Introduction
The discussion begins with a strategic analysis of a selected company and for that purpose; Nokia- the world’s largest cell phone Manufacturer Company has been selected to analyze several aspects in environment, resource capability, selection and implementation of strategies etc. Since the company is operating under the telecommunication industry, it is essential to have a clear concept about this along with the global economic features with the company context. The world’s cell phone market had been grown by 22.2% in 2006 and has been predicted to expand by 125.50% in 2011 relative to the year 2006 turning it as one of the most competitive market in the world while Nokia has captured the major market share of 34.20% of the total.
Short looks of Nokia
is known as a popular Finnish MNC of communication that had been evolved in 1865 by Fredrik Idestam. It’s headquarter is located in Keilaniemi, Finland. From the Annual report 2007 of Nokia Corporation demonstrates that this company is expanded by sales in above 150 countries with annual revenue of €51.1 billions and income of €8 billions by producing 3.5% share in the home country’s GDP. An overview of the strategic management process of Nokia Corporation can be presented as follows-
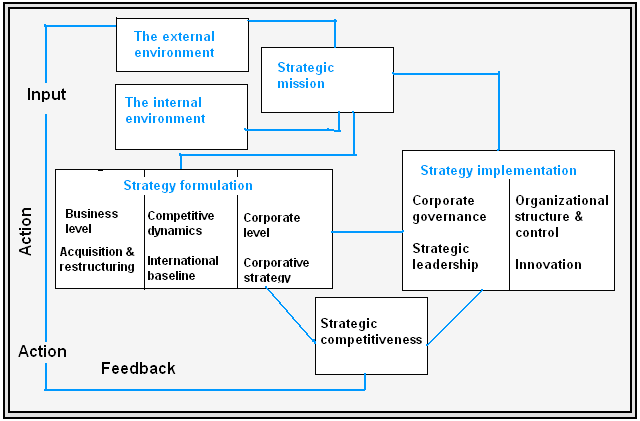
Environmental analysis
The company’s environmental condition is required to analyze by PEST1 analysis which is as following-
Political Factors
Since the company is operating in many countries in the world and the earning a significant amount of profits from them; it has been affected by the local rules and regulations of imports of those. There also exists a chance of political spoilage on sales by such nations. Thompson, A. et al (2007) argued that investment, investment policy, device supply, operation and growth as well as network development materials can be an important topic of risk, over taxation, rate of exchange, savings of personal intelligence, recession, ups and downs of currencies and the other uncertainties.
Economic factors
The view of economic condition of Nokia in comparing with global mobile phone manufacturing leaders can easily be seen through the following chart-
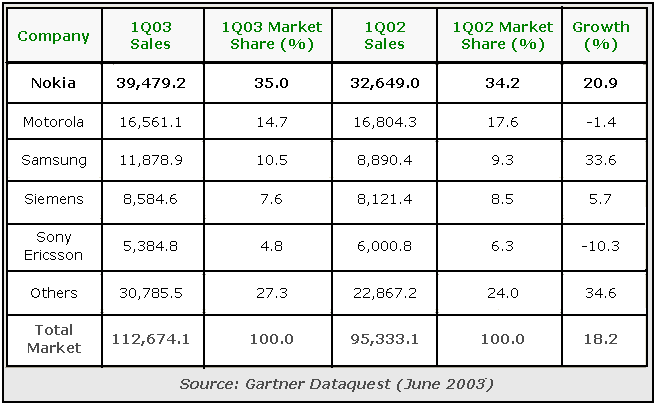
As it is the biggest organization in Finland, it occupies 1/3rd of OMX, Helsinki. Being the 5th top company in the world, it posses a $35.9 billion of brand valuation. The Annual report 2007 of Nokia Corporation shows that the corporate profits have been accounted to €7205 in 2007 with an EPS of 1.85%.
