Executive Summary
Mahindra is an Indian multinational corporation that manufactures automobiles and farm equipment. This company has established subsidiaries in China and the United States as a tactic to reach overseas markets. Mahindra leverages technology development in these foreign nations to manufacture its vehicles and tractors and sell them to neighboring countries. Its chief research and development center is located in Chennai, India, as the city has sophisticated technology and skilled personnel. Mahindra offers employment opportunities to all applicants regardless of their race, faith, gender, and disabilities. Therefore, allowing this organization to invest in a country would boost the income of most households, since it would create employment opportunities for a lot of people. Moreover, this company would act as a major source of revenue to the local government, thus enabling it to provide social services to its citizens. There is a need for a country to control the operations of Mahindra to ensure that it does not subject local industries to unhealthy competition.
Company Description
Mahindra and Mahindra Limited, popularly known as Mahindra, is an Indian company that specializes in the production of automobiles. This firm’s headquarters is in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. As per Mahindra and Mahindra Ltd. (2017), this corporation was established in 1945, and its primary business was trading in steel. Today, Mahindra is renowned for the production and distribution of different classes of automobiles and farm equipment, particularly tractors. In 2018, this company had over 41,673 permanent and casual employees. Moreover, it has offered indirect job opportunities to at least 200,000 people in over 100 nations it operates (Shankar, 2018). Mahindra’s financial report showed that the company made over $4.7 billion in 2018 (Shankar, 2018). In the same year, this company’s net worth was $17.8 billion (Shankar, 2018). This business has invested in numerous industries that drive the economy of India. According to Contractor, Kumar, and Dhanaraj (2015), Mahindra has ventured into the automobile industry where it manufactures utility vehicles. Moreover, this corporation has investments in agribusiness, defense, aerospace, logistics, industrial equipment, two-wheeler industries, and real estate. However, this multinational is mainly renowned for the production of utility and commercial vehicles and farm machinery like tractors and combine harvesters.
In spite of stiff competition from American and European firms, Mahindra seems to be doing well, especially in India. This company has acquired and partnered with multiple firms as a way to boost performance and overcome competition. Moreover, it has launched several new products as a strategy to grow its portfolio. Recently, Mahindra announced that it plans to raise the price of its commercial and passenger cars to cater to its increasing production costs (Press Trust of India, 2019). This announcement may not be received well by the majority of the company’s clients.
Company’s International Strategy
For a multinational company to succeed, it must have a strategic plan to help it to penetrate the global market and assert its influence. Mahindra is not an exception, and this corporation has an efficient global strategy that has enabled it to establish manufacturing plants in overseas states and target foreign customers. According to Thakkar (2015), this business sells completely assembled units of Bolero and Scorpio to China, Japan, and the United States. It also targets different African countries, including South Africa, Ghana, and Kenya. The majority of Mahindra’s assembling plants are in India. However, this organization has built tractor-manufacturing factories in Japan, the United States, Mexico, China, and Brazil. One of the reasons why this firm resolved to erect factories in India was to facilitate logistical operations. It was easy for Mahindra to coordinate communication and teamwork between the head office and the various plants located within India. Thakkar (2017) alleges that this company has targeted countries like the United States, Japan, Mexico, Brazil, and China because of their demand for farm equipment. Additionally, they serve as links to other neighboring states. For instance, the United States helps Mahindra to sell cars and tractors in Canada.
