Abstract
Management of employees all over the world has experienced a dramatic shift in trying to attain the optimum production of various organizations through maximization of their output. There has been a rise in the number of managers trying to establish the most effective way of managing their employees to improve their production at the same time having them highly satisfied at their workplaces. This has demanded that managers of these organizations adapt to the most effective leadership style to be able to cope with competitive pressure in their business environment. This study sought to determine the leadership styles employed by managers and the relationship that exists between these leadership styles and their impact on the employees in terms of their level of satisfaction, motivation, behavior, and level of production. A study population of 5 previous existing studies has been used, with a sample of one of the study, leadership in the apparel manufacturing industry, being used.
Data that was used was secondary data obtain from the study about leadership in apparel manufacturing. The findings of this study indicate that the most commonly used leadership style by managers is leadership that is transformational style. The findings also indicated that leissez fair is also employed but to a very limited extent. The level of effectiveness of employees is greatly impacted by the various leadership styles. From the findings of this study, owners and managers of various organizations are encouraged to adapt to leadership that is transformational to increase the efficiency and the level of satisfaction of their employees. The researchers recommend further studies on the relationship between leadership styles and their impact on the employees.
Introduction
Background
Managers all over the world have embraced various leadership styles in running their organizations. Management of employees all over the world has experienced a dramatic shift in trying to attain the optimum production of various organizations through maximization of their output. Managers of various organizations have in the past few years experienced many challenges in trying to adapt to the most effective leadership style to embrace in managing and leading their employees. Management of employees all over the world has experienced a dramatic shift in trying to attain the optimum production of various organizations through maximization of their output. There has been a rise in the number of managers trying to establish the most effective way of managing their employees to improve their production at the same time having them highly satisfied at their workplaces. This has demanded that managers of these organizations adapt to the most effective leadership style to be able to cope with competitive pressure in their business environment.
This study will focus on the leadership styles of five existing studies. With each leadership style, both positive and negative attributes are likely to emerge and have a unique effect on the process and staff they oversee. This study will provide a unique glance at leadership styles throughout these companies and their effect, if any, it has on the organization. This will provide an ideal leadership style that managers can put in place if they are to increase the overall performance of the organizations that they manage and thus ensuring that they remain competitive. Managers tend to utilize various leadership styles that they think will be ideal in managing and leading their employees. These leadership styles vary with the prevailing situation.
Leadership style is the way of providing direction, implementing policies, and motivating workers. The most used leadership styles include transformational, transactional, and leissez fair. These leadership styles have an impact on the level of motivation of employees and their level of production.
Employee motivation is directly linked to the leadership style within an organization and is a long-standing topic of many organizations. Employee motivation can best be defined as psychological processes within an individual that direct the intensity and persistence of effort spent while at work (Kreitner&Kinicki, 2007). Employees that are motivated are more productive, tend to be loyal, and need less supervision than those employees that have no desire to perform (Bolster, 2007). One aspect of employee motivation is the effectiveness of the leader. The term “leadership” can simply be defined as the process of assigning tasks to others to achieve the desired goal (Kreitner&Kinicki, 2007).
Problem Statement
Throughout many organizations, it has been identified that employees do not interact positively with their bosses, consistently seek out alternate employment, thus creating a high employee turnover, and produce below standard quality and productivity. Leadership styles can grossly affect employee retention, employee motivation, positive communication, training, morale, and especially the quality and productivity of the workflow. Identifying effective and ineffective leadership styles in the organization will allow for organizational growth and improvement, ultimately leading to heightened output, quality and production drove employees who enjoy their jobs, thus leading to happy customers. Although not proven, it is the opinion of the researcher that the above statements are true.
Study Questions and Hypothesis
- What are the leadership styles employed by managers in managing and leading their workers?
- What is the effect of leadership style on employees?
- What is the attitude of the employees of employees on leadership?
H1-To what extend do managers utilize the various leadership styles.
H2- To what effect do these Leadership styles affect employees in terms of their level of motivation, satisfaction, and production?
Objectives of the Study
To establish the effect of leadership styles on the organization’s employees, in terms of their behavior, level of motivation, retention level, and production.
To establish the various leadership styles employed by managers in running their organizations.
