This study analyzes Marriott Hotels’ marketing management and how it is connected with Marriott brand positioning. Keep reading to learn more about Marriott positioning strategy.
Abstract
This report assesses the performance of Marriott Hotels concerning strategic marketing. The report assesses the type of segmentation that the firm has integrated. This goal has been achieved by evaluating the different market segmentation variables that the firm has incorporated. An internal review of the firm’s strategic marketing strategy shows that the firm uses a multi-stage segmentation strategy by adopting diverse market segmentation bases, which include the demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic approaches. The report evaluates the advantages and disadvantages associated with the firm’s brand portfolio. Moreover, a review of the JW Marriott positioning strategy coupled with how the firm can improve its positioning is conducted. The report also reviews the JW Marriott perceptual map, which illustrates its position to the target customers concerning price and quality.
Introduction
Marriott Hotels is a global firm that specializes in the provision of full-service hotel services. The firm was founded in 1957 and it has established operations in 78 countries with 19 hotel brands. By 2013, the company owned over 505 hotels located in different countries. Its global market success can be explained by the adoption of effective marketing management practices such as franchising. The firm insists on offering high-quality products and services, which has remarkably entrenched its industry position.
The firm ranks amongst the pioneers of market segmentation in the global hospitality industry. Dibb and Simkin (2007) affirm that market segmentation forms the cornerstone of modern marketing. Subsequently, the firm incorporated segmentation as one of its fundamental marketing strategies. Dibb and Simkin (2007) further affirm that segmentation provides businesses with an opportunity to maximize their resource utilization by “establishing a bridge between the diverse customer needs and the limited business resources” (p. 81). Before developing any additional hotel chains and the respective brands, the company undertakes an extensive test on the properties. The firm’s marketing strategies are based on findings of extensive market research. The firm seeks and utilizes the customers’ feedback to understand the market. Consequently, the firm is in a position to formulate and implement targeted marketing programs.
A firm can adopt different market segmentation strategies. Marriott recognizes the existence of varied customer preferences, hence their willingness to pay a premium to achieve the desired level of comfort and luxury. To satisfy the varied market needs, Marriott has integrated a multi-stage market segmentation approach. Consequently, the firm has adopted diverse bases of market segmentation.
Some of the market segmentation bases applied include geographic, demographic, behavioral, and psychographic segmentation. This aspect explains why the firm has established different tiers of the hotel. The hotels are specially designed to cater to varied customer needs. This report entails an evaluation of Marriott’s strategic marketing practices concerning segmentation and positioning.
The Application of Market Segmentation across Different Marriot Hotels Brands
The Ritz-Carlton Hotel
The Ritz-Carlton Hotel was established in 1983 in Boston and it has several outlets across the world. Ritz-Carlton has adopted psychological segmentation. The hotel targets customers who are inclined towards the achievement of unique experience through the consumption of luxury hospitality products. The hotel intends to make travelers’ journeys more meaningful. Amongst the categories of customers that the hotel has targeted include the senior executive managers. To access its target customers, the Ritz-Carlton hotel has established luxury outlets, which are located in the most vibrant resort locations and cities in the world. Furthermore, the hotel has integrated brand extensions, hence improving its ability to serve the customers. Its brand extension entails the provision of golf, destination clubs, and residences. Okonkwo (2007) affirms that luxury consumers are concerned with the authenticity and originality of the product. In a bid to satisfy the target customers’ demands, Ritz-Carlton ensures that its products are developed professionally. For example, the golf courses are designed by renowned golfing personalities such as Tom Fazio, Jack Nicklaus, and Greg Norman. The hotel can host Senior PGA events (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2014).
