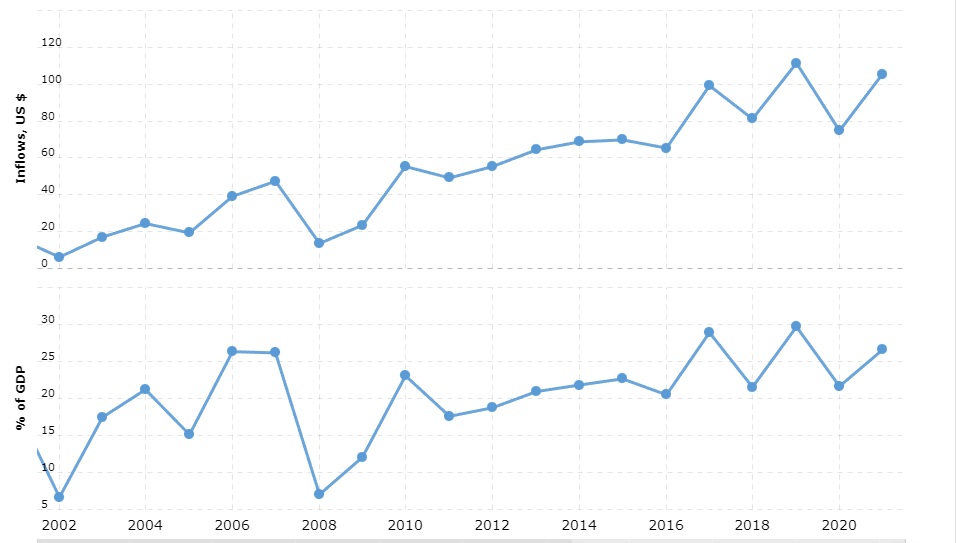
Key Sectors Attracting FDI
The main sectors funded by FDI in Singapore are finance and insurance, which received the most FDIs in 2023, constituting 52% of all the FDI. Wholesale and retail trade and manufacturing follow finance and insurance, constituting 14% and 11% (Singapore Department of Statistics, 2021). The chart in Figure 2 shows the primary industries receiving the most FDI by percentage.
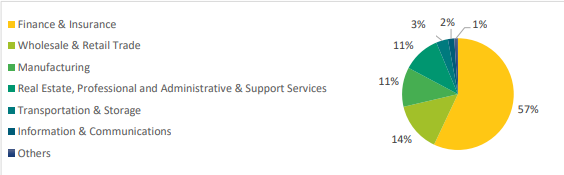
As the finance sector attracts the most FDI, it seems that finance as a type of FDI is the most profitable. However, by taking a closer look at the manufacturing industry, but most importantly, at electronics, which is the most prosperous manufacturing sector, it can be seen that manufacturing is also highly profitable.
Electronics is the fastest-growing manufacturing sector in Singapore and has the most potential for foreign direct investors. There are several reasons why this sector receives the most FDI. Firstly, Singapore has a strategic location, a hub for electronics manufacturing and distribution (Lyttle, 2022). Through Singapore, it is easier for direct investors to access the biggest markets, such as China and India.
Additionally, Singapore has favorable investor conditions, including low taxes and a stable political climate (Lyttle, 2022). Electronics is an industry that requires a highly skilled workforce, which Singapore can provide to foreign investors. Singapore’s education strongly emphasizes STEM professions (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics). This is why electronics companies prefer Singapore when opening a factory there.
Recommendations
The following recommendations could be given to the company considering opening a Singapore factory. Overall, Singapore can be deemed a suitable choice for building a factory. Firstly, Singapore provides favorable conditions to foreign investors, including a stable political situation and a reasonable tax system. Secondly, it has a favorable strategic position: it will be easy for the company to access the other major markets of ASEAN, including the biggest ones, such as China. These aspects justify Singapore’s choice as a general receptor of FDI.
However, the choice regarding receiving the industry is not so obvious. On the one hand, finance is the most apparent choice as it is the main FDI-receiving industry. On the other hand, manufacturing is also important, and electronics constitute the most essential manufacturing sector. The exceptional quality of the workforce, in combination with its favorable strategic location, makes building an electronics factory a logical decision. Therefore, the company should consider moving to Singapore and directing its investments there.
References
Lyttle, C. (2022). How does Singapore punch above its weight when it comes to attracting FDI? Investment Monitor. Web.
Macrotrends. (2023). Singapore foreign direct investment 1970-2023 [Data set]. Web.
Singapore Department of Statistics. (2021). Foreign direct investment in Singapore (stock as at year-end). Web.
Statista. (2023). Electronics – Singapore [Data set]. Web.
The World Bank. (2022). Foreign direct investment, net inflows (BoP, current US$) [Data set]. Web.
The World Bank. (2021). GDP (current US$) [Data set]. Web.