Executive Summary
This marketing plan has been developed to enable Penguin Random House Publishers to sell its new children’s books. The marketing plan is expected to help the company to increase its sales and brand awareness by at least 5% annually. Achieving this target is a challenge because the market is characterized by high competition and infringement of intellectual property rights.
The opportunities that the company can benefit from include increased penetration of the internet, which boosts the demand for e-books. Moreover, the rapid increase in economic growth in emerging economies is expected to support demand. In this respect, the company will position its books as superior products to take advantage of the available opportunities and overcome competition.
The Challenge
The aim of the marketing plan is to help Penguin Random House to market its new children’s books in the US and foreign markets. The books are designed to help children in the age bracket of 4 to 8 years to learn how to read on their own. One of the unique features of the books is that illustrative pictures and text have been used to tell compelling stories.
The strategic goal of the marketing plan is to position the company as the best publisher of children’s books. In this respect, the specific goals/ objectives of the marketing plan include the following. The first objective is to increase sales by 10% in the next 2 years. The second objective is to increase market share by 5% in the next 2 years. The last objective is to increase brand awareness by 10% in the next 2 years.
Situation Analysis
Company Analysis
Penguin Random House aspires to be the leading publisher of children’s books in the world (Penguin Random House). Thus, the company focuses on publishing a variety of fiction and nonfiction children’s books. The company has a market-oriented culture that emphasizes the need to publish high quality content at a good profit margin. This culture helps the company to respond effectively to changing market needs by focusing on innovation to improve the quality of its books.
The main strength of the company is its ability to collaborate with a large number of renowned authors to access high quality content. The company also has a global distribution network that enables it to reach a large customer base. The main weakness of the company is that it focuses on selling print rather than e-books. This exposes it to high competition from sellers of e-books. Currently, the company controls 23% of the global children’s book market (Penguin Random House).
Customer Analysis
The target market has approximately 550 million children who live in nearly 110 million households worldwide (Smithers 2-45). The market consists of discount customers, impulse customers, and need-based customers. Discount customers are interested in cheap but high quality children’s books. Impulse customers include parents who purchase children’s books whenever they find interesting ones. Need-based customers are the most important since they actively seek for high quality books to help their children to read.
The main value drivers in the market are the quality of the content of the books and the ease of reading them. These features determine customers’ decisions concerning the books that they buy for their children.
The purchase decision is often made by parents and teachers. The decision process is simple and involves typical activities such as need recognition, information search, and evaluating the suitability of the available books. The customer base concentration is moderate in most markets. However, the middle-income earners account for the largest percentage of sales (56%) worldwide (Smithers 2-45).
Competitor Analysis
The main competitors of Penguin Random House include Simon-Schuster Children’s Publishing, Little Brown Books, MacMillan Children’s Books, and Scholastic. These companies have a combined market share of approximately 55% (Smithers 2-45). The main strength of these companies is that they are able to sell their books at a low price to gain market share.
However, some of the competitors such as Scholastic and Simon-Schuster have not been able to collaborate with leading authors to publish a variety of high quality books. Moreover, MacMillan’s books are often suitable for teenagers rather than kids who are below 8 years.
Collaborators
Penguin Random House has nearly 50 subsidiaries in various parts of the world. The subsidiaries are responsible for distributing the company’s books. Before 2013, Penguin Group and Random House were owned by different parent companies. However, they formed a joint venture that made them the largest publishing house in the market.
This means that forming joint ventures is one of the main strategies being used by the company to expand its market share. The company also collaborates with several independent distributors to sell its books. These include retailers such as Amazon.com, eBay, and Wal-Mart. Collaborating with independent distributors enables the company to reach customers in markets where it does not have sales offices.
Climate: PEST Analysis
Free primary education in various countries is the main political factor that boosts the sales of the company’s books. Virtually every country is interested in achieving 100% literacy rate. Thus, most governments provide incentives to promote access to learning materials. This includes financing the purchase of children’s books that are used in schools.
Exchange rate and GDP growth rate are the main economic factors that influence the company’s sales. Since Penguin Random House exports its books from the US, an appreciation of the dollar makes its products more expensive in foreign markets and vice versa. Generally, the demand for children’s books is high in countries with high GDP per capita such as the US and Germany (GBO 1-6). However, the demand is very low in Sub-Sahara Africa where household incomes are low.
Population growth and the desire to acquire high quality education are the main social factors that influence the demand for children’s books. In developing countries, the demand for children’s books is supported by the rapid population growth. However, in developed countries the demand is boosted by the desire to access the best literacy skills in childhood.
Technology influences the ease of distributing books. Companies with online sales platforms are able to reach more customers than those that depend on retail stores (Milliot 23). Moreover, companies that publish their books in both print and electronic formats are able to increase their sales. However, increased use of the internet has also led to unauthorized access to publishers’ books in countries where intellectual property rights are not protected effectively by the law.
SWOT Analysis
The main strength of Penguin Random House is its large market share, which enables it to record high profits. Moreover, the company enjoys economies of scale in production and distribution. This allows it to reduce operating costs in order to increase sales by reducing prices.