Autograph Collection Hotels
The Autograph Collection Hotel has adopted an innovative approach by integrating the behavioral market segmentation approach. The hotel focuses on the customers’ behaviors, attitudes, values, activities, interests, and opinions. For example, the hotel targets customers who derive satisfaction from diverse products such as cultural collection, boutique arts, historic hotels, urban edge hotels, and resort (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2014). Each of the Autograph Collection Hotels has a unique identity, which improves the hotels’ ability to appeal to the changing customer needs and preferences. To attract and retain customers, the Autograph Collection has incorporated a guest loyalty program, which applies to over 3,000 hotels located in over 68 countries. The hotels are designed uniquely to reflect the local culture. Additionally, this move has contributed significantly to the hotel’s unique identity (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2014).
Marriott Vacation Club
This brand of Marriot Hotels targets vacationers or travelers. In a bid to meet the customers’ demands, the Marriott Vacation Club has integrated the geographic segmentation strategy. The hotel has achieved this goal by establishing hotels in different locations around the world. The facilities are fully equipped with living and dining areas, fully equipped kitchens, and separate bedrooms. The facilities are available for renting or they can be provided as a vacation package. By 2011, the hotel had established 53 resorts in 33 different destinations in the US and 6 other countries (Marriott Vacations Worldwide, 2012). The geographic segmentation approach has improved the hotel’s ability to enrich the customers’ experience. Marriot Vacation Club provides clients with spacious accommodation and resort amenities.
AC Hotels by Marriott
These brands of hotels have integrated demographic segmentation. Some of the demographic variables that the hotels have integrated entail the consumers’ social status and income. The hotel mainly targets the upper-moderate tier-lifestyle customer group such as the business, leisure, and the conscious travelers who are focused on experiencing the diverse options provided by cosmopolitan hotels. Subsequently, the AC Hotels by Marriott are located in lifestyle, destination, and downtown centers. All the hotels are focused on offering convenience and stylish products. The AC Hotels are designed to attract customers who are concerned with “sleek design with limited food and beverage offerings” (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2012)
Gaylord Hotels
This brand has adopted the behavioral market segmentation variable, as evidenced by targeting customers who are concerned with the benefit sought. The Gaylord Hotels brand offers a wide range of hospitality products in one place. The resorts are characterized by specially designed luxurious rooms in addition to the provision of excellent entertainment, which improves its ability to provide an enchanting getaway. Some of the hotel’s resorts can be found at the Potomac scenic banks and the music city of Nashville and Texas (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2014). The behavioral market segmentation approach has played a remarkable role in improving the ability to give the ‘entertainment lovers’ their desired products.
Protea Hotel
To address diverse customer needs, Marriott Hotels has integrated the geographic segmentation approach through its Protea brand. Protea Hotels mainly operate in African countries such as the Sub-Saharan countries and South Africa. By focusing on the African countries, the hotels are in a position to offer personalized service experience. Additionally, the hotel also uses demographic segmentation by targeting business and leisure travelers (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2014).
Analysis of Marriott’s Brand Portfolio
Brands play a central role in the businesses’ marketing strategy and the pursuit of competitive advantage (Ivens & Valta, 2012). One of the core purposes of business is to develop customer loyalty by providing valuable assets. Panda (2008) argues that brands “can create wealth for the company depending upon how much value they add to the customers’ life” (p. 350). Branding has undergone considerable changes over the past few years from the one-dimensional approach to a multi-dimensional approach.
Businesses are utilizing diverse brand extension approaches, which include emotional, relational, functional, and strategic dimensions (Panda, 2008). Furthermore, Riesenbeck and Perry (2009) contend that businesses are reacting to changing customer behavior by developing larger brand portfolios. Marriott Hotels has integrated the concept of brand extension, which has led to the development of a comprehensive brand portfolio. However, Marriott Hotels encounters some challenges and strengths due to the adoption of an extensive brand portfolio as evaluated herein.