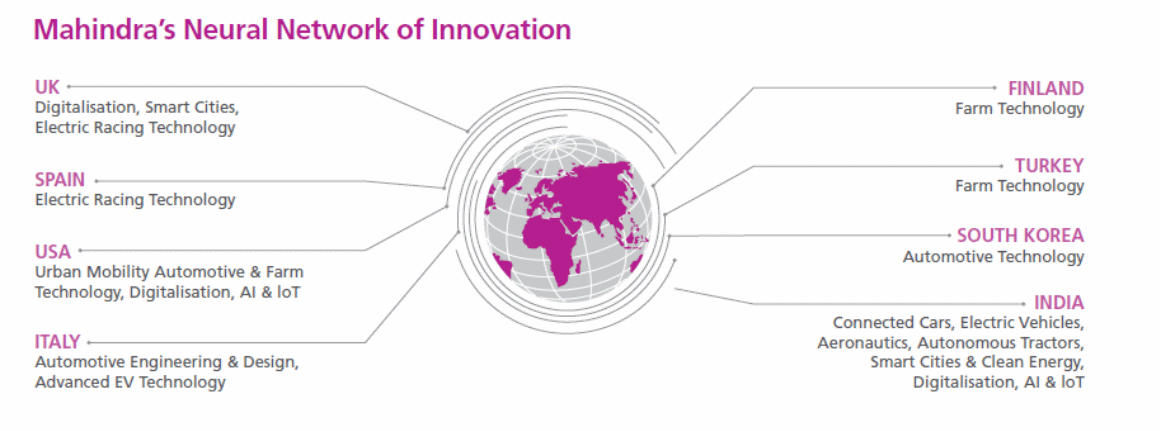
This company has a research and development center dubbed Mahindra Research Valley (MRV), which is located in Chennai. The facility is helpful in the design of new models of automobiles and tractors (Shankar, 2018). The primary reason for building a research hub in this region was the availability of skilled personnel and infrastructural development. This company has additional research and development divisions that are spread across the globe. It has facilities in the United Kingdom, the United States, Turkey, South Korea, Italy, Spain, and Finland as shown in appendix 1 (Shankar, 2018). These countries were selected due to their capacities in terms of technology and human capital. Mahindra faces competition from numerous companies, including Toyota, Tata Motors, Nissan Motors, Ford, Mitsubishi, Volkswagen, and Honda.
One of this business’ strength is its emphasis on innovation which has enabled it to assemble quality automobiles that compete in the global market. Thakkar (2015) maintains that Mahindra’s superior tractor brand has enabled it to dominate the global market in the sale of this essential farm machinery. This company has launched new products, growing its product portfolio and market coverage. The major weakness of Mahindra is that the volume of tractor sales relies on the development of the rural farming sector. Moreover, this company is not doing well in the two-wheeler division. The immediate benefit of Mahindra’s strategy is that it will aid in increasing the company’s sales volume. The long-term advantages include enabling this business to establish factories in foreign countries and growing its global market share.
Company’s Marketing Approach
Mahindra targets both the local and international markets. In India, this company sells lightweight commercial cars, tractors, pickups, trucks, motorcycles, and sport-utility vehicles (SUVs). Mahindra has chosen India due to low competition and a high population that serves as a ready market. Moreover, the demand for farm machinery has led to this firm considering India as one of its main operating bases. Thakkar (2017) alleges that this firm exports automobile to Hungary, Greece, Spain, and Italy. Mahindra targets these countries because they have a high number of affluent families. As per Thakkar (2017), this company sells tractors to the United States, Brazil, Japan, and Mexico. These nations are renowned for agricultural activities; hence they experience high demand for farm equipment. Mahindra manufactures customized varieties of tractors that depend on consumer needs. For instance, it produces small tractors (25HP class) for horticulture and row crop farmers (Mahindra Rise, 2018). It also manufactures electric cars (Reva) for European clients who are environmental-conscious. The production of heavy and light-duty commercial vehicles is meant to meet the needs of different clients, particularly business people.
In India, Mahindra has an effective distribution channel that comprises authorized dealers, service points, sales offices, and stock points. Moreover, this corporation has showrooms which it uses to exhibit automobiles. These outlets facilitate direct marketing, as employees interact with customers and get their feedback. In the overseas market, this company uses assembly plants to distribute cars and tractors. Thakkar (2017) posits that Mahindra has factories in Brazil, the United Kingdom, the United States, and mainland China. This firm uses television, billboards, and celebrity endorsement to promote its products in the local market. Conversely, it relies on social media like YouTube, Google+, Facebook, and Twitter to reach clients in the global market.
Company’s Logistic Approach
Mahindra manufactures its products in different factories that are distributed across the world. This company has plants in the United States, India, and China among other nations. As per Barman and Thakkar (2017), this firm selected the United States because of its advanced technology in the automobile sector. Contractor et al. (2015) claim that Mahindra uses the United States’ superior artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) to improve products. This corporation has opened tractor-manufacturing factories in the United States due to its refined farm technology. Moreover, this country is close to Canada, therefore serving as an essential gateway to the latter’s market. Shipping assembled cars from India to the American market would be costly. It underscores the reason Mahindra opted to assemble tractors and cars in the United States.