Socio- cultural factors
Its culture influences on quick and relax decision formulation on a plain, formulated network though it is characterized by huge bureaucracy. Officially, it uses English in speaking, documentation and the overall electronic communication. Value refinement has been occurred in 2007 may focused on employee offerings as a zest of involvement, achievement, innovative looks and human support. For this, a larger assistance has been provided for help in hearing, conversation tools and software for customers along with picking up 2500 employees of 16 regions for ultra valuation concerning on customers, group wins, communication, motivation and innovation2.
Technological factors
It is most important factor among other factors. Since 1960, it has been manufacturing military as well as commercial telecom technology. After, VHF- radio, ARP- phone, and Mobira Cityman 900 etc. has been innovated. Nokia conducted research with NAVTEQ and CalTrans for further innovation. Sensor technologies offer huge consciousness about the environment. Nokia mobiles are able to contact and control the household electronic instruments. Then, its Multi scanner reduces the uncertainty of language constraint; NFC procedure enables the user a simple touch workforce.
SWOT analysis of Nokia Corporation
Resources and capabilities
Resources
Typically, a company owns tangible and intangible resources which can be categorized into 6 parts according to the resource- based theory (Griffin W. Ricky, 2006, p-90). In this sense, Nokia’s several resources can be demonstrates as follows-
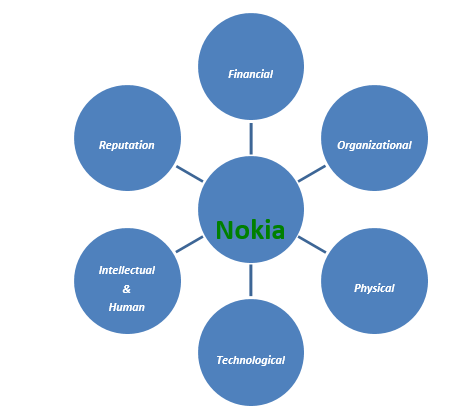
Those are as following
Financial resources
Annual Report 2007 of Nokia gives an idea about its financial resources. This company posses the international revenue of €51.5 billion and €8 billion of operating income during the last year. Nokia Corporation, Form 20-F (2007) indicates that it obtained net sales from Europe, Middle East and Africa, China, Asia- pacific, North- America and others during the year 2005, 2006 and 2007 as following-
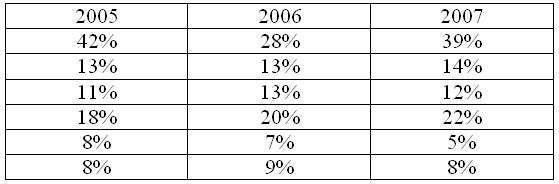
Similarly, Nokia Corporation and the subsidiaries had earned a net cash of €3058, €3525 and €6850 for the year 2005, 2006 and 2006 consequently.
Organizational resources
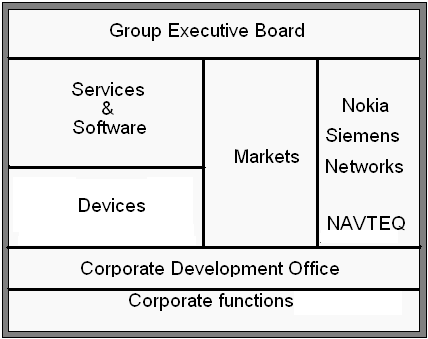
Regarding the corporate structure, the company composed 3 corporate groups namely devices, markets and services and software during 2008, January. April, 2007 has been resulted in the formation of a joint- venture with Siemens with a sole consolidation of Nokia. Device normally offers customer- oriented high volume cell phones on the basis of GSM, WCDMA, and CDMA system.
Physical resources
It involves the plants and equipments of €1912 including buildings and construction, production, measurement and testing machine and other equipment ranging from 1 to 33 years.
Technological resources
The breakthrough of GSM, introduction of NAVTEQ with CalTrans, Personalized Widgets, Mobile Journalism, Nokia 6210 Navigator tool, NFC technology, Multi scanner and finally the introduction of Ovi under the “umbrella concept” along with chipset, camera modules and modems etc. are several aspects of technological assets of Nokia.
