Introduction
In today’s world, technology is inseparable from people’s everyday life. Almost every person has a smartphone or a computer, and even everyday appliances are being connected to the Internet. Such technology provides new, comfortable features and makes living more convenient in many regards. However, this arrangement also creates a uniquely modern problem for users. Smart appliances, phones, and computers are not perfectly secure, and the personal data of any individual can come into the hands of strangers.
Main body
The crime of stealing personal information from people through various methods is called identity theft. The obtained data can be used to commit financial fraud or extort people for money, placing the well-being of individuals in danger. Even if a person protects their privacy, big companies, and organizations that store user data are also vulnerable. The information may be unsafely secured, accidentally leaked, or stolen by hackers. This can apply to passwords, addresses, phone numbers, and other sensitive information one might store on their device. Understanding the issue of identity theft is crucial to protecting oneself and their loved ones from being exploited. In this paper, some of the common methods of identity theft will be discussed, along with their implications for personal freedom and security. The essay will also touch upon the countermeasures and the steps often taken to prevent data leakage.
Identity Theft and Its Targets
As previously mentioned, identity theft is a federal crime pertaining to the use of another person’s data to fake identity for various purposes. A culprit can accidentally or deliberately come into possession of a specific person’s personal and financial information, gaining monetary benefits or causing harm to individuals. The problem of stealing personal data has existed for a long while, but with the popularization of the Internet and the shift to digital operation, it became even more widespread.
The World Wide Web makes financial operations faster and more accessible for people, presenting a tangible benefit compared to the traditional methods of operation. The risks to personal safety, however, cannot be understated. Scammers and hackers prey on vulnerable and ignorant people, often masking their activities under innocuous offers of help or profit. Some Internet websites are designed to closely resemble popular social media and government websites, making people trust them to log passwords or install spyware on their systems. Young children and the elderly are especially susceptible to this kind of trickery due to their limited knowledge of the web, often willingly giving up their passwords and sensitive information to hackers. Therefore, the primary targets of scammers are usually older people with a lot of disposable income, and individuals who are easy to fool, such as children. Webpages promoting get-rich-quick schemes are often used to lure desperate people into giving up their personal and credit card information.
“The Internet of Things” and Data Collection
Blatant scams are not the only way ill-intentioned people can steal data, so exercising awareness is crucial to the safe use of modern technology. In recent years, the production of smart appliances and gadgets has been on the rise. With newer technology slowly becoming more affordable, more and more families are integrating the Internet of Things into their daily life. Be it a fridge that monitors the amount of food left, a portable station to play music, or a personal assistant, they are all connected to the Internet. To properly function, they store and process vast amounts of gathered data, ranging from one’s daily routine, grocery lists, and music preferences to the more private aspects of a person’s life (Turner, para. 2). The information is mainly used for the purposes of machine learning and can be acquired by third parties through unsecured Wi-Fi connections (Turner). While it is improbable that one’s smart appliances would store financial information, personal data can be used by others for the purposes of “social engineering”. The term refers to the practice of convincing people to give up their sensitive data using psychological manipulation (“What Is Social Engineering?”). In the process of social engineering, access to another person’s life details can be easily used to gain trust and scam gullible individuals. The rapid spread of smart appliances therefore can be considered both a benefit to individual convenience and liability to personal security.
Big Internet-based companies and social media platforms also present a comparable danger to personal security. To access many of their services and optimize one’s web experience, a person may need to provide such organizations with their personal information. While a company that collects data from a vast userbase might seem reliable, the opposite was proven many times throughout the Internet’s existence. Such companies as Adobe, Yahoo, and even eBay have compromised their user’s data in the last decade, leading to credit card information and login details being stolen (Swinhoe). Many other platforms accidentally leak user information or insecurely store it, resulting in access breaches and theft of people’s data. There are a number of protocols in place to prevent data misuse in the case of its leakage, but they do not offer full security (Romanosky et al. 256). Therefore, sharing information with third parties can be harmful to people even when the process is consensual.
