Introduction
The aim of this strategic plan of Proctor & Gamble is to analyze the strategic corporate development history, strategic direction for the future, and the current strategic situation of the company. However, this paper will concentrate on the historical background and strategic decision for the last twenty-five years, present economic condition, resources and capabilities, organizational structure, competitive environment, and so on.
Recent past
Proctor and Gamble is a USA based multinational company that produces a large number of consumer products. The company started its operation in 1837, October. From the time of its birth to the last 25 years, the company has been well- recognized for implementing several development strategies especially by concentrating on corporate restructuring, innovativeness, uniqueness, and adequate market research (Grant, 2010).
In the year 1989, P&G initiated a basic change in corporate structure. It developed an international product formation strategy in which per product group was led by a president who directly accounted for the CEO. The local HR was assigned financial, research and development, human and other career-related responsibilities. This global restructuring program style was enlarged within the field of production, procurement, and distribution as a single supply network through an incorporation of international product- supply activity. In 1994, the company adopted another strategy for reorganizing the sales into CBD (Customer Business Development) function to develop closer customer relationships (Grant, 2010).
P & G always had the thrust of innovation although the innovative intensity varied from time to time. For example, in 1982, it introduced feminine- hygiene products and in 1978, Pampers for the French market through the same product was offered in the UK in 1981. In 1990, the company’s major strategic orientation was focused through its corporate divisional model. Then, the operational strategy involved 8 major distinct units regarding supply, HR, legal, external relations finance, control, R and D and IT. The CEO was directly responsible for the global operation that was also divided into 4 major parts and integrated with various product units of North and Latin America, Europe and Asia (Grant, 2010).
After the initial formulation of global strategy, P & G made some changes. Instead of accompanying profit- and- loss responsibility with each of the operating region over the world, the company shifted such responsibility just on the workforces of developed nations. That means, only the rising part of South- East Asia, Eastern Europe, and China gained that accountability. This strategic change was occurred up to 1999 to 2000 (Grant, 2010).
From 2000, P & G had been practicing innovation in each part of its operation along with production. For example, from that period, the company had been implementing innovation in terms of customer prioritization, scale leveraging, resource utilization, acceleration of talent leadership and integrative thinking, etc. (Lafley, 2008).
Offering local brands a global image was also a part of P & G’s strategy. In 2000, it decided to rename its well- known Fairy laundry detergent brand as Dawn for the German market. Although the company did not alter any ingredient of this product, its German market share reduced severely for such a strategy (Grant, 2010).
Organization 2005 was one of the most exclusive strategies designed by P & G. This initiative involved various processes for sophisticated innovation, the closing of factories, alteration in motivational plans and cultural patterns developed for creating the organization more risk-oriented and liable. Additionally, the company planned to increase new product development rate along with compressing speed. This strategy also incorporated changes in organizational structure mainly in terms of the development of GBUs (Global Business Units). These units were developed for performing international product development, production, and marketing. Regional units were divided into 7 major subdivisions for the domestic application of international strategies.
Another GBU was responsible for performing functional activities. Such new forms of GBUs were designed to bear with profit- and- loss concern by encompassing overall corporate responsibilities rather than simple handling of product development. This decision of the company reflected a strategic focus on efficiency enhancement, more cross- border incorporation, a standardized production system, simplified brand assortments, and adjusting marketing tasks, etc. Another strategy was formed for lessening bureaucracy as well as enhancing responsibility by cutting the number of hierarchical phases between line management and CEO. For this, P & G enhanced the number of mid-management having decision- making power so that the company would make speedy decisions that would be implemented within a shorter period (Grant, 2010).
One of the most notable aspects of P & G’s product development strategies were less global standardization. Since for many kinds of household goods, cosmetics, and food items, customer needs and preferences vary across nations or within nations, P & G deeply considered this factor in mind while designing its product lines. Moreover, the company also undertook different strategies for the formation and operation of its multiple distribution networks located at multiple regions in terms of sizing of offers, packaging, sales, and marketing (Grant, 2010).
