This case study provides a thorough Nestle strategy analysis. It contains the marketing mix of Nestle, the company’s competitive advantage, internal and external environment analysis, and other details. Read on to learn the firm’s global strategy!
Nestle Strategy Analysis
The marketing planning processes incorporate 4 stages including the analysis stage, planning stage, implementation stage, and monitoring stage. The analysis stage covers the pertinent information required for framing plans and making decisions. This comprises of the present market condition, the available products of an organization, the viable situation, as well as the SWOT analysis.
The results of these analyses form the basis of the second stage, which is the planning stage. Here, marketing executives are completely conscious of the elements in the institution’s present situation that are likely to affect its marketing activities and thus will consider commercial intents of this information to project marketing strategies and assess strategic options. The implementation and monitoring stage involves the execution of plans and management of plans respectively (Dibb 72).
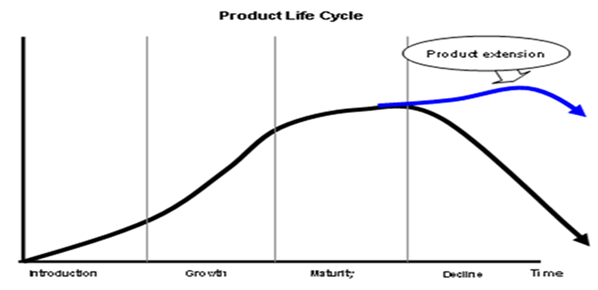
Product Life Cycle
In Nestle, the product life cycle is a critical provision used as a marketing tool. It denotes how Nestle’s products are introduced, grow, mature, and decline in the market.
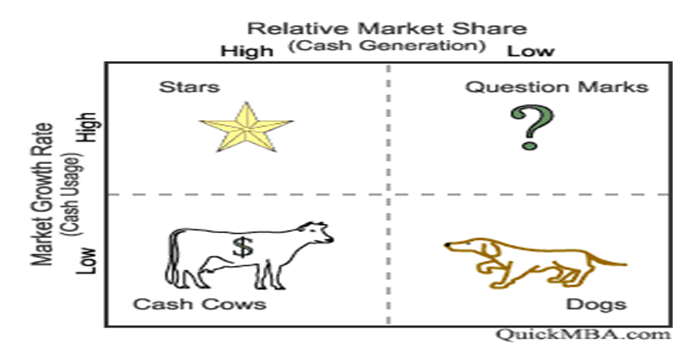
Nestle: BCG Matrix
One of the most famous management tools is the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix. It is dependent upon the product life cycle theory. To build a lasting value conception, Nestle must establish a portfolio of its products for high-growth and low growth alongside market penetration. This concept is used to find out what priorities should have to be provided in the product portfolio of any business unit. The BCG matrix has two dimensions. The first is relative market share and the other is market growth. The fundamental concept behind it is that if a product has a large market share or if the market of the product increases rapidly, then it is considered the best for a particular corporation.
In Nestle’s context, BCG Matrix is staged to analyze the two market dimensions i.e. market share and market growth. The Nestle has always registered bigger market shares and rapid market growth. The BCG Matrix places Nestle’s commodities into 4 discrete groups:
Brief description of Porter’s Model
Porter’s Five Forces are useful in grasping the position of a business venture. Nestle Corporation can easily plan its business strategies in a manner that evades losses. These factors include; supplier power, buyer power, competitive rivalry, the threat of substitution, and the threat of making a new entry. In analyzing Nestle using porter’s five forces, these factors are evident as stipulated in the case study provided.
For example, the threat from new entrants into the industry is applicable in this quarter. Nestle and other existing firms are threatened by the entrance of other competitive rivals. Additionally, there is considerable rivalry from the existing firms in the global market. Other international companies like Kraft Foods, ConAgra, Danone, Heinzand, and Mondelez International, Inc. among others are threatening the survival of Nestle in the food and beverage industry.
Additionally, the bargaining power of buyers is evident in the industry due to competition. Customers go for cheap and reliable airline companies. Additionally, suppliers operating in the industry have equally fronted their bargaining power. The raw material suppliers usually change the cost of their products to suit their business interests. Another apparent force evident in the case is the availability of substitute products/services produced by companies like Kraft Foods, ConAgra, Danone, Heinzand, and Mondelez International, Inc. mentioned earlier. Consumers can resort to other substitute products if such needs arise (Kossowski 325).
The component that normally makes up a mission statement
The main purpose of the mission statement is to describe the aim of the business as well as the methodology that needs to be employed in the business plan. Creating a suitable mission statement forces an individual to consider deeply the major elements of his or her business and making the process a principal part of the business planning. Regardless of the kind of business an individual is involved in, the mission statement interconnects the objective of the business to both insides as well as people outside the organization. It explains what the business is and what it intends to do (Lewis and Trevitt 27).