Common Types of Identity Theft
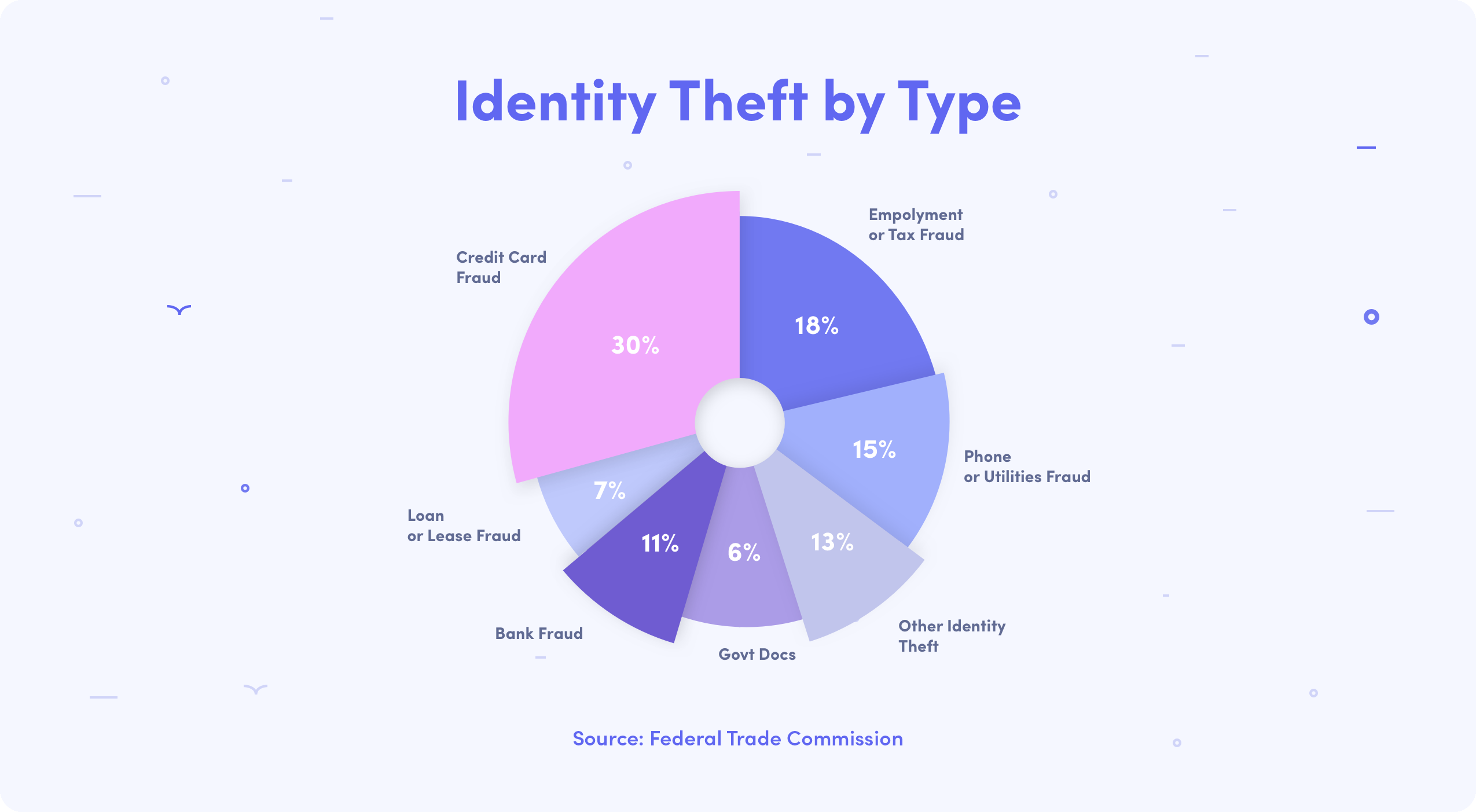
There are a few types of identity theft that can be distinctly noted. By using stolen login data or guessing one’s password, a scammer may possess direct control over a person’s bank account (Porter). Access to banking information gives a malicious individual full influence on a person’s finances and private data. This allows them to freely charge the victim’s credit card, file claims against instated insurance policies, or otherwise damage one’s finances. This method is one of the most effective and impactful, as the stranger can come into possession of large amounts of data. Another approach criminals may use is opening new bank accounts that are filed under a different person’s name (Porter). The method allows for more discreet operation and is harder for the credit card owner to notice. The only way to counteract this type of scam is to check the bills frequently and ask the bank whether any new accounts were opened.