P & G adopted an acquisition strategy to diversify itself along with earning profits. In 2005, it took the ownership of Gillette for becoming the market leader of consumer products. It also added several brands, like- Duracell, razors, Oral- B and Braun, etc. for succeeding such acquisition (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
In 2007, the company adopted 5 strategies under its sustainability concern. That are-
- Product strategy: – P & G adopted to produce and sell a minimum of $50 billion of sustainable innovative products (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
- Operational strategy: – Here, it undertook an environmental sustainability program throughout its operations to lessen 20% of CO2 emissions, water, and energy utilization and waste removal from corporate factories (Annual Report, 2010).
- Social responsibility strategy: – Here, the company decided to advance children’s lives through the prevention of 160 million days of diseases while protecting 20000 lives with the supply of clean water (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
- Employee strategy: – P & G remained highly enthusiastic for training and motivating innovative workforces involved in sustainability practices over their daily tasks. Sourcing of mid-career hire was also a common strategy of this company (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
- Shareholder strategy: – It involved the utilization of renewable resources in production and other sustainable measures for the corporate investors (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
In 2009, P & G updated its growth strategy by enlarging concern on innovation for manufacturing, satisfying the known- served and underserved customers and establishing global leadership as a high margin growth and entity (Annual Report, 2010).
Current Strategic Situation
At a singular form, P & G implements the overarching growth strategy as “Touching and improving lives of more consumers, in more parts of the world, more completely”. Such a single strategy is the strengthened, modified, or restructured form of most of its previous strategic moves. Such as-
Organizational structure
The updated structure of P & G acts as a means of corporate growth. It is designed by considering both global and local visions of the company (Procter & Gamble, 2011). Such as-
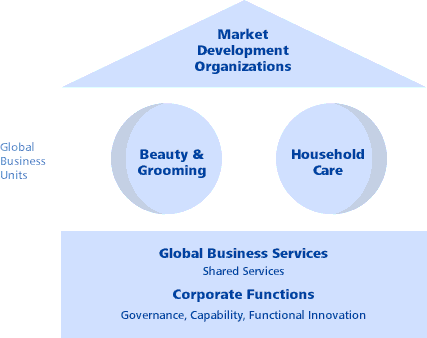
Under GBU’s strategy, it pays attention to global customers, competitors, and brands that act as the media of intended innovation, profitability, and return on investment. Under MDOs (Market Development Organization), it focuses on understanding customers and retailers at each operating arena through the cooperation of innovative flows from GBUs into a nationwide venture plan. Finally, Under the GBS strategy, the company concentrates on using its efficient and skilled HR for delivering their best performances to maintain scale economies as a major way to gain competitive advantage (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
Resources
The company possesses a highly Intellectual team human resources; as per the annual report of the company, the research and development team (which has enriched with scientists, chemists, and so on) of P&G are responsible for the technical improvement of such a wide range of product line of the company. This global giant affords a high brand value, which tends to expand continuously in the future, particularly in far western and emerging markets by continuous improvement of its recognition; this reputation is the outcome of consumer preferences on quality, trust, and ethical factors in its practices – as a consequent effect, in 2010, P&G generated a goodwill of $54,012. Conversely, this MNC has a strong financial position, which tended to decline during the recession. However, from the very beginning of 2010, the business has made a significant recovery in its financial resources as shown in the table below:
Table 1: Financial resources of P&G. Source: Self-generated from P&G (2010).
Capabilities
P&G has a highly efficient perception of the market that concentrates merely on customers as a market-oriented business, which wants to stimulate compassion that sequentially heads towards enormous innovations compelling growth; moreover, it successfully touches the hearts of billions of people and enhance lives by motivating peak-performance – this, according to P&G, is its core capability. To boost growth the business tries to enhance communication by operating as one company; to do this, P&G highlights on specific segments, brands, nations, and purposes decisively and considers that each has exclusive values to add; also, it can run at economies of scale by apportioning resources more purposefully and competently than any competitors.