Marriott Portfolio Brand Advantages
Strong Consumer Knowledge
A strong brand forms the foundation upon which an organization undertakes brand extension (Chitale, 2013). By adopting the concept of brand extension, Marriott Hotels is in a position to develop extensive consumer knowledge. By using the ‘main brand’, Marriott Hotels is in a position to develop, create, and introduce new products into the market. This goal is achieved through extensive market research. Due to its commitment to the development of a strong brand portfolio, the Marriott Hotels undertakes comprehensive consumer market research to understand the customers’ product tastes and preferences. This move has played a considerable role in promoting the firm’s brand awareness and image. Davis (2010) argues that each brand “can maximize impact on market or niches by shaping a sharp and distinctive image” (p. 43). An extensive brand portfolio is critical in improving the connection between a firm and its potentially influential and important customers. Therefore, the firm is in a position to generate a new income stream. Furthermore, the brand portfolio strategy has contributed significantly to the development of strong brand loyalty, as evidenced by the firm’s positive market performance on a global scale.
Low-Cost Advantage
The Marriott’s success in venturing into new markets has been enhanced by the integration of the franchising strategy. This move has enabled the firm to establish new outlets in different parts of the world. Additionally, the integration of brand extension has enabled Marriot Hotels to engage in aggressive market expansion at a low cost. Davis (2010) argues that launching a new brand by implementing the brand extension strategy is cost-effective because the product is based on an already established brand. The low cost associated with a brand portfolio arises from the fact that the firm incurs a low cost in creating market awareness for the new product through advertising.
High Brand Visibility
By developing a strong brand portfolio through its aggressive brand extension strategy, Marriott Hotels has attained an effective and efficient method to build its brand. Thus, the firm has developed a global footprint. Wang (2008) thinks that the aggressive brand extension enables businesses to capture new market segments. Additionally, the approach has provided the firm with a chance to develop a positive perception amongst its target customers regarding the quality of its products. Thus, customers around the world associate the various Marriott brands with quality and unique experience. Therefore, one can argue that developing a broad brand portfolio has enabled Marriott to strengthen its ability to offer quality products across varied contexts. The ultimate result is that customers develop a greater preference for Marriott Hotels as compared to its competitors.
Defensive strategy
The global hospitality industry is becoming very competitive due to its lucrative nature. Firms in the industry are adopting diverse strategies to remain competitive. Some of the strategies entail aggressive market expansion. By adopting the aggressive brand extension strategy, Marriott Hotels has gained a high competitive edge against its competitors. Through its brand extension, the firm has been in a position to enter new markets, thus limiting its competitors’ capacity to encroach on potential new markets. The brand extension enables a firm to adopt an existing brand name in venturing into new market segments.
Brand reinforcement
Products go through several stages in the course of their lifecycle. These stages include the introduction, the growth, maturity, and the decline stage. The market performance of the product varies depending on its stage of the lifecycle. In the maturity stage, a firm experiences an increase in sales at a decreasing rate. Moreover, the market is characterized by a high degree of saturation and excess capacity. Surviving in such a market is a challenge for most organizations (Aaker, 2009).
Adopting an aggressive brand extension strategy has allowed Marriott Hotels to revive its products, hence avoiding a decline. Subsequently, the brand portfolio strategy has played an essential role in sustaining the products’ market performance. Therefore, Marriott Hotels has sustained a positive image as developed by customers regarding its products’ quality across the different brands around the globe. Customers develop a high level of loyalty towards the firm due to its ability to offer a wide range of products. Moreover, the organization is in a position to strengthen the level of brand relationship with its customers, hence increasing the likelihood of brand memorization.
Marriott Portfolio Brand Disadvantages
Dilution of Brand Image
Despite the advantages that Marriott has acquired through its brand portfolio strategy, the firm’s management team should be cognizant of the potential challenges. First, an aggressive brand extension can result in dilution of the existing brand. Some of the existing consumers might change the perception of the brand after its extension. This aspect might arise from the fact that the organization might be forced to enter an association that the consumers consider as undesirable. Aaker (2009) supports this opinion in his assertion that the associations “created by extension can fuzz a sharp image that had been a key asset and at the same time reduce the brand’s credibility within its original setting” (p. 211). Currently, Marriott Hotels has integrated the franchising strategy as one of its core strategic management practices.
