Introduction
One of the largest top Saudi listed stock businesses with a global presence, Saudi Aramco (SA), will be the subject of a brief strategic assessment in this essay. Through the use of a PESTLE analysis, the external environment of SA will be evaluated in this paper. The study will also establish a strong emphasis on analyzing the micro and macro environmental factors that have an impact on operational processes, including a SWOT analysis. As a result, there will be three main components in the report: a firm overview, a PESTLE analysis, and a SWOT analysis. The report’s conclusion will include suggestions for how the business might meet its key challenges.
Overview of the Company
Saudi Aramco (SA) is regarded as one of the most prominent companies in the entire globe. In 2017, its estimated value would range from $2 trillion to $8 trillion (Blas & Mahdi, 2017). It controls the largest hydrocarbon transportation network in the world and controls the bulk of the unrefined petroleum reserves in Saudi Arabia and several other international locations. When the Saudi government intended to create a company to compete with Standard Oil, the U.S. big oil-producing company Saudi Aramco was set.
The Saudi government finally acquired controlling holdings in the business after encountering a number of difficulties, political situations, and several periods of advancement. The company is involved in shipping as well as other diverse businesses, including oil drilling, processing, exploration, petroleum products, and distribution. SA planned and carried out several projects with the support of the government. At Saudi Aramco, the strategy process revolves around the company’s key strengths, such as its large unrefined oil resources.
Strategic Evaluation of Saudi Aramco
In order to acquire insight into the future, it is crucial for enterprises to do a thorough examination of the surroundings in which they operate. This section draws ideas from Chapter 3: Evaluating a Company’s External Environment (Thompson, Peteraf, Gamble & Strickland, 2022). Environmental factors have a significant influence on both the performance of individual firms and the sector as a whole as discussed in PESTLE analysis (Thompson et al., 2022). Below is a table showing the PESTLE analysis of Saudi Aramco.
Table 1: PESTLE Analyses
Assessing the Company’s Industry and Competitive Environment
PESTLE Analysis
Political. The political climate in Saudi Arabia is stable thanks to the monarch’s leadership. However, a lot of detractors debate Saudi Arabia’s “political situation.” The Saudi royal family is in charge of the country’s political system. A rough estimate places the number of male descendants of the Saud dynasty who control the 7000 princes of the nation at 200 (House, 2018). Princes and members of the royal family are given priority for the important cabinet positions.
Economical. Saudi Arabia’s primary business and source of wealth is the exploitation of oil and gas. In 2021, Saudi Arabia’s nominal annual Gross domestic product (GDP), which ranked 19th in the world, is 833.54 billion dollars (O’Neill, 2022). From this, the nation’s per capita income, which makes up 80% of the total GDP and ranks 39th in the world, was 19018.49 US dollars (O’Neill, 2022). The unexpected global lockdown and company closures spurred on by the COVID-19 epidemic reduced demand for oil and gas. The retail price decreased dramatically as well, and by 2021, the yearly GDP had decreased by 6.8% (O’Neill, 2022). According to Losier (2019), Aramco generated $315.2 billion in income in 2018. From figure 1 below, Saudi Aramco was ranked second in the world after Royal Dutch Shell.