Intellectual and human resources
The most efficient R & D sector holds numerous intellectuals for the research and manufacturing from a number of countries of the world. It occupies 30415 people from 10 countries for this constituting 27% of the total workforce including 800 researchers, scientists and engineers. Besides, 98% of its personnel are acquainted with codes of conduct, the financial and management team is contributing with greater intelligence for the vast expansion of it.
Reputation resources
Worldwide Nokia brand acquires the brand value of $35.9 billion being the top brand of Europe and Asia. A high value of IPR (Intellectual Property Rights), solutions of multi radio, technological diversifications etc.
Capabilities
Hitt A. Michael (2006) mentioned that a capability enables the company for creation and exploitation of opportunities for the development of sustainable advantages while a utilization of adroitness and insights. The flow of capabilities of the company can be shown as-
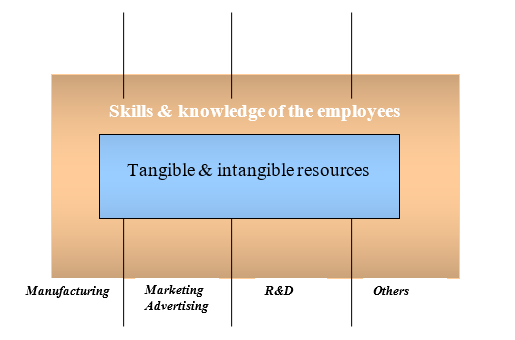
The core capabilities of the organization are based on developing, carrying and exchanging information and knowledge by the firm’s intellectual and human resources. Few examples are-
- Proof of connectivity in reaming internationally through taking part in GSM.
- Maintaining of stronger logistics through the larger economies of scale over the major competitors.
- Starting up of a new flagship store, introduction of Nokia N series and E series, introduction of e- marketing campaigns and reformulation of the pattern of distribution channels take a major role in marketing of the company.
- Core competency and effectiveness in manufacturing of cell phones.
- Highly automated technology at every plant.
- Association of strong R&D for generating highly technological, stylist and materialistic goods.
Generation of strategies
Strategic options are coordinated and interrelated set of actions that has been designed for exploiting the core capacities and competencies for achieving competitive advantage. According to the first diagram, Nokia can generate several strategic options through some systematic phases from business- level to co- operative strategy-
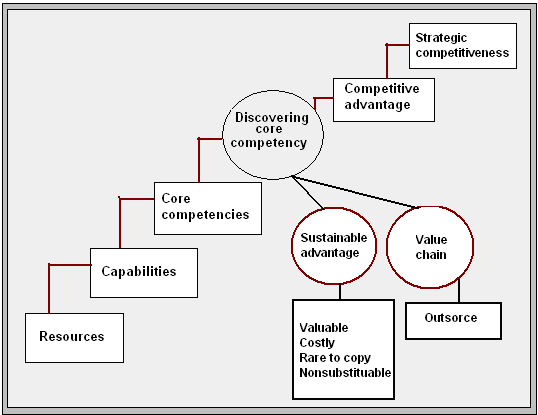
Thus, the entire stages of strategy formulation are as below:
Business- level strategy
It indicates Nokia’s industry position in relation with other rivals as it has been indicated as 88th biggest company in the world focusing on 10% growth rate annually. Thus, the company can generate Porter’s 5 forces view as its business- oriented strategy. Such as-
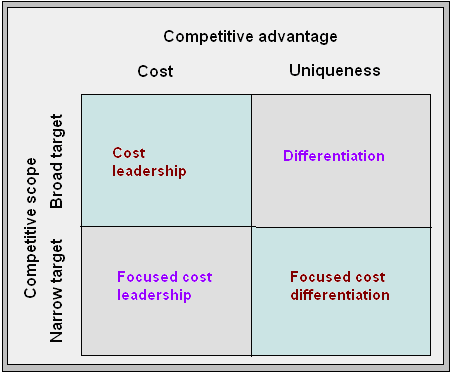
Under the cost leadership strategy, the company can deliver the highly sophisticated electronics home set and commercial cellular phones at lower costs relative to Samsung, Sony Ericsson, Motorola, Bird, Gionee, K- touch and other major competitors.