To implement this strategy successfully, the hotel is required to enter a franchising agreement with franchisees. Customers might develop the perception that brand extension will lead to the dilution of the sought benefits. For example, some consumers might associate products with value. Therefore, the brand extension strategy might lead to the development of the perception that the value of the product has been compromised. The ability to sustain the positive image developed depends on the franchisees’ adherence to the franchising strategy. Thus, failure to comply or lose focus by the franchisees might culminate in the dilution of brand image, thus affecting the firm’s market existence.
Risk of Cannibalization
The extensive brand portfolio adopted by Marriott Hotels can lead to the cannibalization of its existing products especially if the brands are located in markets close to each other. Under such circumstances, the firm might experience an increase in sales especially amongst the newly introduced brands, while those of the existing brands diminish. Aaker (2009) argues that it is difficult for the sales of a new brand extension to overcome those of the original brands due to the damage coming from the loss of the original brand equity. This situation is likely to occur if the original and the brand extensions cannot be differentiated optimally. The outcome can result in a reduction in the organization’s overall market share because there is no sufficient value, which is added to result in incremental growth.
Reduction in brand reputation
The extensive brand portfolio might lead to a reduction in the already developed brand image and reputation. Therefore, the firm might not be in a position to sustain its positive market performance. Under such circumstances, the organization might not attract potential franchisees due to the lost brand reputation (Chitale, 2013).
Increase in Resources, Costs, and Expenses
Implementing the concept of the brand extension might require the firm to incur substantial costs in the product development phase.
Maintaining Product Distinctiveness
The aggressive brand extension strategy might present a major challenge to Marriott in its quest to integrate product differentiation. Thus, the firm’s ability to sustain its products’ image and distinctiveness might be reduced remarkably.
JW Marriott Brand Positioning Strategy
Positioning is a fundamental element in an organization’s pursuit of competitive advantage. Ferrell and Hartline (2012) argue that positioning leads to the creation of a mental image amongst the target customers regarding a firm’s product offering concerning its distinct features. The mental image can be based on reality or perception in comparison with the competitors’ products. Therefore, positioning is concerned with the consumers’ perception regarding the product being offered (Diabe, 2015).
In the course of its operation, JW Marriot Hotel, which is one of Marriott’s brands, appreciates the importance of optimal market positioning. The firm has integrated the concept of positioning by attribute as its core strategy. The firm has achieved this goal by creating an image of affordable luxury and considering three main aspects, which include
- Brand mantra
- Frame of reference
- Points of Difference [POD] and Point of Parity [POP]
The firm frame of reference takes into account the target market and its competitors. The firm’s target market is comprised of high-end customers and business travelers. In its positioning strategy, the firm assesses the products and services offered by its core competitors such as the Fairmont Hotel & Resort Incorporation. Furthermore, the firm’s positioning strategy is guided by an effective brand mantra, which focuses on three aspects, viz. wellness, culture, and culinary.
Aaker (2009) argues that the importance of a brand mantra is to communicate and define brand boundaries. Thus, a firm is in a position to communicate the uniqueness of its products. The wellness mantra has enabled the firm to develop a strong image amongst the target customers regarding its commitment to healthy eating and fitness. Conversely, culture enables customers to relate to different cultural aspects such as art and music, while the culinary mantra emphasizes the firm’s focus towards fine dining and the provision of high-quality wine, spirits, and food. The firm considers its ability to make customers believe in the unique benefits associated with its products as its source of points of difference. On the other hand, the points of parity arise from its effectiveness in infusing local details in its product portfolio. By considering the points of parity, JW Marriott Hotel is in a position to sustain its organizational culture.
Despite the contribution of the firm’s positioning strategy in attaining optimal market positioning, the firm’s management team must appreciate the numerous transformations occurring in the global hospitality industry. Consequently, the firm should adjust its positioning strategy.