To find out the most effective leadership style utilized by the managers of various organizations
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to identify the overall leadership style in five existing studies and assess its effect on the organization’s employees in regards to employee behavior, employee motivation, employee retention, and overall production. Leadership styles have both positive and negative outcomes depending on the style. This study will identify if the reported relationships are supported by the data, as it relates to the sources in question. The researcher hypothesizes that most managers embrace leadership that is transformational style as the most effective way of managing and leading the staff.
The researcher hypothesizes that leadership style is directly related to employee motivation, employee retention, positive communication, employee morale, quality, productivity, and overall job satisfaction and, when lacking, can have a detrimental effect on a positive employee experience. It is the opinion of the researcher that the Participative leadership style is the most effective and applicable in any organizational setting, regardless of the overall atmosphere. Hence managers ought to find the involvement of day to day of the employees that they lead, in running their organizations if they are to achieve the ultimate goals of the organization and increase the productivity of the organization.
Definition of terms
Leadership style is the way of providing direction, implementing policies, and motivating workers.
Inspirational Motivation – this is an inspiring and influential level of articulation of the vision and objectives by the leader. Employees must be motivated and their morale increased for them to act. For this to happen, there is a need for increased communication in the group and in the organization to communicate and make clear the vision and mission of the group.
Employees will gain self-confidence and be highly motivated in the workplace through idealized influence kind of leadership.
Transactional leadership – is the style where a leader provides enticements for followers to do what the leader wants. Employees who follow the given instructions correctly and achieve the required results are usually given rewards that motivate them even further. The reward is withheld if the employee does not attain what is required of him/her. The focus of transactional leaders is the providence of rewards for high performing employees and deviant employees being punished.
Laissez-faire leadership–Leaders depicting this style give their followers limited direction and employees being managed by such leaders have more freedom. The employees must determine the goals that they want to achieve, make decisions on their own, and come up with solutions to various problems. This leadership style is ideal when employees are well motivated and can carry out their assigned duties. Employees need also to be highly skilled in carrying out the duties, which require technical expertise. While utilizing this leadership style, managers have complete trust in the employees that they are leading.
Literature Review
Researchers have been particularly interested in examining those leadership styles that do not require the spending of additional funding, yet can help organizations reach their strategic outcomes (Wyatt, 1996). Employee turnover is currently at an all-time high and is increasing each year. What is the recipe for a happy employee? What does it take to retain employees? How do you boost employee self-esteem all while maintaining quality and productivity? Will a higher salary make up for leadership insufficiencies? This survey seeks to answer these questions.
Microsoft, one of the top-rated businesses to work for in the United States, retains happy, satisfied employees, who in turn provide a high-quality product. “Microsoft is dedicated to a corporate culture that inspires and rewards its employees” (Microsoft). Microsoft incorporates a Participate leadership approach, which has been proven to work well within the organization.
Moral dilemmas in organizations have long been a factor regarding effective leadership. Typically, organizations delegate work, value employees, and govern their organization on what their employees should and should not be doing based on such values. Leadership styles, along with the motivational effects of using versus not using point systems are evaluated before put in place (Sayer 2008).
Another example of good leadership is Google. Their belief, “we believe that in addition to hiring the best talent, the diversity of perspectives, ideas, and cultures leads to the creation of better products and services. The diversity of our employees and partners serves as the foundation for us to better serve our diverse customers and stakeholders all over the world” (Google).
Passive-aggressive leadership tactics can work temporarily in an organizational setting when combined with other leadership styles. The repercussions of the passive-aggressive leadership style, when used frequently will bolster employee morale, and create a negative environment in which the employee will likely have a non-trustworthy relationship with his/her manager/supervisor (Johnson).
You cannot run an organization without leadership, and with leadership comes leadership styles that can have a positive or negative impact on an organization. An organization would need to arrange a leadership style that embodies its mission and goals. The organization will also need to decide on the importance of its employees and the certainty of leadership styles that can promote employee growth and stunt creativity. Given this, managers utilize various leadership styles, which include transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and Leissez fair leadership.
Transformational leaders motivate their followers to work for their transcendental goals instead of immediate self-interest, for achievement and self-actualization rather than safety and security (Murray and Feitler, 1989). It also creates within followers a capacity to develop higher levels of commitment to organizational goals (Leithwood and Jantzi, 2000). Burns (1978), argue that transformational leaders are more effective than transactional leadership, where the appeal is to more selfish concerns. Transformational leaders depict their leadership styles by innovating new products, restructuring the organization, encouraging networking and collaboration with other parties in the supply chain (Sillins, 1994).