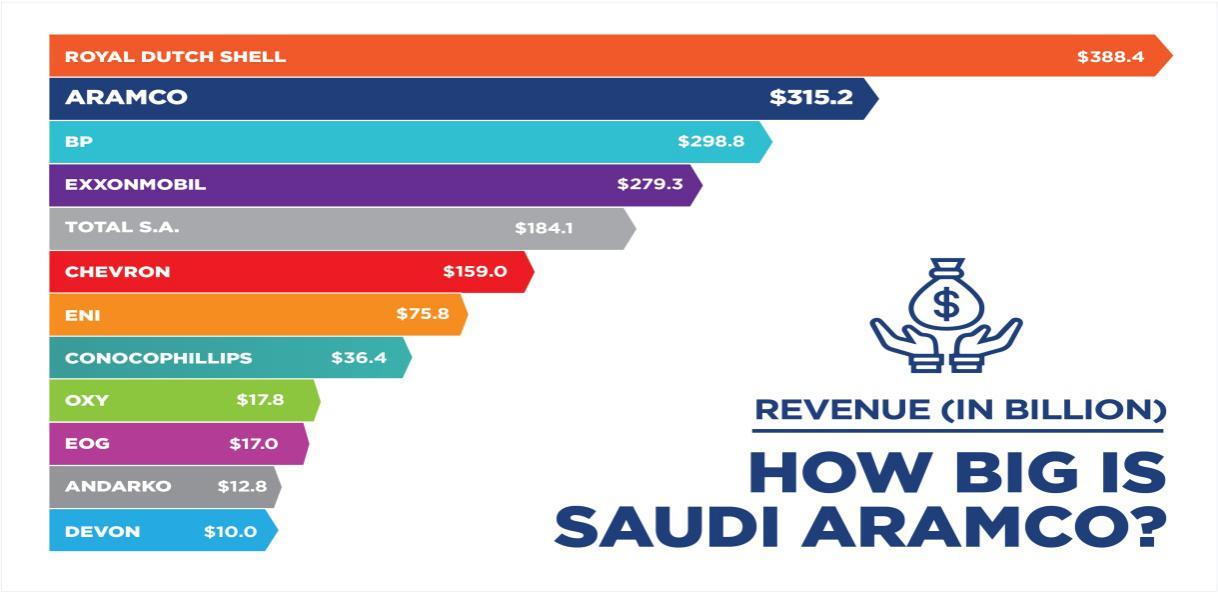
Social. One of Saudi Aramco’s guiding philosophies has been to enhance the communities in which it exists by adopting a variety of corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs and activities since the company’s foundation. The Company uses a Safety Management System (SMS) to promote occupational health and safety, which outlines safety duties and activities for management, staff, and partners (Saudi Arabian Oil Co., 2022). Its corporate principles are treating everyone fairly and respectfully, inclusive practice, and tolerating individual differences.
Technological. Massive financial reserves enable Aramco to consistently concentrate on innovation and boost productivity. The “open innovation” concept used by Saudi Aramco, for instance, aims to maximize the utilization of the natural resource. However, the company’s ability to increase its resources is only made feasible by extraordinarily strong cash reserves. Strategic initiatives and joint ventures by Aramco in downstream business growth have been shown to be beneficial. An Aramco subsidiary that focuses on upstream and downstream projects in fuel efficiency, natural gas, and petrochemical products is Saudi Aramco Energy Ventures.
Legal. The fact that Saudi Aramco enjoys strong connections with the Saudi government is a definite asset. As a result, Saudi Aramco plays a crucial role in the Saudi system as a state machine in charge of the country’s vital oil reserves (Almulhim & Abubakar, 2021). An increased danger of legal action under the two U.S. statutes may result from having the New York or London exchanges in control. For instance, JASTA, which limits the use of foreign power immunity, permitted the litigation against Saudi Arabia pertaining to the 9/11 attacks to move forward. NOPEC, a piece of proposed legislation, would permit legal action against nations that attempt to take oil off the market in order to raise prices.
Environmental. The aim to establish an atmosphere with few threats to the ecology informs the approach to assure regulated productivity. Aramco’s Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage Program and the development of the Hawiyah Gas Treatment Plant are two concrete instances of the company’s continued devotion to addressing the issues posed by pollution (Al-Saidi, 2022). The corporation invested a significant amount of money in the construction of the aforementioned facilities, which may reduce pollution by about 30% (Al-Saidi, 2022). The firm’s interest was also drawn to the ongoing Aramco Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage Program building project.
The Five Forces Framework
The Saudi Aramco Oil Company has acquired a number of companies that have helped it diversify and raise the prominence of its products. Figure 2 below is a summary of Porter’s five forces framework with a thorough explanation of Porter’s design of 5 forces.
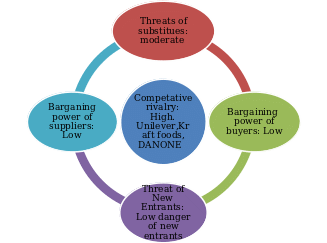
Competitive Rivalry. One of the leading firms in this demanding industry, Saudi Aramco Oil Company faces high stiff competition from Unilever, Kraft Foods, and Group DANONE. For the past years, Saudi Aramco Oil Company has been performing well in this race. However, the firm faces a huge amount of competition from other businesses.