One of the strategies that the organization should take into account entails the triple benefits strategy. Currently, the firm’s positioning strategy is based on benefits and affordability. JW Marriot has positioned itself as a firm that offers affordable luxury. Thus, customers associate the firm with luxury. However, the firm needs to consider transforming itself into a market leader. In a bid to achieve this goal, JW Marriott should focus on extending its commitment to serve a large number of customers by integrating the concept of quality.
To position its products and services based on quality, the organization should undertake extensive consumer market research. Ferrell and Hartline (2012) accentuate that quality is a unique differentiation point. Moreover, consumers use quality as a benchmark in determining the extent to which a product is in a position to deliver a memorable experience. In its pursuit of quality as one of the market positioning elements, JW Marriott’s marketing manager should seek the services of professionals in the hospitality industry. For example, to reflect the local culture in its products, the firm should utilize local talent. This approach will enable the firm to be effective in its product localization. The outcome is that the firm’s products will lead to the attainment of a high level of satisfaction amongst the target customers.
The firm should ensure that its products are designed effectively to reflect the quality demand amongst the target customers. By adopting the triple benefit positioning strategy, JW Marriott will be in a position to appeal to new market segments (Groucutt, Forsyth & Leadley, 2004). Additionally, the firm will entrench its market dominance by finding an optimal spot between the mainstream and luxury hotels. Missy (2011) asserts that customers are seeking fancier and less extravagant hospitality products.
JW Marriott should consider the importance of continuous assessment of the changes within the target customers. The assessment should evaluate the adjustments being undertaken by the competitors in their positioning strategy. By integrating quality in its products, the organization will receive accreditation and rewards from renowned bodies in the hospitality industry, which is critical in promoting the firm’s global reputation.
Perceptual map for JW Marriott Hotel
JW Marriott Hotel has positioned itself optimally in the global hospitality industry by addressing the customers’ tastes and preferences. The chart below illustrates the firm’s perceptual map amongst the target customers.
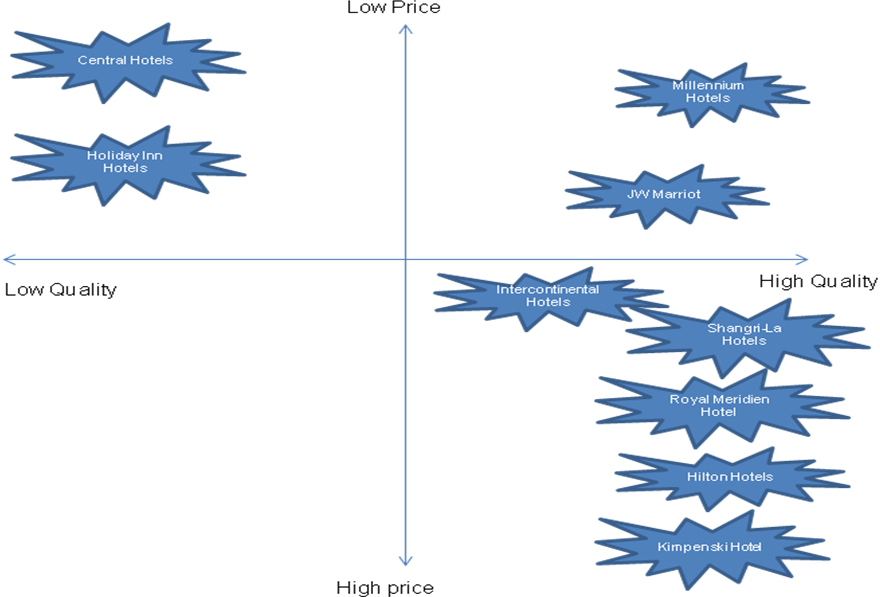
The above perceptual map shows that the JW Marriott Hotel has managed to offer high-quality products at a relatively low price. However, the perceptual map illustrates that there is an opportunity for the firm to improve its perception amongst the target customers by exploiting the concept of quality. This move will play a fundamental role in improving the firm’s resilience in the changing hospitality industry. Additionally, the firm’s competitive advantage will improve considerably.