Differentiation strategy suggests to the selling of non- standardization of phones to match to the unique demand of the customers through the addition of portable computers, cameras, TV, games, TV, internet, e- mail and other digital convergence with the Nokia handsets. For developing Thus, besides customer satisfaction with connecting people, it is also possible to charge premium prices although there lay a number of influential factors like rivalry with competitors, buyers and suppliers bargaining power, substitutes, threats of entrants etc. The formulation of differentiation strategy can be exemplified as following-
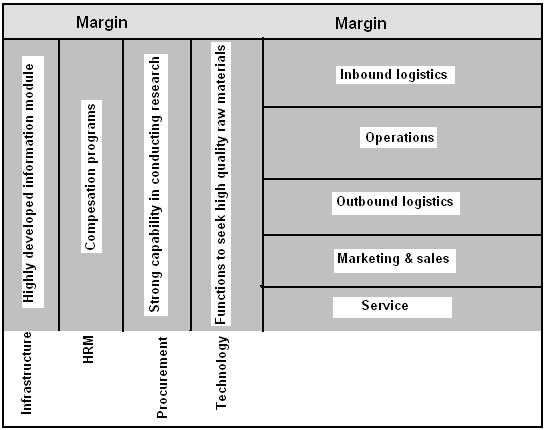
Service and software can be developed by Ad business, Intellisync E- mail, music store, maps etc with an additional emphasize on software “Ovi”, Nokia 6300 GSM device, 3110 Evolve, 6110 Navigator, 6500 classic, 5310 XpressMusic, 7900 and 7500 prism etc. for adding ultra value.
By introducing the focus strategy, Nokia would have to design its items for serving the needs and demand of particular segmented customers while it is characterized as the exploitation of the short- focused target differences from the equalization of the industry with centralized efficiency and effectiveness. Finally, the focused- differentiation concerns with highly differentiated goods along with above- average return.
Competitive dynamics
At this phase, Nokia can obtain competitive dynamics through a series of competitive actions as well as aggressive responding among the competing firms of the industry by analyzing market commonality, resource similarity, market dependency, own size, innovation, quality etc.
Corporate- level strategy
According to this concept, Nokia can emphasize on diversification from low to moderate to very high level while in low level it can earn 95% of total profit from telecommunication sector and 70% to 95% from the dominant business. Related level is ranged from less than 70% of all sources and the same from dominant and limited once while very few offers from only dominating part.
Acquisition and restructuring strategies
Through the acquisition strategy, Nokia can purchase controlling or 100% interest in other business with an intension of utilizing an effective core competency through converting that firm as its subsidiary. It can adopt such strategy to gain-
- Increase market power.
- Effective service in customer internet.
- Self- managed mobile organs.
- Formulation and share of photos, videos as well as customized media through the users’ mobiles ands desktops.
- Enthusiast plan, execute and optimize cell advertising campaigns.
- Acquire NAVTAQ which is the world’s leader in serving digital maps as well as public and corporate solution.
Additionally, through restructuring, Nokia will be able to sustain the fall in acquisition with others by changing the operating sets or financial structure. It can take many forms, like-
- Downsizing will reduce the worldwide employees and existing units by or by not changing the company’s portfolio.
- Downscoping tends to work- out or spin off some branches of business that are not related to the whole core competency.
- By LBO, privatization is occurred through the purchase of assets.