The main weakness of the company is that it focuses on online marketing rather than selling its books in electronic format. As a result, the company will not be able to outperform its competitors that have focused on electronic publishing (Milliot 23).
The increased penetration of the internet and computers in the world is an opportunity to the company to increase its sales by serving the children’s e-book market. Furthermore, the rapid economic growth in developing countries such as India and South Africa is an opportunity to the company to increase its sales.
High competition is the main threat in the industry. Companies such as Amazon.com have obtained licenses from authors to distribute their content in digital format, thereby increasing competition. Access to high quality content is also a serious threat to the company’s competitiveness because of the limited availability of talented authors.
Market Segmentation
Segment 1: Children Aged 4-5 Years
The first market segment consists of parents with four and five year old kids. Children in this age bracket are transitioning from using learning materials that are dominated with pictures to those that have text. Thus, customers in this segment want books that motivate children to read.
Parents and teachers use the books by reading them along with the children. This helps children to acquire reading skills by imitating their parents or teachers. The use of illustrative pictures is the main support required to improve the effectiveness of the books used by children who have less than years.
The customers can be reached through advertising in print and electronic media. Price sensitivity among customers in this segment tends to be high in developing countries such as Nigeria where early childhood education is not prioritized. However, price sensitivity is low in North America and Europe where incomes are high and parents value early childhood education. Overall, this market segment accounts for approximately 15% of the total sales in the market (Smithers 2-45).
Segment 2: Children Aged 6-8 Years
The second segment consists of parents whose children are in the age bracket of six to eight years. This segment also includes schools in countries where formal education begins at the age of six years. In this segment, parents and teachers want books that enable children to acquire advanced reading skills. Thus, the books are used to enhance the children’s capacity to read independently. The support required in this segment is audio-visual aids such as videos to help children to comprehend the content of the books.
The customers can be reached through direct selling and advertising. Generally, price sensitivity tends to be high in emerging economies. Overall, this segment accounts for approximately 20% of the sales in the market (Smithers 2-45).
Alternative Marketing Strategies
The marketing strategies that are available to the company include discounting, rebranding, and positioning the books as premium products. Discounting involves selling the books at a reduced price to increase sales. This strategy is likely to increase the company’s market share (Kazmi 45). However, it is likely to reduce the company’s profit margins.
Rebranding is the process of creating “a new look and feel for an established product in order to differentiate it from its competitors” (Ranchord and Marandi 63). Rebranding strategies include changing the packaging or name of a product to make it attractive to customers.
Rebranding will enable Penguin Random House to create a strong brand image. However, rebranding is not likely to be effective since the company is launching a new product. In this case, the branding strategy should portray the books as new rather than rebranded products.
Positioning the books as premium products will involve emphasizing their superior qualities through promotional strategies such as advertising. The disadvantage of this strategy is that premium products are often associated with high prices. Thus, customers might avoid the books if they believe that they are expensive (Kazmi 96). However, the strategy will enable the company to create the perception that it is the only publisher of high quality children’s books in the market. The resulting increase in customer loyalty will improve the company’s profits (Kazmi 53).
Selected Marketing Strategy
The company will use the premium positioning strategy to sell the books. The strategy will enable the company to focus on differentiation to satisfy market needs (Cordy 35-44). Moreover, the strategy will allow the company to charge premium prices, thereby avoiding price-based competition. Consequently, the company will enjoy high profit margins (Ranchord and Marandi 79).
Product
The brand name will be penguin easy reader. Penguin is already a well established brand in the market. Thus, using the word penguin will enhance brand identity. The main feature of the books is their high quality content that promotes reading. The books have interesting stories, which create the desire to read. This quality will be leveraged by providing a video version of the books. The videos will motivate children to read the books to learn more about their favorite characters (Kazmi 78).
Thus, the scope of the product line will include movies and video games that are based on the stories in the books. The packaging strategy will focus on improving the attractiveness of the books. Specifically, each book’s cover page will have colored images of the key characters in the stories to attract children’s attention. Moreover, customers will be able to choose between hardback and paperback books.
Price
The company will adopt a value based pricing strategy to sell the books. The products will be sold as a single bundle that includes the books, video games, and movies. However, customers will also be allowed to buy the items separately. The bundling strategy will benefit customers by allowing them to access different versions of the books at a favorable price. The recommended retail price for the bundle is $50.
The cash-on-delivery payment method will be used to sell the books to individual customers. However, corporate buyers will be allowed to purchase the books on credit. Financing will be arranged in conjunction with select commercial banks that will provide short-term loans to the buyers. Discounts of up to 5% will be available only to corporate buyers who are able to make purchases worth at least $50,000.
Distribution
The selected distribution channels include direct sales, retail stores, online stores, and independent distributors. The distributers will be evaluated based on their market coverage. The company will collaborate with distributors whose premises are located in strategic places such as popular shopping malls in urban areas. Using a variety of distribution channels will enable the company to reach a large number of customers (Ranchord and Marandi 85).