This business has factories in Mainland China that specialize in the manufacture of tractors. The Mahindra Tractor Company was established to facilitate the production of farm machinery that is sold in the local market (Shankar, 2018). Mahindra chose China due to its demand for farm equipment and superior technology in the automobile industry. It is difficult for this corporation to ship many tractors from India due to their size and weight. Opening a manufacturing plant in China has enabled Mahindra to increase the production of these essential machines, therefore being capable of satisfying the market demand.
Human Resource Management
Mahindra’s goal is to become one of the most esteemed brands in the world. This company acknowledges the role of human capital in the realization of its objectives. Consequently, it has initiated programs meant to equip employees with the requisite skills to assist them to discharge their mandates without difficulties (Mandavia, 2015). This corporation is renowned for emphasizing diversity and inclusion in its workforce. Mahindra’s human resource managers are discouraged from discriminating against workers based on their race, ethnicity, gender, disability, or belief (Shankar, 2018). This company offers employment opportunities to local employees in foreign countries. Mahindra is renowned for not being ethnocentric in hiring managers. Hence, local employees who serve in overseas plants have equal opportunities to be promoted to leadership positions. This organization is committed to assisting young recruits in India and overseas to build their careers. Consequently, it helps in developing the human capital of the host nation.
Analysis
Allowing multinational companies to invest in a country has numerous benefits and risks to the host nation. The advantages include the development of human capital, the creation of job opportunities, technology transfer, and government revenue. Agnihotri (2014) cites increased competition, political interference, and repatriation of profit as some of the risks associated with allowing a multinational corporation to invest in a country. Mahindra offers employment opportunities to people from a host nation. Thus, allowing this company to operate in one’s country would not only boost the economy of the state but also create jobs. The level of income in many households would rise, thereby improving their buying power. In addition, letting Mahindra invest in one’s country would help to improve the human capital of the nation. This company has invested in technology, and it encourages employee growth. Consequently, the local workers would get a chance to advance their skills, thus boosting productivity. Multinationals serve as major sources of revenue to local governments. Hence, permitting Mahindra to establish factories in a country would boost the government’s revenue, as this company would have to remit taxes.
A country requires protecting local industries from unhealthy competition that might arise due to multinationals investing in a nation. Letting Mahindra invest in a country would affect the performance of local car-manufacturing firms because of competition. Many multinationals interfere with the affairs of a host nation as they tend to promote the political ideologies of their home countries. Consequently, allowing Mahindra to invest in a country may lead to the local government introducing changes that do not benefit the public.
Recommendation and Conclusion
The local government should evaluate the benefits and demerits of a multinational company before allowing it to invest in the country. As discussed above, letting Mahindra into a nation would have numerous benefits to both the local government and society. This company would create employment opportunities for people; thereby boost the income of most households. It would also serve as a critical source of revenue to the local government, hence enabling it to provide essential social services. Based on these benefits, there is a need for a country not to turn away from this corporation. Nevertheless, the government must regulate the operations of Mahindra to ensure that it does not pose a threat to the local industries.
Appendix 1
References
Agnihotri, A. (2014). Low-cost innovation in emerging markets. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 23(5), 399-411.
Barman, A., & Thakkar, K. (2017). Mahindra & Mahindra heads to US; manufacturing unit to start operations soon. The Economic Times. Web.
Contractor, F. J., Kumar, V., & Dhanaraj, C. (2015). Leveraging India: Global interconnectedness and locational competitive advantage. Management International Review, 55(2), 159-179.
Mahindra and Mahindra Ltd. (2017). Integrated report FY 206-2017. Web.
Mahindra Rise. (2018). Mahindra the world’s no. 1 tractor player by volume, records its highest ever domestic annual sales. Web.
Mandavia, M. (2015). Mahindra to select 32 from group to groom them into new leaders. The Economic Times. Web.
Press Trust of India. (2019). Mahindra to increase prices of vehicles by up to Rs 73,000 from April. Business Standard. Web.
Shankar, N. (2018). Integrated annual report 2017-2018. Web.
Thakkar, K. (2015). SUV maker Mahindra & Mahindra adopts new strategy to take on competitors, rev up market share. The Economic Times. Web.
Thakkar, K. (2017). Mahindra & Mahindra eyes overseas markets for growth. The Economic Times. Web.