In nursing, theories are used as systematic explanations of a certain event and concepts which may be identified in terms of their relations and possible impact on people. Each nursing theory is the possibility to structure and organize nursing knowledge in a proper way (McEwen & Wills, 2014). It is hard to define which theory is important in nursing, and which model can be neglected because the role of every theory is to improve nursing from different perspectives. In this paper, Johnson’s behavioral system model will be discussed, explaining its main concepts, sub-concepts, the possible areas of practice, and its strengths alongside with its weaknesses.
Background
Dorothy Johnson is the developer of the behavioral system model under analysis. She spent her childhood in Savannah, Georgia, and graduated from Vanderbilt University with a bachelor’s degree in nursing (McEwen & Wills, 2014). In 1948, she got her master’s degree at Harvard and used it to develop her teaching career first in Vanderbilt, and then in Los Angeles. During her education and teaching career, Johnson got access to numerous theories and concepts developed before. She believed that nursing was a profession with its main goal of patient welfare, and the clarification of the social interactions played an important role in the process (Holaday, 2014).
Influence
In 1968, Johnson offered the behavioral system model relying on the book Notes on Nursing, written by Florence Nightingale. The main idea was the necessity to focus on efficient and effective behavioral functions of nursing that could prevent illnesses and stresses among patients. Therefore, Johnson used different works of the experts in the fields of psychology, sociology, and even ethnography to prove the correctness of her direction and the necessity to understand the transition to a proper behavioral system in nursing care (Holaday, 2014).
Conceptual Framework
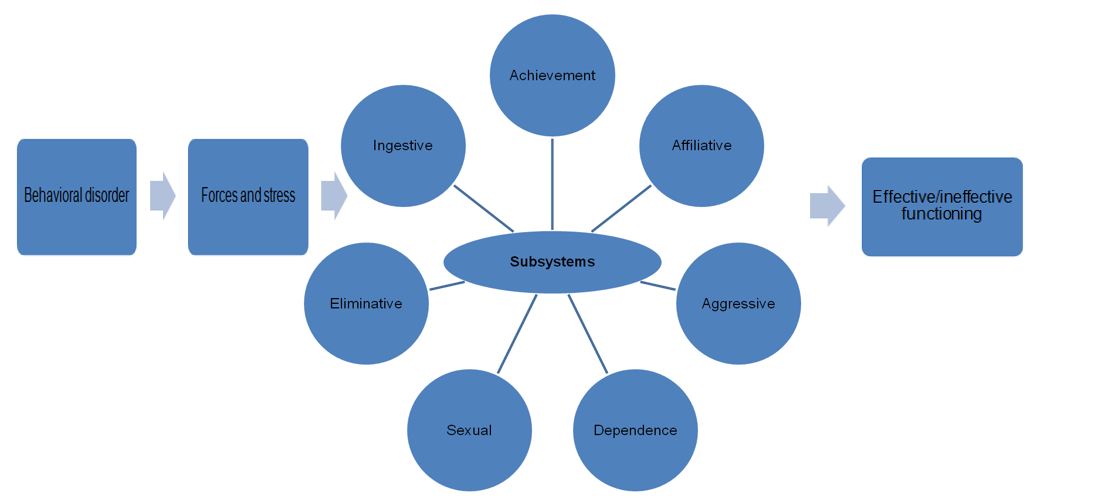
Johnson believes that human beings may have two systems: biological (where medicine plays a crucial role) and behavioral (where nursing care is an integral factor). Besides, several important subsystems cannot be neglected or misunderstood because they define the quality of care offered to a patient. The following model could be used as a guide for all people, who want to improve their motivational drives and achieve good results in nursing (Masters, 2013).
Major Concepts
In Johnson’s theory, there are several major concepts which make it unique and helpful for many nurses:
- A human being is a behavioral system that should take certain continual adjustments and achieve balance in its development.
- Health is an effective function of a system where balance and stability are achieved (Masters, 2013).
- The environment is the combination of all elements that may surround a human system, as well as internal and external factors.
- Nursing is a type of regulatory force that could be used to preserve the patients’ behavior at a required level under certain conditions.
- The system is a combination of all nursing interactions.
- The behavioral system is represented as a person with several behaviors within one system.
- The subsystem is defined as a mini-system with several factors excluding the environment.
Explanation of the Theory
With the help of this model, it is possible to regard a person as a behavioral system with several subsystems interrelated with each other in the way the integration of human behaviors is possible. It is not enough for nursing to identify a problem and choose an appropriate treatment process. It is expected that the classification and management of problems may promote the balance and stability of a patient as a whole system of behaviors (Masters, 2013). According to this theory, it is possible to clarify how to regulate human behavior, and why such regulations do matter. Johnson explains that it is a nurse’s responsibility to support a patient and restore the expected balance between what is lost and what should be found. It is necessary to find out the status quo and return to a normal state.
Areas of Nursing Practice
The peculiar feature of Johnson’s model is the possibility to recognize several areas of nursing practice at the same time. On the one hand, it is necessary to improve the environment, develop physical skills, improve social skills, and introduce new mechanical and creative skills with the help of which nurses could help their patients to stabilize their behaviors. On the other hand, it could be used in nursing research and education as an attempt to clarify human strengths and weaknesses regarding their abilities. For example, this model could be used as a framework for the analysis of human fears and their impact on a person’s health (McEwen & Wills, 2014). At the same time, this model could help young mothers necessarily perceive the environment and provide their chronically ill children with an ability to live providing care, safety, and support.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In general, Johnson’s behavioral system model is the possibility to create a framework based on individual needs and expectations. Though it is suggested to use the model to stabilize human behavior, it is also possible to ensure people of their readiness to restore their balance and function properly. Aggressive behavior could be easily fixed in case the environment is improved, and the problem is identified.
References
Holaday, B. (2014). Dorothy E. Johnson: Behavioral system model. In M.R. Alligood (Ed.), Nursing theorists and their work (pp. 332-357). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
Masters, K. (2013). Role development in professional nursing practice. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
McEwen, M., & Wills, E.M. (2014). Theoretical basis for nursing (4th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.