Introduction
Business organizations need to implement superior measures to improve their operations and maximize profitability. The selected company that can benefit from a new strategy is General Motors (GM). In 2014, this organization had a scandal that exposed the major challenges that were affecting its business operations. This project presents the idea of just-in-time (JIT) to maximize efficiency at GM and make the corporation more profitable.
Selected Idea
The concept of JIT makes it possible for companies to minimize lead time, identify and reduce defects, and allow materials or parts to be delivered to the assembly line when required. In 20014, GM released 2.6 cars into the market that had faulty ignition switches (Rushe, 2015). This problem led to over 94 deaths in different parts of the world, thereby forcing the company to recall them (Rushe, 2015). This occurrence can become a new opportunity for GM to implement the concept of JIT. Such an approach requires computerized systems to manage inventory and ensure that different materials are delivered in a timely manner. Additionally, GM will have to give specific units or departments adequate time to analyze and test the targeted parts thoroughly before delivering them during assembly.
The case of Toyota explains how the implementation of the suggested method supports the manufacturing and delivery of quality cars that meet the demands of more customers. This corporation minimizes errors and ensures that all materials meet the required standards and are delivered in a timely manner. For GM, the proposal should be introduced in every part of the manufacturing process to streamline operations and reduce the lead time (Shepherd & Vardiman, 2016). GM can hire competent professionals to monitor and test all parts before they are fitted. The intended change will need to be completed in 12 months to improve operations.
Motivated Conclusions and Proposals
GM is a leading company that designs, manufactures, and markets classic vehicles that meet the demands of more customers. The established business model is effective and resonates with the demands of more stakeholders. However, some gaps might emerge in different phases of production. The consideration of an effective JIT approach will support the rate and speed at which different materials are acquired and delivered in the assembly line (Calderone, 2017). The consideration of such a strategy means that the established system will analyze and test all parts thoroughly to ensure that they match with the intended cars. The installed robotic system should also be able to handle them efficiently (Shepherd & Vardiman, 2016). The leaders and engineers need to be involved to solve emerging obstacles while streamlining the process to maximize productivity.
The success of this model will depend on the actions and initiatives of all key partners. The management at GM needs to offer the relevant skill sets, guide suppliers to maintain the required standards and testing procedures, and consider a power change strategy. The consideration of emerging challenges would be essential before implementing the JIT process successfully (Calderone, 2017). When introduced effectively, GM will find it easier to improve the process of assembly, minimize defects, and meet the demands of future customers. The concepts of continuous monitoring and improvement are proposed to ensure that positive results are recorded.
Implementation Plan and Outcomes
GM would require several tools and techniques to ensure that positive results are recorded. The consideration of such attributes will address the existing challenges and take the organization to the next level. The major ones are outlined below.
- Just in Time (JIT) technique
- Kurt Lewin’s change model
- Improved robotic systems
- Human resources
All these tools and techniques will make a difference at GM and eventually ensure that all vehicles meet the outlined quality standards. The implementation of this new project means that Kurt Lewin’s change model will come first. The HR department will also have to be involved to streamline operations and support the intended process (Rushe, 2015). The JIT technique needs to become a company-wide project whereby all partners, employees, and customers will offer their views and guide the implementation team to make the relevant adjustments. When this new project or initiative is implemented, the company’s production model will change significantly and improve profitability.
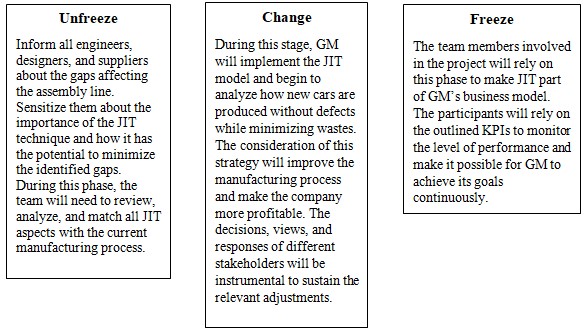
The consideration of a powerful implementation plan is necessary to make it possible for all departments and stakeholders to remain supportive and eventually improve the overall GM’s performance. Kurt Lewin’s theory offers the best plan for introducing and making the proposed change a reality (Calderone, 2017). A detailed breakdown of the model or structure is presented above (see Figure 1). The contributions of all leaders and followers will make it possible for GM to address the current gaps and become more productive.
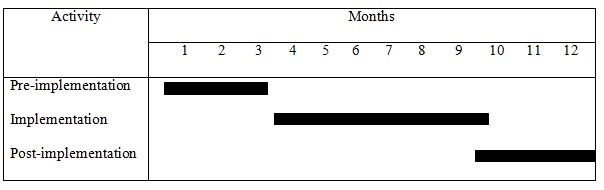
In terms of implementation, the team members need to complete the entire process within a year. The first three months will be essential for sensitizing all key stakeholders and focusing on areas that can benefit from the JIT model (see Figure 2). During the next six months, the JIT technique will become part of GM’s manufacturing process. The participants will present their ideas and skills to support the process. The last three months will be essential for the freezing stage to improve operations continuously (Calderone, 2017). The use of key performance indicators (KPIs) will be critical to identify positive gains and challenges that the organization needs to resolve. Some of the key issues to consider will include the rate at which defects and errors are recorded, car recalls, and customers’ complaints (Shepherd & Vardiman, 2016). When desirable results are recorded, the company will generalize the model and make the introduced actions part of its business model.
From the above analysis, it is evident that Lewin’s change approach will remain essential during this implementation process. The existing resources and manufacturing procedures will support this new approach or the second phase of change implementation. The main issue that GM needs to address in the current system is the speed and rate at which parts are acquired and tested from different suppliers (Rushe, 2015). There is no potential for pushback with this case or proposal. Suppliers need to receive additional guidelines for improving productivity and analysis of their parts and materials. The success of this effort will empower more team members and improve customers’ experiences. The current technologies and robotic systems will support the intended JIT methods. This aspect makes them available and costs justifiable (Shepherd & Vardiman, 2016). Finally, a reward system to entice more suppliers will become part of the new process and allow the refreeze phase to take effect. These attributes will continue to dictate the nature of operations and how the new JIT process will continue to improve overall organizational performance.
Conclusion
The above discussion has described a powerful model that the leaders at GM need to consider to ensure that the challenges it has recorded in the past do not reoccur. The JIT approach stands out as a powerful strategy for identifying potential sources of defects and avoiding them accordingly. The presented structure can address some of the identified obstacles, maximize the involvement of all key stakeholders, and eventually support the delivery of high-quality vehicles to the targeted customers. Such attributes will make GM a leading competitor in the global automobile industry.
References
Calderone, L. (2017). The benefits of just-in-time inventory. Manufacturing Tomorrow.
Rushe, D. (2015). General Motors protected from faulty ignition-switch lawsuits, judge rules. The Guardian.
Shepherd, I. J., & Vardiman, P. (2016). The General Motors ignition switch incident viewed through a proposed economic impact severity index. Journal of Management Policy and Practice, 17(1), 36-59.