International strategy
As Nokia is operating in manufacturing and distributing the products in Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia- Pacific, China, North and Latin America, specific international strategy for being successful in each of those regions are required. Important considerations are-
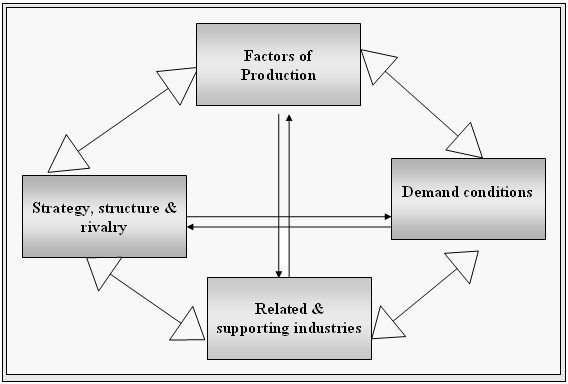
As the company’s sales are running on merely 150 countries with production of a large variety of products including GSM, CDMA, solutions, services and other amenities it must consider the use of above factors and should take different strategy each of the region. Developing international cost leadership strategy will enable it to gain the economies of scale with vast demand, like- third world countries as delivered by China Nokia.
By emphasizing on R&D and developing N- series, E- series, sub- brands through quality and competitive costs module, it can imply on differentiation globally. As corporate- level strategy, it can go for multi- domestic plan for decentralization of operations in a single country for tailoring products to local market. By global strategy, it can develop standardized products regardless competition and demand. By transitional strategy, it can go for global capacity and local responses.
Cooperative strategy
Nokia has a number of strategic options regarding this. As-
- By strategic alliances, it can formulate partnership with firms through a mutual interest of resources and capabilities from designing to distribution.
- By a joint venture, it can promote a new venture with other by combination of resources.
Appropriate choice of strategies
Among the huge number of proposed strategies, Nokia should choose the following-
- Its first and foremost strategy is to connect people globally at in improved means.
- Differentiation strategy for leading, growing and accelerating internet and business solutions for mobility solution, single devices, connectivity, protection, selling, service level and marketing.
- Increase in volume of device more than 90%, 80%, 75% and 80% in relevant regions than previous year.
- Increase in manufacturing capacity on broadest zone basis including India and China.
- Strengthen of customer logistics on the basis of 3 times model for 4 units of globe.
- Transformation of infrastructural solution.
- Competitive dynamics and global strategy by understanding consumers, brand development, supply chain and channels and technology.
- Specific concern on service, software and device.
- Acquisition of Intellisync, Lodueya, Twango, Enpocket and NAVTEQ.
- Outsourcing of mobile engine production amount involving hardware and software at more than 20%.
- Choosing of multi- domestic strategy by using worldwide supplier network evolving chipset, electrical parts, cameras, display, chargers of battery, antennas, microprocessor, key- mats etc.
- Future growth and integrated supportive management of corporate- level strategy.
- Joint venture of Nokia- Siemens network with Nokia consolidation, R&D and manufacturing.
- And finally, Collaborative strategy for research, authority and other organizations within the same industry.
Implementation of strategies
Implementation of the above strategies is run by the following parties-
Corporate governance
It indicates the co-relation of stakeholders for determining the control and directive performance of Nokia formatted on Finnish Companies Act that is responsible for carrying out strategies by some sequential stages. As-
Board of directors
This group is responsible conforming guidelines, previous plan approval and investment as well as divestment strategies. Hence, the corporate, audit, personnel committee, governance and nomination committee conducts the operations and self- evaluation for refining the strategies.
Group Executive Board: Operational management of Nokia is its main task.
Compensation
It should be designed for attracting and deriving the talent human resource for successful strategic implementation that focuses on base rate of pay, competitive compensation package over time, balance of gifts etc. Personnel committee is important for using outsider consultant for tracking market trends, CRM, evaluation of strategic direction etc.
Organizational structure and control
Organizational structure of Nokia consists of configuration, process, governance and control for implementing strategies as-
Since, Nokia is largely differentiation oriented, it should use the functional structure of consensus decision making among the top –management team as shown below-
Creation of marketing of sub- branding campaign for Nokia N95, N81, E65, flagship store, digital campaign and 8 step programs. Production through different raw materials supplier of the world, technological platforms and outsider suppliers oriented R&D, and increase in structural finance in €566 millions is some key issues.