Serving more customers
At present, P & G is focusing on serving more customers by implementing continuous innovation and expansion of the brand portfolio through upper, vertical, or downward value integration. Along with performance development, the company adopts an alternative low price strategy through which the price-sensitive customers can get better value at lower costs (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
More global expansion
P & G is serving its multiple products in about 300 countries by undergoing continuous product improvement, adjustment, or simple introduction. As a global expansion strategy, the company is targeting developing markets for generating more sales by creating brand affordability, consciousness, and convenience (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
Branding strategy
Regarding the global branding strategy, P&G utilizes various options as a line extension, brand extension, or multi- branding. For this purpose, some sub-strategies are also undertaken, like- scale economies and costs minimization in the production of new or modified products (Kotler and Armstrong, 2006).
Progress measurement
For measuring projected success with attained results, P & G follows a technique by integrating its consumer and monetary goals. Additionally, the company prioritizes beneficial share growth (Procter & Gamble, 2011). Other important factors are-
- Calculation of rate of international penetration per house.
- Calculation of net sales growth regardless of the effects of per year taking over, foreign trade and divestitures.
- Calculation of net EPS.
- Growth of adjusted free cash flow.
Innovation
Innovation is the first and foremost strategic bone for P & G forever. Currently, it has invested about $2 billion, which is almost 50% above than its closest national and international rivals. The innovation wing of the company is associated with a core corporate structure and acts as a strategic path of achieving goals (Lafley, 2008). Apart from these, it has been practicing innovation for the development of its various brands, as-
- Horizontal and vertical expansion of male grooming brands.
- Introduction of second wave in toothpaste or oral care brand.
- Coverage of Western Europe by Pampers Dry Max.
- Ingredient variation in Pantene.
- Aggressive move for combining goods innovation and global expansion tasks of Ambi Pur with Febreze contract.
Investment
The investment strategy is closely linked with higher growth in terms, which is fuelled by attaining economies of scale in production and improved production capability of P & G. As it is highly disciplined in cost-cutting and cash management, this trend has become a strategic orientation today under which the company simplifies the routine tasks for enhancing productivity. According to David (2008), this is crucial for a company.
Simplification also entails various criteria, involving color, label, packaging and so on. Such a simplification strategy is developed for implementing throughout the company led by lower management and controlled in a similar way as for global brands. Digitization is another component of the productivity strategy of P & G. At this point, the company standardizes, coordinates, and automates procedures as well as information for developing real-time functional and decision- making situations.
Under the logistics strategy, P & G digitizes its transport management technique, which is termed as “Control Tower”. This technique is useful for synchronizing the schedule and rounding of trucks for the entire outbound and inbound vehicle. As a result, it is possible to reduce multiple vacant truck deliveries at the rate of above 15%. It also owns control tower systems that can cover approximately 25% of its operation is not only developed but also developing industries (Procter & Gamble, 2011).
Leverage of scale
P & G’s competitive analysis encompasses various results regarding profit margin, market share, and several patent issues but overlooks some of the simple and smooth strategies, which drive P & G’s superiority. One of such simple but powerful strategies is its process of leveraging scale as it affects each task of the company (EMM Group, 2011). Various divisions of this strategy are-
- Scale leveraging for retailing: P & G has an investment of over $10 million to develop an efficient distribution network to become a low- cost supplier, introduce innovative supply idea and finally market its benefits to the retailers with the help of advanced software tools (EMM Group, 2011). Another customer-oriented retail strategic moves are-
- Explanation based consumer research.
- Multidimensional consumer research and software integration.
- Arrangement of theme events for strengthening retailer image to the buyers.
- Utilization of organizational- funded project: Many competitors including Nestle or Unilever entail nations, zones, or brands for taking the monetary liability of expensive projects. However, P & G wishes to do this by organizational top-down programs so that such tasks would be completed quickly (VSA Partners, 2010).
- Customer partnerships: The Company focuses on high- value buyer partnerships throughout its target marketing process. It is gathering names and forming programs for catching crucial scope of market entry while two points are significant as profit potentiality and long-run targets for considering relationship marketing (EMM Group, 2011).
- Defeating inertia: P & G uses 5 strategies through which scale can be used to defeat bureaucratic inactivity (EMM Group, 2011). Such as-
- Implementation of marketing- based inertia- broken IT support that speeds up the corporate sales and marketing.
- Integration of marketing techniques in software in better ways than industry competitors. This system also enables the domestic managers to realize the internationally important issue along with the identification of local significance.
