Introduction
Financial analysis pertains to corporate finance and investment business economics. Internal financial reporting is a corporate practice involving the compilation of financial records for frequent internal usage (Khoja et al., 2019). The documentation may contain classified data, such as institution metrics, economic condition, scorecards, net present value (NPV), and internal rate of return (IRR), which are used to determine which initiatives are worthwhile to execute (Khoja et al., 2019). As the internal annual statements are not visible to the public, the corporation is not obligated to adhere to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) when generating them. This essay analyzes some of the financial leverage ratios, collects and evaluates data about bond performance, and considers the market ratios of Southwest (LUV). Moreover, this paper provides a specific recommendation based on the assessment’s results to the company’s management.
Evaluation of Financial Leverage Ratios
Table 1: Southwest’s (LUV) Financial Leverage Ratios (Southwest Airlines Co., 2022a)
Analysis
Southwest (LUV) finances its assets using equity, as observed in its financial leverage ratios. Southwest Airlines’ debt-to-asset ratio of 0.23, as of 2022, is below 1, which indicates that equities finance more of the enterprise’s assets. Moreover, Southwest Airlines’ asset financing is backed by the company’s debt-to-equity ratio of 2.29 as of 2022, which is considered generally attractive. Nuryani & Sunarsi (2020) insinuated that a debt-to-equity ratio between 2 and 2.5 is generally satisfactory.
Risk in finance is the likelihood that actual performance will deviate from expectations. Financial risk is the danger of incurring losses on a venture or business endeavor. Default risk, financial leverage, and regulatory vulnerabilities are among the more prevalent and unique financial hazards. Southwest Airlines’ economic structure faces moderate credit risk. Since the company borrows funds to finance a part of its assets, it will forfeit if it cannot repay the portion of the debt. As such, default risk would reduce shareholders’ earnings from loan repayments and causes them to lose interest and principal.
Lenders evaluate creditworthiness using customized risk rating instruments, which vary by organization or region and are predicated on whether the borrower is an individual or a corporate client. Since Southwest (LUV) participates in conventional financing, its default risk measurement necessitates quantitative methodologies. Southwest’s credit evaluation will result in points based on the creditor’s unique analysis processes, algorithms, and eligibility factors. The score may also be alluded to as credit ratings, such as AAA or BB+ in the case of Southwest’s public corporate bonds. The score determines the possibility that the company will initiate a default event. The higher Southwest’s (LUV) score or creditworthiness, the less probable the company will default. However, the lesser the grade, the greater the likelihood of forfeiture.
Southwest Airlines Bond Performance
Table 2: Illustration of Two Bond Quotations Issued by Southwest (LUV) (Bonds – Search Results, 2013)
The last price represents the value at which the most recent bond acquisition or sell operation occurred. It is the most appropriate predictor of the Current Market Price (CMP) or trading Price. If the par value of the bond is $1,000, the investor must pay the following:
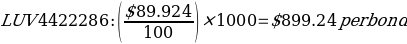
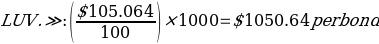
The annual coupon interest payments for the two bonds are given as follows:
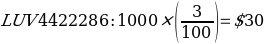
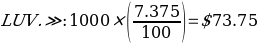
The current yield of bonds is calculated using the formula
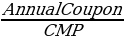
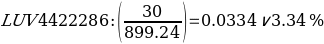
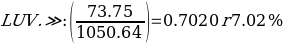
The yield to maturity (YTM) of LUV4422286 is 5.849, while that of LUV.GG is 6.020. The YTM is the overall rate of return generated by a bond when it has made all loan repayments and recovered the principal.
In purchasing a bond at Southwest (LUV), I would buy the LUV.GG bond type. The rationale for choosing the above-mentioned bond is that it has higher annual coupon interest payments ($73.75) than LUV4422286 ($30). This alludes to the fact that LUV.GG has a greater coupon rate (7.375) as compared to LUV4422286 (3.000). A coupon rate is a return a fixed-income instrument pays on a nominal basis. It is the entity’s yearly coupon distributions proportional to the face or par value of the asset (Kavussanos et al., 2021). Bonds with higher coupon percentages appeal more to purchasers than those with lesser coupon levels, all else being constant.
The fact that the bonds provided in table 2 are callable will change my thought on acquiring them. The reason for the aforementioned decision is that Southwest Airlines (LUV) will terminate the assets when interest rates are low. This call exposes the shareholder to the risk of replacing the commitment at a value that will not generate the same amount of income (Mocanu et al., 2021). Consequently, investors who invest money in a low-yielding product risk falling behind when market interest rates rise. Moreover, callable bonds profit companies more than entrepreneurs (Mocanu et al., 2021). In the event that the market interest rate falls below the percentage paid to bondholders, Southwest (LUV) may terminate the note. Then, it may restructure the loan at a cheaper rate of interest. Therefore, this versatility is typically more advantageous for the firm than bondholders, hence the reason for not purchasing callable bonds.
As an investor wanting to acquire Southwest (LUV) bonds, I would buy any bond I choose from the institution. From the organization’s income statements and balance sheet, the bond and debt-to-equity ratios justify my perspective. The bond ratio is a financial indicator that reflects the indebtedness of a bond issuer by assessing the existing bond valuation and maturity date. In addition, it technically indicates the proportion of a company’s issued bonds to its overall capital architecture. Capital structure describes how a corporation funds its activities and expansion using a combination of debt and equity. According to Southwest Airlines Co. (2022a), the organization has a bond ratio of 4.75% while its debt-to-equity ratio is 2.29. With such minimal debts, Southwest Airlines can repay its liabilities and avoid bankruptcy in the case of a drop in income; hence, the company is an attractive investment opportunity.