Threat of New Entrants. There are several obstacles in the way of newcomers entering the consumer food market. Only a few newcomers succeed in this business since it takes time to comprehend client needs, whereas competitors today are informed and have advanced with consumer devotion to their products through time. Since Saudi Aramco Oil Company already has a significant worldwide distribution network and a well-respected reputation, there is little risk of new competitors joining the company in the food sector.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers. The suppliers’ ability to bargain is limited. The largest market share in the food and beverage industry belongs to Saudi Aramco Oil Company, which necessitates the use of more supply chains. In response, Saudi Aramco Oil Company, which values long-term relationships, has expressed concern for its suppliers.
Low Bargaining Power of Buyers. The Saudi Aramco Oil Company strives to maintain customer satisfaction by offering high-quality oil products. Due to this, customers view Saudi Aramco Oil Company as one of the most dependable companies, hence, high demand for their products.
Moderate Threat of Substitutes. There has been a serious risk of substitutes because to the availability of alternatives for several Nestlé products, including pasteurized milk and boiled water. The Saudi Aramco market share has seen the introduction of biofuels, which have also supplanted the usage of oil. There have also been allegations that some of its products are unsafe for use, which has hurt sales. In order to compete with the alternatives, Saudi Aramco Oil Company started emphasizing the health advantages of its products.
Aramco’s Performance in the COVID-19 Period and Post-COVID-19
In December 2019, Aramco went public, becoming the most lucrative corporation in the world at the moment. A few months later, the Covid-19 epidemic struck and decimated the global financial system. The company’s net income significantly decreased in the second quarter as a result of a decline in both worldwide demand and oil prices. However, Aramco opted to increase its dividend payout to $18.75 billion in an effort to sharpen its edge in terms of insights, commitment, and execution, as suggested by McKinsey (Birshan, Sternfels, & Seth, 2022; El-Gamal, 2020). The initiative was intended to retain investor optimism and to increase the State’s fiscal budget, as their budget was originally predicated on a $60–70 per barrel estimate (El-Gamal, 2020). As a consequence, Aramco’s stock prices maintained a consistent level during the period in comparison to other significant oil and gas firms.
Aramco was able to close a transaction with Saudi Basic Industries Corp (SABIC). In the first half of 2020. To be more precise, SABIC bought a 70% share in the business to mitigate the effects of Covid-19 on the Company (El-Gamal, 2020). As a result, after Covid-19, the agreement gave Aramco access to petrochemical businesses in more than 50 nations, with potential for future growth. Although Aramco’s petrochemical capacity is mostly concentrated in the Middle East, this investment indicates that there are intentions to expand internationally.
Saudi Aramco Resources, Capabilities and Competitiveness
The objective of Saudi Aramco, which, as per Saudi Arabian Oil Co., is the producer of the petroleum used to create the energy industry, is to maintain its position as a global leader in the sector. As of 2020, Saudi Aramco had a market value of over $2 trillion (Granville, 2022). By 2023, it will have generated a profit of nearly $69 billion (Saudi Aramco, 2022). The company makes sure it stays devoted to resolving difficulties that arise in its industry in order to guarantee that its objective is reachable.
Table 2: Summary Statistics about Saudi Aramco Company
Aramco’s Competitive Analysis and Personal Opinion on the Success of Past Strategic Decisions
To maintain its position, Saudi Aramco must contend with powerful rivals in its market. BP, ExxonMobil, Marathon Petroleum Corporation (MPC), and Shell are a few of the main rivals Saudi Aramco must battle within the market. An examination of Aramco’s internal Strengths and Weaknesses and external Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) is essential to comprehending its rivals, as indicated in Chapter 4 of the book Crafting & executing strategy: The Quest for competitive advantage: Concepts and Cases (Thompson et al., 2022). A summary of the SWOT analysis (see Table 3) is indicated.