Transformational Leaders use various dimensions in leading their staff and they include Individualized Consideration, which measures the level at which the leader attends to each follower’s needs. The leader usually supports the followers, maintains high levels of communication with the followers, and gives them challenges. This also entails the need for respect for each individual’s contribution. The followers are characterized by the will and desire to develop themselves hence the availability of inherent motivation for work. According to Barker (1990), leaders who are characterized by intellectual stimulation challenge assumptions takes risks, and ask for ideas of their followers.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational theories of leadership focus on the connection between followers and leaders, which is mainly depicted by the way the leaders inspire and motivate people making them good in task performance. As mentioned by Powell and Graves (2003), a transformational manager/leader acts as subordinates’ role model by establishing high behavioral standards. Transformational leadership defines ideal managerial behavior. Individualized mentorship provides more empowerment, constant stimulation, and inspiration. Such management style obtains maximum contribution of subordinates to the firm’s capabilities. This is normally referred to as the transaction style of management, which links management and subordinates in exchange relationships.
However, Wood et al. (1997) argued that most of the features of transformational leadership might not be defined by gender stereotypes. However, the intense social behavior that is observed in feminine places women managers better in terms of offering encouragement and mentoring to their subordinates. Managers who are transformationally styled add high value to their organizations by enhancing more and better productive labor relationships; this means that there is frequent subordinates-managers contact. In such organizations, reporting of incidents, suggestions, and concerns is done on a timely basis. Such effectiveness in communication is found where leadership is more interpersonally based.
Transformational leadership is interpersonally based. From gender stereotypes women are more interpersonal oriented than men, research study conducted by (Wagner & Berger, 1997) argued that women managers are more transformational in style, they would spend time evaluating the challenging views in the tasks of their subordinates in an effort transmit to them their organizational values and objectives and this facilitates goals achievement in the organization. This concludes that in organizations where women outnumber men in the managerial ranks feedback and reporting of concerns, suggestions, and incidences by staff to management is more direct and managers and the firm value employees’ development and mentorship.
Employee Motivation
Employee motivation is directly linked to the leadership style within an organization and is a long-standing topic of many organizations. Employee motivation can best be defined as psychological processes within an individual that direct the intensity and persistence of effort spent while at work (Kreitner&Kinicki, 2007). Employees that are motivated are more productive, tend to be loyal, and need less supervision than those employees that have no desire to perform (Bolster, 2007). One aspect of employee motivation is the effectiveness of the leader. The term “leadership” can simply be defined as the process of assigning tasks to others to achieve the desired goal (Kreitner&Kinicki, 2007).
Money is not the only source of employee motivation. While most employees feel their compensation is fair for the type of work that they perform, they also feel that other factors motivate them (Bolster, 2007). These factors include recognition, communication, learning opportunities, a positive work environment, and supportive team members – all of which are the trademarks of effective leadership. Moline (2005) agrees that communication and recognition are calling cards of effective leadership, but also adds frequent feedback and delegation of “how” decisions.
Rewarding of performance
According to a study done by Wajcman (1996), transactional leaders offer suitable rewards and delegate tasks for objective accomplishment. They manage subordinates by exception and intervene only where they want to correct performance. A managerial style that us laissez-fare avoids decision-making responsibilities and thereby fail to provide feedback on subordinates’ performance, this style of management may not be effective in employee development. While performance rewarding has little connection with feminine or masculine managerial styles, there are yet gender differences that are linked to specific aspects of the two styles. From gender stereotypes, male managers are likely to offer performance rewards explicitly since they define individual tasks and goals more explicitly enabling performance to be measured objectively. This concludes that males’ pre-eminence in organizations’ management results in a high incidence of payment schemes that are based on results (Rowold & Wolff, 2009).