Conclusion
The hospitality sector ranks amongst the most volatile economic sectors due to the influence of diverse macro-environmental forces such as political, economic, social, technological, and legal factors. Despite the high degree of volatility, the industry is very lucrative, which increases the intensity of competition. Surviving in such an industry requires investors to incorporate effective strategic marketing practices.
From the analysis undertaken, it is evident that Marriott Hotels has appreciated the importance of strategic marketing, which has contributed to its success. For example, the integration of the franchising strategy has enabled the firm to penetrate the global hospitality market. In addition to effective business and corporate-level strategies, the hotel has integrated effective marketing strategies such as market segmentation. Marriott Hotels has integrated the multistage segmentation strategy. Some of the segmentation dimensions that the firm has integrated include the demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic approaches. The different hotel brands have utilized varied segmentation approaches to maximize sales revenue and profitability. The segmentation strategy has enhanced the firm’s capacity to satisfy diverse customer tastes and preferences.
Marriott’s success in the global market has further been enhanced by the integration of the concept of brand extension. Through this move, the firm is in a position to leverage its strong brand name, hence attaining a high-level of market acceptability and penetration. However, the firm’s management team must be conscious of the challenges associated with the broad brand extension such as cannibalization, loss of reputation, and dilution of brand image. To counter such challenges, the hotel should base its branding strategy on extensive market research. Consequently, the firm will be in a position to differentiate its products optimally. Thus, the likelihood of developing a positive perception amongst the target customers on the quality of the product will improve substantially.
The firm’s success has further been promoted by integrating the elements of affordability and luxury as its core market positioning strategy. However, to promote its long-term competitiveness, the hotel should integrate the concept of quality in its positioning approach. This move will enhance the extent to which customers associate the firm’s products with value. The outcome of adjusting its positioning strategy will be an improvement in brand perception. The adjustment should be undertaken across all the firm’s brands to attain a high competitive edge.
References
Aaker, D. (2009). Brand portfolio strategy; creating relevance, differentiation, energy, Leverage, and clarity. Chichester, UK: Simon and Schuster.
Chitale, A. (2013). Product policy and brand management; text and cases. New Delhi, India: Prentice-Hall of India.
Davis, J. (2010). Competitive success; how branding adds value. Chichester, UK: John Wiley.
Dibb, S., & Simkin, S. (2013). Market segmentation success; making; making it happen. New York, NY: Routledge.
Diabe, H. (2015). Marketing strategy; expand your business, increase sales and promote social media. New York, NY: Comet Content Providers.
Ferrell, O., & Hartline, M. (2012). Marketing strategy. New Jersey, NJ: Cengage.
Groucutt, J., Forsyth, P., & Leadley, P. (2004). Marketing; essential principles, new realities. London, UK: Kogan Page.
Ivens, B., & Valta, K. (2012). Customer brand personality perception: A taxonomic Analysis. Journal of Marketing Management, 28(10), 1062-1093.
Marriott Vacations Worldwide: Marriott Vacation Worldwide corporation. (2012). Web.
Missy, F. (2011). Marriott International’s JW brand being repositioned in the market. Web.
Okonkwo, U. (2007). Luxury fashion brand; trends, tactics, techniques. Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Panda, T. (2008). Marketing management. New Delhi, India: Excel Books.
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission: Form 10-K; Marriott International Incorporation. (2012). Web.
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission: Form 10-K; Marriott International Incorporation. (2014). Web.
Riesenbeck, H., & Perry, J. (2009). Power brands; measuring, making and managing Brand success. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley.
Wang, J. (2008). Brand new China; advertising, media, and commercial culture. Cambridge, MA.: Harvard University Press.