Finally, Nokia can implement the multi- domestic strategy by the following diagram-
Corporate entrepreneurship and innovation
It refers to the formation of committed employees, effective organizational culture involving on- line participation of employees in decision making and balanced control. Ethics is also important by maintaining the sustainable development by the garbage of toxic elements, recycling, less influential negativity of climate rather than the giant electronic agents. In this regard, it can introduce new concept of cell phones aluminum, plastic and tire of cars.
Feasibility of conclusion
After the above discussion, it can be identified that Nokia can take upon an effective strategic program through the consideration of corporate resources along with several capabilities to gain competitive marketplace and to remain the telecommunication in the global marketplace. Having a huge facility of talent and committed workforce, renowned personnel in corporate governance and R&D, physical and instrumental accessibility, partnership in effective fields, successful acquisition, hybrid networking, huge demand and the most important strategic focus of the desire of connecting people globally make the company as an efficient player of maintaining competent strategy although the company should be conscious in some aspects for sharpening its strategic motives.
Recommendation
To become more effective in operation, Nokia should concentrate on-
- Formation of products, services and solutions portfolio on the basis of competitive operations appearing as balanced offerings of design, aesthetic image and value- recognition.
- Focus on mass customization, functions and co- branding with other companies.
- Consideration of adverse economic circumstances for which the global profitability may reduce.
- Strong and conscious maintenance of brand name to sustain and expand current market share and operation.
- In case of slow expansion of world’s total subscriber, replacement of sales of current devices through the demand impulsive services should be introduced.
- Ability to cope with the changing telecommunication world by sustaining quality, demand and effort to protect the segment sales and profitability.
- Continuous investment in the infrastructure of network equipment.
- Avoidance of acquiring higher valuable firm rather than Nokia.
- Cost management is mostly important to protect price erosion by analyzing the future pricing graphics of the company through the introduction of cost- saving devices.
- Careful response in the telescope of competition associated with the fixed and new telecommunication operators along with related products manufacturer.
- Acquisition and commercialization of critical technologies.
- Avoidance of procedure that may cause high license costs, product limitation and extra litigation.
- Consciousness about the deterioration of intangible assets rights and the hyper technologies.
- Efficient and effective execution of logistics for ensuring customer’s safety, trust and value.
- Wide expansion of suppliers.
- Concern on economic, political and legal constraints of manufacturing countries.
- Fluctuation among euro, US dollar, yen and related currencies.
- Proper implementation of the recent organizational structure
Conclusion
Thus the entire strategic analysis of Nokia, addressing real life problems and issues has focused on the company’s recent position in the global market, its major competitors, several strengths and weaknesses along with opportunities and threats etc. Regarding its electronics appliances product line from a number of other products and services, it has been identified that Nokia’s main goals and objectives are to maximize profit through the electronics items by improving the sales, promotion, advertisement, brand development by using overall marketing mix elements. The specific strategies that are suggested will be applied to achieve those goals, it can be predicted that the company will be ever successful in strategic management issues with long run customer satisfaction. Thus, through the creation of proper planning, implementation and become cautious of some fundamental issues, Nokia can be recognized as the better adopter of strategic functions.
Reference
Griffin W. Ricky, Management, and 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company: New York, ISBN: 0 618-35459x, 2006.
Hitt A. Michael, Ireland. R. Duane and Hoskisson. Robert E., Strategic Management Concepts, 7th edition, South-Western College, ISBN: 978-0324405361, 2006.
Hitt A. Michael, Ireland. R. Duane and Hoskisson. Robert E., Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization, Concepts and Cases, 7th edition, South-Western College, ISBN: 0324655592, 2008.
Nokia Corporation, United States Securities and Exchange Commission, Form 20-F, 2007. Web.
Nokia Corporation, Review by the Board of Directors and Nokia Annual Accounts 2007. Web.
Stoner A.F. James, Freeman R. Edward., and Gilbert D. R. Management, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2, 2006
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.