Job Delegation
According to Li et al. (2004), the degree of delegation of decision making to employees differs among managers, from gender stereotypes, women’s management styles are perceived to be more participative compared to men, this is further linked to democracy in decision-making. This ensures high participation of subordinates in the organization’s administration functions; this enables subordinates to make a decision that influences their work contexts from experience. This concludes that women managers delegate more to subordinates while male managers accumulate decision-making responsibilities to themselves or those in high ranks meaning that a high number of women in management yields a higher degree and delegation of decisions. According to Mazlan (2009) male managers, tend to control the vision and goals more and thereby delegate less while women managers embark on using their subordinate teams to achieve defined vision and goals. Leadership Praise
The general rule of thumb in regards to employee recognition is to give more positive feedback than negative feedback (Bolster, 2007). It is also important to recognize the employee as soon as possible after the event occurred. Mathews (2007) states that to continually motivate her employees she will make the effort to recognize them in a public forum. This approach will allow the individual to be visible while taking credit for their work (Bolster, 2007). Recognizing an employee publicly for a job well done is one aspect of effective leadership that sends a positive message to all other employees.
Moline (2005), states that compliments and recognition are well appreciated and tend to reinforce desired performance when the praise is related to a specific act.
Ironically, a lack of feedback is a de-motivator (Moline, 2005). Employees need to know how they are doing. Effective leadership notes strengths/weaknesses and areas of improvement in employees (Moline, 2005). If an employee needs improvement, then that needs to be communicated as soon as possible (Bolster, 2007). When it comes to feedback in regards to improvement, the feedback needs to be based on observable work performance and concrete (Moline, 2005). Once the employee has achieved the new goals set for them by management, then that individual should receive positive feedback.
Communication
Communication is important for all leadership styles. Whether the communication is provided face to face or via a “communication board”, it is necessary because it helps to break down barriers between employees and leadership. Essentially, it gives the employee a sense that there are not any secrets (Bolster, 2007). Effective leaders must communicate to employees the what, the why, and the consequences of any job that needs to be completed (Moline, 2007). This approach will give the employees an understanding of their contribution to the project and will help them to have a sense of ownership (Moline, 2007).
Training and Education
Training and education will only increase motivation among employees.
Baptist Health Care in Pensacola, Florida utilizes an approach known as “the daily line-up” (Bolster, 2007). These sessions are roughly 10 minutes in length and allow for departments to get together, learn something new about health care, and to build team participation (Bolster, 2007). Baptist Health Care also utilizes leadership development programs, quarterly employee forums, and other continued education (Bolster, 2007).
Employee Morale
If employees are to be motivated in the workplace, then their work environment must be positive. To create a positive work environment, managers need to lead by example (Bolster, 2007). Employees also need to know that managers and supervisors support them. If a mistake is made, it is a team issue and not an individual’s issue (Bolster, 2007). Recognition is also a part of a positive work environment.
Leadership Styles Relationship to Job Satisfaction
Kruglanski, Pierro, and Higgins (2007) implemented four different studies across multiple industries to determine what effect leadership style, either forceful or advisory, had on job satisfaction for employees with certain characteristics. The characteristics helped the researchers determine the type of self-regulatory mode of each employee. Those modes were labeled as locomotion and assessment. For this study, forceful is defined as being demanding, directive, and coercive (Kruglanski et al., 2007). Likewise, an advisory is defined as being counseling in nature, consultative, and participative (Kruglanski et al., 2007). Individuals with characteristics more in line with the mode of locomotion are more interested in taking action, getting started, and not assessing all options (Kruglanski et al., 2007). Individuals with characteristics of assessment are more interested in evaluating all goals and options to judge the quality and they want to look at all possibilities before making a decision (Kruglanski et al., 2007).
A survey of 100 employees in an organization in Rome, Italy revealed that there was a positive correlation between locomotion characteristics and forceful power (Kruglanski et al., 2007). Besides, it was concluded that there was a positive correlation between assessment characteristics and advisory power (Kruglanski et al., 2007).
The researchers implemented the same survey three more times to replicate the results of study number one, only with different populations (Kruglanski et al., 2007). The second consisted of 73 participants in the field of firefighting, the third consisted of 141 participants employed with a German investment company and the fourth consisted of 179 participants, all of whom are members of a police force. All participants were located in Rome, Italy. As expected, the results of all subsequent studies were comparable to those of the first.