A specific recommendation for investors of Southwest Airlines Co. is to take advantage of the firm’s equity financing. Equity financing entails the purchase of firm shares for capitalization purposes. When shareholders acquire institution shares, they also get ownership and control. Crowdfunding can encompass the issuance of all equity securities, including common stock, marketable securities, and share certificates. The primary benefit of equity funding for investors is that corporate owners relinquish a percentage of their management and involvement. If the firm becomes prosperous and productive in the future, a portion of profits must be distributed to investors through payouts. As such, when corporations choose to raise capital by selling equity shares to prospective investors, they are obligated to share their earnings and communicate with these speculators before making decisions that will significantly influence the company.
Stock Performance
Table 3: Stock Performance of Southwest and Alaska Airlines (Southwest Airlines Co., 2022a; Alaska Air, 2022)
As discussed, this section answers the question, are the common stockholders receiving an adequate return on their investment in Southwest Airlines? The following conclusions can be made from the summary of the market ratios of Southwest Airlines compared to Alaska Air in table 3. As of 2022 and the preceding two years, Southwest Airlines has outperformed Alaska Company in all the ratios shown in table 3. The market-to-book proportion, also referred to as the price-to-book ratio, is a financial indicator used to compare the present marketplace worth of a company to its book value. The fact that the ratios of 2.02 and 1.49 are more than one may indicate that the firm’s stock is overvalued. However, Southwest’s market-to-book ratio is greater than Alaska’s, showing that Southwest outperformed Alaska in 2022 hence a higher return to investors.
On the other hand, the earnings per share ratio, earnings per share (EPS), is the corporation’s net income divided by the number of existing ordinary shares. EPS is a commonly used indicator for determining the worth of a company since it reveals how much finances a company earns per share of stock. The higher EPS of 0.44 by Southwest suggests a larger value since investors would pay more for its shares because they believe it generates huge returns compared to its stock price. Finally, the cash earnings per share (CEPS), also known as operating income, is a measurable statistic that compares cash flow to the outstanding shares. Investors, lenders, and economists like a CEPS ratio greater than one since it indicates that a business can pay its present short-term commitments and yet have earnings remaining. As such, Southwest’s CEPS of $643 indicates that its investors expect more earnings as it is in a position to meet its liabilities. Corporations with a high or rising operating cash flow are generally deemed to be in good fiscal shape.
The P/E ratio of Southwest Airlines stands at 29.87 compared to the industry’s 5-year average of 12.69. The high return suggests that shareholders anticipate the business to expand faster than the market and that the business’s stock is overvalued. Venture capitalists use the P/E proportion not just to evaluate the market value of a stock but also to forecast future profitability. For instance, if investors anticipate that Southwest Airlines’ revenues will improve, they may anticipate that the firm will boost its dividends. Higher incomes and dividend growth often result in a stock price increase.
Analysis of Historical Stock Prices
Figure 1 illustrates the stock prices of Southwest Airlines from 9th August 2021 to 1st November 2021. Due to the large amount of data available on stock prices, the above-mentioned range was picked for analysis. From figure 1, the opening stock price for the firm has been decreasing gradually, from 38.75 on 9th August 2021 to 37.71 on 1st November 2021. Consequently, the company’s highest stock price registered at 40.39 as of 15/08/2021, representing a volume sold of 4722597 shares. However, the value fluctuated between the months, failing to maintain a steady decrease rate. On the other hand, the lowest stock price of 30.2 was registered on 03/10/2021. The closing stock costs of the firm have fallen steadily from 38.34 on 9/08/2021 to 37.08 on 04/11/2021.
Specific Recommendation
The specific solution I would suggest to Southwest Airlines’ management is to adopt debt financing as part of its financial strategy. Debt financing has several benefits, one of which is that Southwest (LUV) would retain ownership of the company. When a company borrows money from a bank or another type of lender, they are responsible for making timely payments during and before the loan amount expiration. Conversely, suppose it continues to give up equity in the form of securities in compensation for capital as it does now. In that case, Southwest (LUV) may find itself dissatisfied with opinions expressed by outside parties about the direction of the company.
Conclusion
In conclusion, by utilizing internal sources of financing, the financial manager assists the organization in retaining ownership and control. If the corporation instead issued new shares to raise capital, it would cede a certain amount of control to its existing owners. Therefore, financial ratios provide business owners with a method for evaluating their company’s performance and comparing it to other comparable businesses in their industry. Southwest (LUV) should utilize debt financing since it would allow it to retain business control. Southwest (LUV) may find itself dissatisfied with the thoughts of outside stakeholders regarding the corporation’s future if it persists in giving up equity in the form of securities as remuneration for finance as it does now.
References
Alaska Air Financial Statements 2009-2022 | ALK. (2022). Macrotrends.net. Web.
Bonds – Search Results. (2013). Morningstar.com. Web.
Kavussanos, M. G., Tsouknidis, D. A., & Visvikis, I. D. (2021). Interest rate derivatives. In Freight Derivatives and Risk Management in Shipping (pp. 389-413). Routledge.
Khoja, L., Chipulu, M., & Jayasekera, R. (2019). Analysis of financial distress cross countries: Using macroeconomic, industrial indicators and accounting data. International Review of Financial Analysis, 66, 1-33. Web.
Mocanu, M., Constantin, L. G., & Cernat-Gruici, B. (2021). Sustainability bonds. An international event study. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 22(6), 1551-1576. Web.
Nuryani, Y., & Sunarsi, D. (2020). The effect of current ratio and debt to equity ratio on dividing growth. Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Accounting Information Systems, 4(2), 304-312. Web.
Southwest Airlines Co. (2022a). Wsj.com. Web.
Southwest Airlines Co. (2022b). Wsj.com. Web.