Table 3: SWOT Analysis
Strengths of Saudi Aramco. The most crucial element that aids Saudi Aramco in keeping its market dominance is its strengths. The following are some of Saudi Aramco’s advantages: Substantial capacity for processing and refinery – Saudi Aramco is equipped with a sizable facility for the production and refinement of its materials. This enables the business to provide its items to a wide market. Technologies innovation: Saudi Aramco produces and manages its goods using the most recent technology. For instance, the use of low Cost – Aramco technology produces the lowest cost-per-barrel production rates on the global market.
Weaknesses of Saudi Aramco. The aspects that function as a defect in Saudi Aramco’s expansion are its weaknesses. It must identify these weaknesses in its business and work to correct them as quickly as feasible. The following are some of Saudi Aramco’s shortcomings: High reliance on a single product – Saudi Aramco is increasingly reliant on the success of a single commodity, namely crude oil. If this continues, the business can run into issues down the road if the viability of that product shifts. Corporate governance and accountability – Saudi Aramco is at a serious disadvantage as a result of these issues.
Opportunities for Saudi Aramco. Opportunities are what drive Saudi Aramco’s rapid rise in its sector. The business must identify these possibilities that might benefit it and turn them into strengths. The following are some of Saudi Aramco’s opportunities: global economic expansion the rising need for energy and growing reliance on fuels may present Saudi Aramco with a chance to advance in its industry. IPO of Saudi Aramco – The disclosure of Saudi Aramco’s initial market offerings will aid in revealing the true worth of the business.
Threats to Saudi Aramco. Threats are Saudi Aramco’s external elements that adversely impact the company’s expansion. It must be equipped with the appropriate safety precautions and mindful of such incidents in the future. The following are a few dangers facing Saudi Aramco: Development of merchandise – If other nations are successful in their exploration of innovative products, Saudi Aramco’s worldwide market share may decline. Eco-friendly fuel – If the reliance on non-conventional and alternative energy sources rises, the corporation may suffer greatly.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Recommendations
Based on my opinion of the success of past strategic decisions, Saudi Aramco should boost the agglomeration of its natural gas and oil resources if it aspires to become one of the top producers and reserves of oil on the market. The business must be proactive in finding new oil deposits in order to accomplish this goal. As a result, the corporation should continue using a low-cost strategy, since it has been a success from the past strategic decisions, to increase its critical oil resources by setting aside enough money in an attempt to make this plan viable. The state-owned company should concentrate on boosting the size of its gas fields since rising oil consumption causes constraints in supply.
Conclusion
The differentiation strategy of Saudi Aramco in relation to the social, technological, economic, political, and legal settings as well as environmental preservation, has been thoroughly examined in the paper. According to the research, Saudi Aramco relies on three key tactics to help it reach its objectives. Asset management, wealth maximization, and cultural diversification are some of these tactics. Due to its massive output, Saudi Aramco, one of the top NOCs in the world, has profited from economies of scale. The company has efficiently invested in technological advancements in an effort to find affordable oil and gas to meet the constantly rising local and international demand in order to preserve its petroleum reserves.
References
Almulhim, A. I., & Abubakar, I. R. (2021). Understanding public environmental awareness and attitudes toward circular economy transition in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 13(18), 1-15.
Al-Saidi, M. (2022). Energy transition in Saudi Arabia: Giant leap or necessary adjustment for a large carbon economy? Energy Reports, 8(1), 312-318.
Birshan, M., Sternfels, B., & Seth, I. (2022). Strategic courage in an age of volatility. Web.
Blas, J., & Mahdi, W. (2017). Saudi Arabia’s oil wealth is about to get a reality check. Web.
El-Gamal, R. (2020). Saudi Aramco will use cash, debt to pay dividends, says CEO. Web.
Granville, K. (2022). Saudi Aramco’s profit jumps 90 percent on high oil prices. Web.
House, K. E. (2018). The model for a Saudi reformer. Web.
Losier, T. (2019). How big is Saudi Aramco? Web.
O’Neill, A. (2022). Saudi Arabia: Gross domestic product from 1987 to 20267(in billion U.S. dollars). Web.
Saudi Arabian Oil Co. (2022). Social Responsibility. Web.
Thompson, A., Peteraf, M., Gamble, J., & Strickland, A. (2022). Crafting & executing strategy: The quest for competitive advantage: Concepts and cases. (23rd ed.). New York, NW: McGraw Hill.