- Local learning but global acting is another most crucial strategy undertaken by P & G. Although it lacks equal industry position, experience, or global heritage of Nestle or Unilever, it is fully entrusted to think and do globally. It never feels itself as an American entity, rather than develops its corporate culture in such a way that it can overlook the ego and prioritize host country culture.
- Management around multi-operational groups on a locality basis can communicate with their partners of other locality for quickly recognizing and solving their problems with faster growth.
- Development of partnerships for controlling vendors. Along with the traditional leveraging of scaling through purchasing of raw materials and media, P & G is recently leveraging vendor’s capacities in terms of building exclusive partnerships, for example, BASF.
Strategic Direction for the future
Clarification of Scale: Each criterion would explain and give a score between 1 and 5, where 1 indicates extremely unfavorable, and 5 being greatly favorable.
Direction 1: Develop an IMC campaign
The marketer of P&G should focus on the marketing strategy of the competitors of the local and international markets to sustain in the market as a market leader. The aim of the research team of this company should find out the problems of the customers to use the competitors’ products, market trends, and target groups, customers’ attitudes towards the new features of the offered products, market size, and the demand for the particular products. However, the management should carry out an integrated marketing communication program to develop public awareness regarding the products of other multinationals to give a broad idea about the ethical value of the brand. In this stage, the marketer of P&G would get the opportunity to aware of the target customers regarding the above information and to compare the products of the company with the competitors’ similar products and services.
Direction 2: Reformation of the Pricing Strategy:
The top management of P&G should conduct in-depth research on the market trends, peripheral surroundings of the industry, the effect of global economic downturn, demand patterns, competition and consumer behavior to reorganize its pricing strategy. Nevertheless, although the company possesses extensive knowledge to run business in the domestic and global market as a foremost competitor, but it can lose its wonderful market position because of advanced rivalry and price war from the UK companies. Consequently, reformatting pricing policy is one of the most indispensable measures to maintain its position in the competitive market while the competitors set price considering consumers’ buying capacity.
Direction 3: Joint Venture and Acquisition strategy
P&G can attain competitive advantages by joint venturing with other competitors or retailers in the market to allocate their competencies and expand the business more proficiently across the world.
Direction 4: Combination of Direction 1 and Direction 2
Recommendation
It is important to recommend that Direction 4 is the finest resolution considering the evaluation criteria of the decision-making process, which would help P&G to create brand awareness in the home market as well as in the emerging BRIC economies and other countries. Direction 4 considers how an effective pricing strategy can increase the affordability of the customers and enhance the market share of the business increasing the sales and customer base by promoting the products most appropriately through the IMC campaign to capture a larger portion of the global market by lowering the demand of the competitors’ products. As a consequent effect, a combination of the pricing strategy with the IMC campaign that P&G would carry out should be the most appropriate strategy to recommend to gaining a further stronger market position and establishing the company as a market leader in the global industry.
Reference List
Annual Report (2010) Letter to Shareholders. Web.
David, F. (2008) Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. 12th ed. London: Prentice Hall.
EMM Group (2011) How P&G Leverages Its Scale- In Ways Competitors Don’t Fully Appreciate. Web.
Grant, R. M, (2010) Contemporary Strategy Analysis, and Cases: Text and Cases. 7th ed. London: Wiley, John & Sons.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
Johansson, J. K. (2008) Global Marketing. 4th ed. New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company Limited.
Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 8th ed. London: FT Prentrice Hall.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G. (2006) Principles of Marketing. 11th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2006) Marketing Management. 11th ed. Prentice Hall.
Lafley. A.G. (2008) P&G’s Innovation Culture.
Miller, A. (1998) Strategic Management. 3rd ed. Boston: Irwin McGraw- Hill.
Procter & Gamble (2011) Company Strategy. Web.
Procter & Gamble (2011) Corporate Structure. Web.
Procter & Gamble (2011) Strategy, Goals & Progress. Web.
Rau, A. (2008) Proctor & Gamble & the devil. Web.
VSA Partners (2010) Strategy Meets Storytelling on P&G Annual Report Site. Web.