Summary of Article
The selected article is about a case study for IT4IT authored by the Open Group (2015). The article posits that the information technology (IT) value chain complements service delivery and improves compliance to organizational plans. Therefore, IT processes are critical to the success of organizational processes because they measure performance and provide insights about compliance procedures through conceptual, logical, and realized service models.
Thus, companies should use IT-focused business strategies to create value for organizations. The value should be channeled through an assessment platform, which includes a strategy to portfolio analysis, a requirement to deploy strategic plans, a request to fulfill business orders, and the detection of weak points to improve service delivery (The Open Group, 2015). The section below discusses how key insights gathered from this article could help in developing UPS’s compliance plan.
Compliance Plan
UPS has different functional areas, including accounting, finance, and human resource (HR). The IT compliance plan should concentrate data analysis processes within the human resource department because the success of project tasks is pegged on individual performance. In other words, the contributions of each team member will be instrumental in evaluating project success. Therefore, the HR team should oversee the IT compliance process because it understands personal factors affecting corporate performance (Weiss & Solomon, 2015).
Compliance policies should be reviewed annually because one year provides enough time to establish the effectiveness of new policies (Manish, Raj, John, & Pavankumar, 2017). Weiss and Solomon (2015) also support an annual review of policies for IT compliance procedures. Conducting the yearly evaluations would be instrumental in identifying key gaps in the policy implementation process and formulating new procedures that would address them. Stakeholders that should be involved in the compliance plan include UPS’s customers, its managers, the company’s legal department, government agencies, and employees.
The company’s customers need to be consulted because UPS’s policies are aimed at improving user experiences. Comparatively, employees will be included in the stakeholder plan because they implement company strategies. Lastly, it is important to consult government agencies because they oversee the implementation of corporate strategies, while UPS’s managers provide a general direction for the execution of UPS’s strategies.
The proposed value chain model that UPS should use to promote compliance procedures appears below.
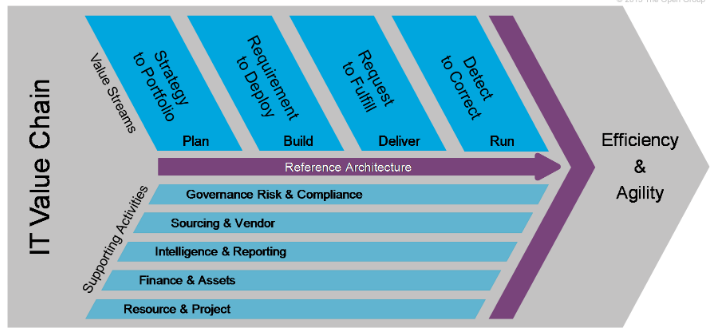
The above framework is ideal for implementation at UPS because it focuses on improving the efficiency and agility of organizational processes, which are key objectives for the company. Furthermore, the robust nature of the framework makes it easy to match vital processes with value streams.
Overall, the above-mentioned model relates to UPS’s compliance processes because it outlines the reference architecture for executing its strategies. At the same time, it provides direction and guidelines on how to navigate the complex regulatory environment that is associated with a giant multinational firm such as UPS. For example, the separation of value streams from supporting activities minimizes the possibility of role confusion in the implementation of compliance procedures. Therefore, the model provides a robust outline for implementing UPS’s IT management plan.
How to Incorporate Data Analysis in the Compliance Plan
Data analysis will be used to assess how well UPS complies with its IT management plan. This strategy will be implemented by using statistics to evaluate whether project team members have completed specific aspects of the plan as expected. For example, project milestones will be assessed based on how well they are implemented within the proposed budget. In other words, numbers will be used to answer compliance questions. It is expected that the use of data analysis to assess compliance procedures would provide an accurate assessment of the organization’s implementation process compared to traditional models of review, such as sampling, which have a high margin of error (Manish et al., 2017).
References
Manish, G., Raj, S., John, W., & Pavankumar, M. (Eds.) (2017). Information technology risk management and compliance in modern organizations. New York, NY: IGI Global.
The Open Group. (2015). IT4IT reference architecture, version 2.0 technical standard. Web.
Weiss, M., & Solomon, M. (2015). Auditing IT infrastructures for compliance. New York, NY: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.