In conclusion, the researchers were able to identify a link between leadership style and job satisfaction. It has been documented that the fit between leadership style and employee self-regulatory model does influence how satisfied an individual is with their job (Kruglanski et al., 2007). It was also noted by the researchers that employees tend to have a measure of both self-regulatory modes; it just so happens that one mode is more dominant over the other.
Effects of Supervisor Personality on employees
Smith and Canger (2004) implemented a study to look at the effect of supervisor personality on employee job satisfaction using the big five personality model. The Big Five Personality model factors are emotional stability, extraversion, openness, conscientiousness, and agreeableness (Smith &Canger, 2004).
In particular, Smith and Canger (2004) developed two hypotheses for their study. Hypothesis 1 was that supervisor personality would show stronger relationships with employee satisfaction, particularly with supervision (Smith &Canger, 2004). The second hypothesis indicates that supervisor personality and style will be positively related to employee attitude (Smith &Canger, 2004). To test the hypotheses, the researchers initially asked 685 participants to complete the CFI Personality Inventory, which included a six-point Likert Scale. Shortly thereafter, the researchers then asked the same participants to complete two other surveys.
Results for the study indicated average satisfaction with the supervisor (Smith &Canger, 2004). The researchers also indicated that the five personality characteristics did not predict the outcome of job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention (Smith &Canger, 2004). Smith and Canger (2004) then conclude that supervisor personality has more to do with employee satisfaction and supervision as opposed to employee satisfaction with other work-related issues.
This study also indicated that the personality trait of supervisor agreeableness has somewhat of a positive relationship with supervisor satisfaction (Smith &Canger, 2004). Smith and Canger (2004) also go on to say that extraversion is not related to employee turnover intentions and that supervisor emotional stability has a positive relationship with employee supervisor satisfaction.
In conclusion, Smith, and Canger (2004) state that additional research is needed to clearly define the relationship between supervisor personality and subordinate attitudes and job satisfaction. Also, it was concluded that the sample size of participants and the total number of job titles might have been too small (Smith & Canger, 2004)
Relationship between Employee Involvement and Fulfillment
Wright and Kim (2004) implemented a survey of eighty-eight questions to 477 participants from a government agency in New York; however, only 409 returned responses. This equaled a response rate of roughly 85% (Wright & Kim, 2004). An organized task force that focused on using items from previously validated surveys (Wright & Kim, 2004) designed the survey instrument. Within the survey, five specific investigative categories existed. Those categories were; Employee perceptions of the work context, Psychological climate, Job characteristics, Work incentives, and employee job satisfaction. The variables of job satisfaction, the impression of career development, the impression of goal specificity, task significance, job-related performance feedback, and participation all fall into one of the above categories. Wright and Kim (2004), state that composite scores for each measure were computed as the sum of the standardized item scores. The purpose of the study was to measure the outcome of the relationship between certain management strategies and employee participation and the overall effects on job satisfaction.
In conclusion, the study conducted by Wright and Kim (2004) verified that the level of participation by an employee appears to have a positive influence on job satisfaction. Wright and Kim (2004) went on to detail that any organization that would like to increase job satisfaction should remember the importance of feedback, job specificity, task significance, and career development.
Research Methodology
Research Design
The descriptive research design was employed because of the data under study. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the data by way of percentages. These were appropriate because of the quantitative and qualitative nature of the variables. Graphs have been drawn to represent the various data under study.
Study Population
The population of the study is collected from five existing studies with data on the effect these leadership styles have on an organization’s employees, such as employee behavior, employee motivation, employee retention, and production will be assessed.
Sample Size and Selection
Random sampling was used. A sample of one study was used, that being ‘leadership in the apparel-manufacturing environment: Analysis based on the Multi t-Factor leadership Questionnaire.’ The researcher chooses random sampling because it provides an equal opportunity for selecting results that can be generalized to a large population. The researcher assigned numbers on the paper and some were left blank. Those with the number corresponded to the data he/she wanted to use. He mixed all the papers and picked one of the papers.
Data Collection
The data collection method for this study will be gathered by assessing five existing studies with the same key characteristics regarding leadership styles and identify the effect these leadership styles have on organization employees.
Data Analysis, Findings, and Discussions
This study sought to establish the relationship between leadership styles and their effect on the organization. In the analysis, pie charts and bar graphs have been used to portray the data under study. Transformational leadership has been established as the most effective mode of leadership style employed by managers.