The distributors will enjoy a profit margin of 5% per book to motivate them to increase sales. Similarly, the company’s sales team will earn a commission of 1.5% of gross sales as shown in exhibit 5. The commission is expected to motivate the sales executives to meet their annual sales targets.
The company will be responsible for fulfilling orders, whereas its supply chain partners will provide transportation and warehousing services. Outsourcing transportation and warehousing services will enable the company to reduce the cost of distributing the books.
Promotion
The company will advertise the books in magazines and newspapers with nationwide circulation. The adverts will also be posted on popular TV and radio channels, as well as, social media websites such as Facebook and Google+. The advertising campaigns will run for five months every year.
Public relations activities such as press release and media interviews will be used to influence customers to develop a positive attitude towards the books. The company will also implement two promotional programs that will involve rewarding customers with a penguin-branded gift such as a toy for every three books purchased.
This strategy is expected to promote bulk purchases and strengthen brand identity. Overall, the promotional programs are expected to increase sales and brand awareness by at least 5% annually. Exhibit 6 (budget) shows that the company will require $765.1 million to implement the promotional activities in three years. The breakeven analysis in exhibit 7 shows that the company will have to sell at least 5,622,586 units in order to recover the cost of the promotional activities.
Short-term and Long-term Projections
The immediate effect of the selected strategy (premium positioning) will be a significant increase in marketing expenses. The increase is attributed to the fact that the company has to invest a lot of funds in promotional activities in the first year to inform the public about the quality of its books. In the long-term, the marketing expenses will be recovered as sales increase.
Exhibit 1 shows that the company will realize $1,200 million in revenues in the first year. According to exhibit 3, the company’s market share will be 24% if it achieves $1,200 million in sales in the first year. The revenue is expected to increase by at least 5% annually in the subsequent 2 years. The company expects a net profit of only $22.9 million in the first year. However, the net profit is expected to increase to $74.75 million in the third year as operating costs reduce.
According to exhibit 4, the pretax profit margin in the first year will be 2.9%, whereas the net profit margin will be 1.9%. However, the pretax profit margin and the net profit margin will increase to 8.69% and 5.65% respectively in the third year. The breakeven analysis in exhibit 2 shows that the company will have to sell at least 15,970,000 books in order to breakeven in the first year.
Conclusion
Penguin Random House intends to launch a new set of children’s books that target kids in the age bracket of 4 to 8 years. The books have high quality content that will enable children to learn how to read easily. The main threats in the market include high competition and infringement of intellectual property rights.
The opportunities in the market include increased penetration of the internet, which boosts the demand for e-books. In addition, the rapid increase in population and economic growth is expected to support demand in emerging economies. In order to take advantage of these opportunities the company will position its books as premium products.
Appendix
Exhibit 1: Revenue Forecasts
Projected Profit and Loss Account for the First Three Years
Exhibit 2: Breakeven Analysis
Since retail prices vary from region to region, breakeven analysis is based on the wholesale price of $45 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $15 and the fixed cost in the first year is $479,100,000. Based on this information breakeven can be calculated as:
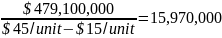 units
unitsExhibit 3: Market Share
In 2013, the industry reported USD 3.5 billion in sales. The sales are expected to reach USD 5 billion by the end of 2015. Penguin Random House expects to realize USD 1.2 billion in sales in 2015 (first year). Thus, its market share can be calculated as:
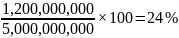
Exhibit 4: Profit Margins
Exhibit 5: Sales Commission
The sales commission paid to employees will be 1.5% of the gross sales. Thus, the commissions to paid are:
Exhibit 6: Budget for Promotional Activities
Exhibit 7: Breakeven Point for Marketing
The selling price per unit is $45 and the variable per unit cost of the promotional activities is $16. The fixed cost of the promotional activities in the first year is $163,055,000. However, the fixed cost will increase to $164,333,343 and $167,620,000 in the second and third year respectively. Thus, the breakeven point or the number of units needed to recover the cost of the promotional activities is calculated as:
First year
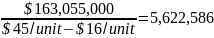 units
unitsSecond year
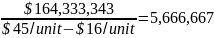 units
unitsThird year
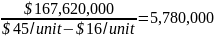 units
unitsWorks Cited
Cordy, Dawn. “Marketing to Children and Mums through Children’s Magazines.” Young Consumers 5.1(2003): 35-44. Print.
GBO. The US Book Market, New York: German Book Office, 2013. Print.
Kazmi, Sayed. Marketing Management, London: Sage, 2007. Print.
Milliot, Jim. “BEA 2014: Can Anyone Compete with Amazon?” Publishers Weekly 2014: 23. PW Archives.
Penguin Random House. About Us. 2014.
Ranchord, Anthony and Edward Marandi. Strategic Marketing in Practice, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005. Print.
Smithers. Global Printing Market to Top $980 billion by 2018, Surrey: Smithers Pira, 2014. Print.