Another popular type of scam is tax identity theft. By filing taxes under another individual’s name and claiming returns, frauds can earn a profit (Porter). These kinds of schemes often use trickery and manipulation to acquire personal data, organize phishing attacks, and pretend to be a legitimate institution on the phone (Porter). Medical identity theft, another type of this crime, is also extremely harmful to individuals and can threaten a person’s well-being directly. A scammer may try to use the medical insurance of a different person to get treatment, leaving the victim to pay for the service (Porter). This operation can affect individuals both financially and physically, as the doctors can use the impostor’s recorded medical information for legitimate treatment. There are, of course, numerous other types of identity theft, but the aforementioned ones are the most common, as well as the most dangerous.
Influence of Internet Culture on Security
The development of the Internet and its culture have had a significant effect on the spread of identity theft crime. At its conception, the World Wide Web was regarded as a new, uncharted territory, a dangerous and unpredictable space. Since there were no big social media websites, most people only used the computer to find the information they need, work, or explore their interests. The practice of sharing information was largely frowned upon, as many people did not understand the Internet and did not want to put their privacy at risk. Without the existence of such platforms as Facebook or even MySpace, there was no need to share details of one’s life with strangers, and people took the issue of frauds and scams seriously.
In more recent years, however, the situation changed dramatically. With the advent of massive social platforms where people meet, interact, and learn about others, the need to present one’s true self has risen. Creating an authentic persona on the Internet to make others understand and connect with one another is one of the main appeals for the web of today. This change, while understandable, creates a starkly different climate to the one existing before. People become more willing to trust and share their personal information, including their phones and addresses. The notion of “stranger danger” on the Internet has somewhat faded into obscurity, and many users underplay the importance of personal security and privacy. Changes to the culture have made the World Wide Web far more open to the machinations of scammers and extortioners.
Countermeasures
Preventing information leaks is one of the primary concerns for people on the Internet, and there are multiple ways to accomplish that. The first common guideline is to carefully examine websites before submitting any sensitive information (Luthi). Examining the links on a website before opening them and checking the URLs is especially important. Another sensible piece of advice is having the firewall and the antivirus software of one’s computer updated (Luthi). Protective programs can detect and warn a person about harmful websites and programs, making the process of phishing information much harder for the scammer. Many also suggest using specialized browser software that detects suspicious websites and notifies the user, although their effectiveness is questionable (Chou et al.). The last piece of advice is to use complex password and multi-factor authentication systems for every website (Luthi). A long password ensures that a hacker would not be able to break into one’s account through brute force or guesswork, and the difficult authentication process will not allow them to gain access at all.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the topic of identity theft is important to examine and understand for any modern person. Due to the change in Internet customs, it has become easier for scammers to gain trust and steal personal information. The need to ensure personal security is now higher than ever, with newer methods of tricking people and bypassing security being devised each day. There are a few common types of fraud, the theft of banking information and credit cards, insurance theft, and others. Individuals must be informed and keep themselves safe by exercising self-awareness and caution. Securing one’s internet connection, carefully examining websites and links, as well as regularly running an antivirus can immensely aid in this endeavor.
Works Cited
“What Is Social Engineering?” Kaspersky, 2020, Web.
Chou, Neil, et al. “Client-Side Defense against Web-Based Identity Theft.” Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, NDSS 2004, San Diego, California, USA
Luthi, Ben. “How to Reduce the Risk of Identity Theft.” Experian, 2020, Web.
Porter, Kim. “10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About.” LifeLock Official Site, Web.
Romanosky, Sasha, et al. “Do Data Breach Disclosure Laws Reduce Identity Theft?” Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, vol. 30, no. 2, September 16, 2008, pp. 256-286.
Swinhoe, Dan. “The 15 Biggest Data Breaches of the 21st Century.” CSO. 2020, Web.
Turner, Steve. “Smart Home Threats: Securing Your IoT Devices Against Cybercrime and Oversharing.” Fighting Identity Crimes Powered by EZShield, 2020. Web.