Fig. 1 shows the percentage by which the managers use the three leadership styles
Table 1.
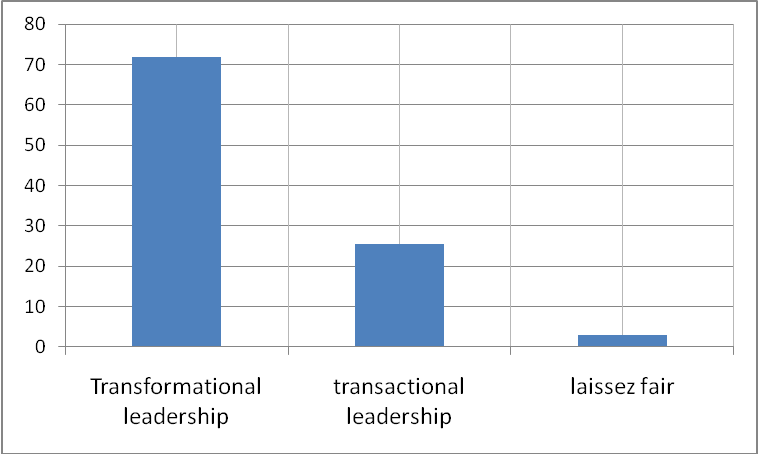
Fig. 1 shows that the majority of managers use leadership that is transformational style with a percentage of 71.78%, transactional leadership is employed at 25.46% and Laissez fair is least used at 3.01%. Transformational leadership has various dimensions that managers find ideal in utilizing, thus it accounts for a higher proportion of the leadership style employed by the managers in all organizations. Employee morale is greatly boosted when managers embrace leadership that is transformational because they tend to prefer managers who recognize and treat them with respect. Thus, in line with this the managers all over the world this various leadership styles in running their organization. Due to this, leadership that is transformational style has been the dominant leadership style employed by managers in running their organizations, as clearly indicated in the study (Wajcman, 1996).
Transformational leadership is the ideal way of leading employees. It has a variety of dimensions that managers can utilize in managing their organizations which include; Individualized Consideration, Intellectual Stimulation, Idealized Influence, and Inspirational Motivation. If employees are to be motivated in the workplace, then their work environment must be positive. To create a positive work environment, managers need to lead by example (Bolster, 2007). Employees also need to know that managers and supervisors support them. If a mistake is made, it is a team issue and not an individual’s issue (Bolster, 2007). Recognition is part of a positive work environment. Both, work together to increase the motivation levels of employees
Transactional leadership is used to some degree when the employee’s value reward for the assignment that they accomplish, hence some managers find it ideal in accomplishing some tasks at relatively limited time. Transactional leaders focus on the administration of rewards and punishment (Viitanen & Konu, 2009).
Leissez fair is least used, because not all of the employees are well motivated, can be trusted, or are all well equipped with the relevant skills in handling their various assigned tasks. This leadership style is ideal when employees are well motivated and can carry out their assigned duties. Employees need also to be highly skilled in carrying out the duties, which require technical expertise. While utilizing this leadership style, managers have complete trust in the employees that they are leading.
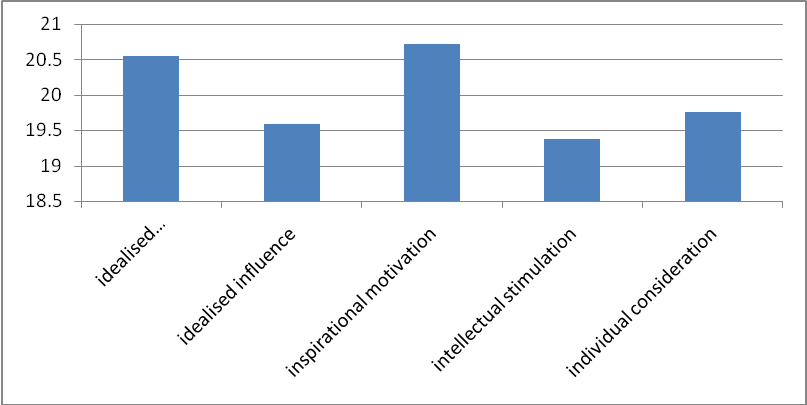
If employees are to be motivated in the workplace, then their work environment has to be positive. Managers have to lead by example (Bolster, 2007). The inspirational motivation was greatly employed by the managers employing leadership.