External Environment Analysis of Nestle
PESTLE Analysis: Nestle
The PEST analysis is a very significant tool for analyzing the business’s external position.
Porter Five Forces Model of Nestle
Porter’s 5 forces are applied in the food and beverage industry concerning Nestle Company. For example, the threat from new entrants into the industry is applicable in this context. Nestle and other existing airline firms are threatened by the entrance of other competitive rivals. Second, there is also competition from Kraft Foods, ConAgra, Danone, Heinzand, and Mondelez International, Inc. among others. Thirdly, the bargaining power of buyers is evident in the industry due to competition. Customers go for cheap and reliable consumer goods. Forth, suppliers operating in the industry have equally fronted their bargaining power. The fifth is the availability of substitute products/services provided by Kraft Foods, ConAgra, and Danone companies among others.
Nestle: Internal Environment
Mckinsey 7s Framework: Nestle
From the case provided, Nestle can be subjected to Mckinsey’s 7s to assess its internal prominence and success in the food and beverage industry. The model relies on the ideology that, for an organization to perform exemplarily, the 7 elements (Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff) should be realigned for mutual reinforcement. On strategy, Nestle has adopted novel business strategies and advanced marketing provisions to widen its global market reach. Concurrently, the organizational structure is strategic enough to ensure proficiency within the organizational operations.
Also, Nestle’s systems are diverse to incorporate the aspects of technology and customer focus as evident from the case study provided. On shared values, the management of the organization incorporates other junior staff in the operations of the company.
The values of the organization are embraced to ensure customer focus. The company is also “skill” focused. For instance, the success of the company has involved various business strategies to counter numerous challenges encountered in the industry. Nestle’s “style” in the management, marketing, and customer focus is inclusive. The staffs are also committed to organizational progress.
Marketing Mix of Nestle
Nestle: SWOT Analysis
Identifying key external driver affecting Nestle (inflation, legislation, and unemployment, etc)
There are numerous external; drivers affecting Nestle including inflation, unemployment, legal provisions, and unemployment. Inflation denotes a period of consistent increases in the price level of commodities. This results in the devaluation of the currency in the international markets. The level of inflation in a country has both direct and indirect influences on the economic development of that country. Positive changes in the economic development imply an improvement in the standards of living of the people from that particular region. Inflation often leads to slowed or negative economic development. The unemployment rate depicts the percentage of unemployed individuals within the labor force of a given country.
How Nestle managed growth and profitability through its marketing strategy
From the case study provide, Nestle has selected its specific target markets to serve them exceedingly. Customers demand goods, which satisfy their needs with the utmost precision and satisfaction. It is from this context that the entire business prospects lie in selecting the target market. Additionally, the need to execute efficient production mechanisms has always helped Nestle to deliver its business objectives as it addresses its targeted customers’ demands, growth, and profitability quests. Nestle strives to produce quality and affordable consumer products.
Nestle: Competitive Advantage
Nestle faces stiff competition from various companies globally. These include Kraft Foods, ConAgra, Danone, Heinzand, and Mondelez International, Inc. among others. Nonetheless, the company has developed and embraced critical competitive advantages to remain afloat in the 5the market. Nestle recognizes the significance of brand name as contemporary culture in its marketing provisions. The recognition/recall of a brand name is a fundamental aspect and a competitive advantage that can be used in judging.
Ansoff Matrix of Nestle
The use of Ansoff’s Growth matrix provides a credible planning tool that can help Nestle to establish its commodities and advance its marketing tactics. In this context, the company can market both new and/or existing commodities in the market. Opportunities incorporate emerging markets, well-developed competitive advantages, new technologies, novel products, and a high number of customers. Contextually, one distinctive opportunity prospected by Nestle is the rapid growth in the global market size. Strategically, the company should increase its production in response to the expected rise in demand to improve its profits. Customers prefer quality but affordable products.
Works Cited
Dibb, Sally. Marketing Planning: A Workbook for Marketing Managers. London: South-Western Cengage Learning, 2008. Print.
Fortenberry, John. Health Care Marketing: Tools and Techniques. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2010. Print.
Kossowski, Alexandra. Strategic Management: Porter’s Model of Generic Competitive Strategies – Theory and Analysis. München: GRIN Verlag GmbH, 2007. Print.
Lewis, Roger, and Roger Trevitt. Business: Vocational a Level. Cheltenham: Stanley Thornes, 2000. Print.