Life insurance can be defined as the contract between the insurer and the person who owns the policy. Some countries include some events like bills and death expenses are included in the premium policy. The insurer is bound to pay some money in case an event happens to occur.
If the insurer enters the contract, he pays an annual or monthly amount known as premium. If an event occurs, the benefit is paid to the beneficiaries. The insurance only considers the people who are included in the life policy. If any kind of event happens, the people who are insured are the only ones who are considered since it’s a contract between two parties, i.e., the policy owner and the insurer.
The only person allowed to pay for the policy is only the policy owner, and he also acts as the guarantee. They don’t consider the insurer as being a party to the contract since he acts as a participant. In life insurance, the insurer plays different roles compared to the roles of the policy owner. They sometimes seem to be the same, but they are totally different.
The owner appoints the beneficiary, although he is not entitled to the policy. If the beneficially happens to revoke the insurance contract, any changes that come along must be agreed upon by the beneficiary. This means that the owner has the right to change the beneficiary unless the beneficiary chooses to change or withdraw the policy. The changes might include cash value borrowing or policy assignments.
In life insurance, there are special requirements which are found in it. If the person commits suicide within a given period of time, this type of section is highly considered. If the application is misrepresented by the insured is considered as part of nullification. In most of the states in the US feel that the period of contestability cannot be more than two years.
The insurer will be considered to have a legal right to follow the claim relating to misrepresentation and ask additional information before denying the claim or accepting to pay only if the insured passes on within the mentioned period. In life insurance, the face amount on the policy is the one that the insurer is paid if he dies, and it’s still the original sum paid by the policy when the policy happens to mature.
In most cases, life insurance and life assurance always go together. In life, any of the events is most likely bound to happen. In life insurance, they are only events that are bound to happen e.g., floods, theft, the fire they come unexpectedly, causing a lot of damage. The events that are covered life assurance are events that one is sure they are going to happen in future e.g., death.
Types of insurance
Life assurance is basically divided into two categories, permanent and temporary.
(a) Temporary insurance is also known as term insurance; this type of life insurance does not accumulate cash value since it covers for a specified term of years and for a specified premium. The premium is termed as pure as it covers and buys protection in the events of death only. The only major areas which are considered in this term insurance are only the length of coverage, face amount which caters to protection or death benefits, and the premium which is going to be paid.
(b) Permanent; this type of insurance remains contact until the policy matures. If the owner is not in a position to pay the premiums on time, the policy becomes outdated or the policy lapses. The law defines that any type of policy cannot be canceled by the insurer for any reason, not unless signs of fraud are detected in the application. If there is any cancellation, there is a specific time given, which is normally two years. There are three types of permanent insurance;
(1) Whole life insurance; in this type of insurance, the cash value is included in the policy guaranteed by the company since they provide a level premium. The advantages of this insurance are that the whole life is guaranteed cash value, fixed and known annual premiums, and death benefits. We can also see that the disadvantages of whole life insurance are that the internal rate of return in the policy is usually not competitive with other savings. They also don’t have flexibility in their premiums.
(2) Endowments; endowments are considered to more expensive in terms of annual premiums compared with the rest of the insurance policies. Comparing with whole life or universal life, the period of the endowment is shortened, and it has earlier dates. In this policy, the cash value is built up inside the policy. The face amount has death benefits at a specific age. The age in which it starts is known as the endowment age. The endowment insurance is usually paid at a specific period e.g., 15 years or if the insured is living or dead.
(3) Universal life coverage; this is a new insurance cover which plans to offer a permanent insurance cover which has flexible premiums payments affordable for everyone with a quality higher internal rate of return. This insurance has a cash account, which is increased by the premium. The interest is paid within the policy, and it also recorded and credited at the rates decided by the company.
(4) Accidental death; this is limited insurance, and it only covers the insured when they pass away because of an accident. These accidents might be in the form of injury; they don’t cover any death that might occur due to health problems or any type of suicide. The policies are less expensive because they only cover death compared to other life insurances. The benefits are much better because they not only cover accidental death, but they also benefit those who have lost their limbs and also their bodily functions e.g., hearing and sight.
(5) Limited-pay; in this type of permanent insurance, all its premiums are paid over a specified duration of time. There are no extra premiums that are due to keep the policy in force.
When you come to look at life insurance, there are actually two main functions that make it operate fully. They include cash function and mortality function. In mortality function, the premium of everybody else covers the death benefits of anybody who die within a given period of time. In cash, function age varies, meaning that the policy matures and endows the face value of the policy depending on sate and company.
Time value of money
This concept refers to any type of interest that one happens to receive from any kind of payment. This is a present formula, which is the core formula for the time value of money. All the formulae are derived from the formula below;
The present value (PV) formula has four variables
PV value at time=0
FV value at time=n
I rate of compounding
N number of periods
![]()
Summing the contributions of FV the value of the cash flow, you will get the cumulative value.
![]()
The present value of growing perpetuity, if it grows at different fixed rates, you easily determine the value at looking at the following formula. There are various qualifications and modifications to this valuation application. It’s not easy to find a growing perpetual annuity with true perpetual cash flow or fixed rates.
When you want to calculate the value of the regular savings deposit in the future, you first calculate the present value of a stream of deposits of $1,000 every year for 20 years, earning an interest of 7%. (Steven A. Finkler, 1992)
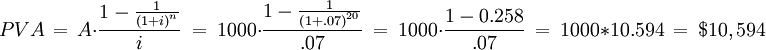
Calculating the value at a duration of 20 years
![]()
This formula can be put together into a single formula.
![]()
References
Lester William Zartman, Life Insurance, 1914
Joseph Brotherton maclean, Life Insurance, 1962
Robert Irwin Mehr: Life Insurance: Theory and Practice, 1977
Solomon Stephen Huebner, George Lawrence Amrhein, Chester Alexander Kline, Life Insurance, 1935
Steven A. Finkler, Christina M. Graf, Budgeting Concepts for Nurse Managers, 1992
Jae K. Shim, Accounting and Finance for the Nonfinancial Executive: An Integrated, 2000