Managers find it ideal to articulate the vision they have for the organization in employees as their ultimate goal because this shared vision is what drives the employees in achieving the organization’s goals (Murray & Feitler, 1989). This creates within followers a capacity to develop higher levels of commitment to organizational goals (Leithwood and Jantzi, 2000) and thus the managers tend to employ the various transformational dimensions illustrated in the diagram above (Sillins, 1994).
The style of leadership that is transactional leadership is usually applied when the leader makes contact with the followers for exchanging valued things (Burns, 1978). This necessitates the managers to employ the use of contingent rewards to a higher level as compared to other dimensions of this leadership style (Barker, 1990; Kirby, Paradise and King, 1992).
The level of effectiveness is highly impacted by employees
Table 3.
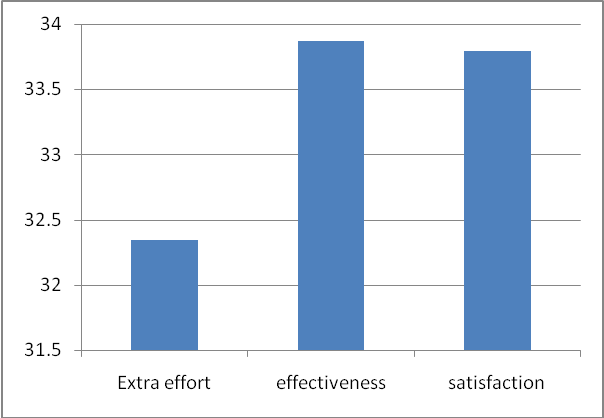
The above fig 4 shows that the leadership styles affect the employees, having a greater impact on their level of effectiveness. At 33.87 Production of employees is greatly influenced by the various leadership styles embraced by the managers.
Summary, conclusion, recommendations, and limitations
Summary of Introduction
This study aimed to determine the effect of various leadership styles on the organization, in terms of employee satisfaction, employee motivation, and employee production.
The findings from the study indicated that most of the managers use leadership that is a transformational style in running their organizations. This could be due to the great effect it has on the employees.
The results also indicated that most managers employing transactional leadership style prefer contingent reward in influencing their employees towards enhanced production. Results indicated the existence of the effect of leadership styles on employees in most of the organizations.
Summary of leadership styles employed by the managers
This study found out that the majority of managers use leadership that is transformational style with a percentage of 71.78%, transactional leadership is employed at 25.46% and Laissez fair is least used at 3.01%. Transformational leadership has various dimensions that managers find ideal in utilizing, thus it accounts for a higher proportion of the leadership style employed by the managers in all organizations. Employee morale is greatly boosted when managers embrace transformational leadership because they tend to prefer managers who recognize and treat them with respect. Thus in line with this, managers all over the world have embraced these various leadership styles in running their organization. Due to this transformational leadership, the style has been the dominant leadership style employed by managers in running their organizations (Kirby, King, and paradise, 1992).
Summary of dimensions of transformational leadership
Managers tend to use inspirational motivation in leading their employees compared to other dimensions of transformational leadership.
Summary of various aspects of transactional leadership
Managers tend to prefer a transactional relationship with the employees and hence give a reward for the accomplished task and thereby they are more inclined to use a contingent reward system as illustrated by this study.
Summary of the effect of leadership styles
The study found out that employee effectiveness is greatly impacted by the three leadership styles. Moreover, the leadership styles had an influence on the employee level of motivation at the workplace. Employees who are highly recognized by their managers tend to be highly motivated because self-recognition is much better than monetary recognition.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study found out that most of the managers employed leadership that is a transformational style in managing their organizations. Transformational leadership has great appeal to the managers because it encourages social values and thereby encouraging workers to co-operate and thus attain great organizational goals. This was necessitated by the fact that employees prefer leaders who lead by example, and that most employees tend to be motivated when the managers highly regard them. Laissez-faire leadership is least used because managers are adamant to let their workers carry out duties on their own, Moreover, employee effectiveness was greatly enhanced by the various leadership styles employed by the managers, no matter which leadership style managers embrace there is a positive impact on the employees’ production.
From the findings of this study, owners and managers of various organizations are encouraged to adapt to leadership that is transformational to increase the efficiency and the level of satisfaction of their employees. Moreover, managers cannot run their organization without leadership, and with leadership comes leadership styles that can have a positive or negative impact on an organization. An organization would need to arrange a leadership style that embodies its mission and goals. The organization will also need to decide the importance of its employees, make decisions on good leadership styles that promote employee growth, and increased creativity. Given this, managers utilize various leadership styles, which include transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and Leissez fair leadership (Wajcman, 1996).
Recommendations for Further Researches
From the findings of this study, the researcher recommends the study to be undertaken on other sectors of the economy to establish the effect of leadership styles on their employees in terms of their level of motivation, behavior, and their oval output. Moreover, the researcher recommends further studies to be undertaken in developing economies to establish the leadership styles employed by the managers in managing their organizations. The researchers recommend further research in establishing what constitutes effective leadership.
Limitations of the Study
The major limitation of this study is that not all sectors of the economy were considered. Sectors of the economy range from the service industry to the manufacturing industry. The data collected may be subjected to the feelings and interpretations of the respondents thus not reflect a clear picture of the events in the area of the study. The study was also hindered by the financial strain especially payment of fare, lunch, and typing. The other limitation was the lack of adequate time for the study.
References
Alahmad, A. (2010). To Be Ethical or not to be: An International Code Of Ethics For Leadership. Journal of Diversity Management, 5(1), 31-35.
Belasen, A.T., Benke, M., DiPadova, L.N. & Fortunato, V.M. (1996). Downsizing and the hyper effective manager: the shifting importance of managerial roles during organizational transformation. Human Resource Management Journal, Vol. 35 No. 1, pp. 87-117.
Bennett, T. (2009). A study of the management leadership style preferred by it subordinates. Journal of Organizational Culture, 13(2), 1-25.
Bolster, C.J. (2007). Take this job and love it. Healthcare Financial Management, 61, pp. 56-60.
Johnson, et al. (2007). Passive-Aggressive Behavior and Leadership Styles in Organizations. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 14(2), 130-142.
Kreitner, R. & Kinicki, A. (2007). Organizational Behavior. New York, NY: McGraw Hill. pp. 193, 236, 509, 511.
Kruglanski, A., Pierro, A. & Higgins, E. (2007). Regulatory mode and preferred leadership styles: how fit increases job satisfaction. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 29, 137-149.
Lebediker, J. (1995). Taking inventory of management skills. Training & Development, 49, 59-60.
McCann, J. (2008). Leadership in the Apparel Manufacturing Environment: An Analysis Based on the Multi-Factor Leadership Questionnaire. S.A.M. Advanced Management Journal, 73(4), 20-30, 50.
Microsoft, (2008). Microsoft Careers. Web.
Moline, L. (2005). Unlocking the Potential of your Employees: the not-so-secret secrets of motivational leadership. Government Finance, 21, 13-16.
Newstrom, J. & Davis, K. (1993). Organizational behavior: Human behavior at work. New York, N.Y: McGraw-Hill.
Rowold, J. & Wolff, S. (2009). Transformational and Transactional Leadership and Followers’ Chronic Stress, Leadership Review, Vol. 9, pp. 35-48.
Sayer. (2008). Moral Economic Regulation in Organizations: A University Example. Organization. 15(2), 147-164.
Skakon, J. et al. (2010). Are leaders’ well-being, behaviors and style associated with the affective well-being of their employees? A systematic review of three decades of research. Work & Stress, 24(2), 107-139.
Smith, M. Canger, J. (2004). Effects of supervisor “big five” personality on subordinate attitudes. Journal of Business and Psychology, 18, 465-481.
Tannenbaum, R. & Schmidt, W. (1958). How to choose Leadership Pattern. Harvard Business Review, 1973, No. 73311.
Viitanen, E. & Konu, A. (2009). Leadership style profiles of middle-level managers in social and health care: Leadership in Health Services, 22(2), 108-120.
Wajcman, J. (1996). Desperately Seeking Differences: Is Management Style Gendered. British Journal of Industrial Relations, Vol. 34(3), pp.333-349.
Wright, B. & Kim, S. (2004). Participation’s Influence on Job Satisfaction. Review of Public Personnel Administration, 24, 18-40.