Case Analysis Overview
Southwest Airlines is one of the most competitive airlines in the World. The company, which serves more local populations than international ones, has registered profits since it was started. Indeed, the company has never experienced a significant setback close to one posed by the COVID-19 crisis. As of 2019, the firm has been in its top-earning years, with after-tax profits of $2.3 billion (Thompson & Gamble, 2021).
Southwest’s most current strategies that have significantly contributed to its success are a supportive culture, an open-door management policy, and expansion. The airline has continued improving its supportive culture by prioritizing employees and enhancing customer experiences. The management encourages an open-door policy where employees can easily access the executive leadership and raise issues.
The approach has recently enabled management to listen to employees and address their concerns actively. The expansion strategy saw the company adding more Boeing Max aircraft and increasing destinations. Southwest is currently faced with the challenge of grounded Boeing Max aircraft and losses associated with the COVID-19 outbreak.
Strategic Diagnosis
The problem of the Boeing Max grounding results from strictly operating with one aircraft type. However, it has decreased the company’s opportunities to have a wide range of experiences with other aircraft. Consequently, Southwest mechanics have minimal experience handling large aircraft. According to the Federal Aviation Administration, Boeing jets require design changes to make them airworthy (Thompson & Gamble, 2021).
The challenge of COVID-19 is beyond any management control, and there is no strategy the company could have applied to prevent the effects. The no-layoff policy might have pushed Southwest to more losses during the lockdown. The policy states that the company cannot conduct layoffs, no matter how bad the economic conditions are. During the 2020 health crisis, the firm cut salaries slightly and continued to pay all employees, even those not working (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). The argument is that if the company had performed some layoffs during the lockdown, it would have reduced losses.
Effectiveness of Company Strategy
The generic strategy of Southwest is cost leadership, where the company charges the lowest fares within the United States destinations. The generic strategy produces satisfactory results based on the most recent record-breaking profits. From the case study data, Southwest continues to register an increase of 162,681,000 passengers in 2019, from 144,575,000 in 2015 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021).
Furthermore, the company accrued a net income of 2.3 billion in 2019 from 2.1 billion in 2015, yet some planes were grounded in 2019 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Southwest was profitable from 1973 to 2019 and was listed among the most admired companies for 27 consecutive years (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Among many other indicators, the lower fare strategy earns Southwest satisfactory results.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Southwest Airlines has one of the most priceless strengths of all time: resilience. The case study operational challenges and legal issues have proven that the company can overcome almost all business-related obstacles. The company began in 1971 from secondary airports with minor traffic but beat the challenges of the dramatic increase in jet fuel prices, drop in airline traffic due to terrorist attacks, fare wars, business rivalry, and economic recessions (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). In addition to overcoming all these barriers, Southwest managed to add more flights and airports.
Between 1970 and 1978, the company fought three legal battles when rivals wanted to stop it from gaining a foothold in the airline industry (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Herb Kelleher, the firm’s legal representative, won against sets of more than ten lawyers in the various battles. Winning these battles brought a ‘can-do’ culture of resilience to Southwest. The airline personnel developed a strong ‘esprit de corps’ and a drive to survive and prosper against all odds.
The company enjoys the strength of providing the lowest fares, a point-to-point flight model, and a top-notch travel experience. Being an exceptional airline offering the lowest fares in the market makes it the best choice for most middle- and low-income travelers. Compared to its competitors, which operate in a system that allows customers to join flights locally and internationally, Southwest flies from point to point, making the travel experience more convenient and faster.
The combination of low fares and point-to-point strategies has helped the firm to grow in terms of customers and expand its flights and destinations (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Southwest management prioritizes employees, relying on the understanding that happy employees treat customers better. Consequently, the organization has provided a top-notch customer experience with minimal complaints.
Weaknesses
However, Southwest is currently challenged by Boeing’s design and no-layoff policy. On October 29, 2018, a Boeing Max crashed in Jakarta, Indonesia, where 189 crew and passengers were lost. Another incident on March 10, 2019, hit Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302, leading to the loss of 157 people (Thompson & Gamble, 2021).
On October 13, 2019, President Trump grounded the operations of Boeing Max until the company could identify existing mechanical problems with these aircraft and resolve them (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Southwest is required to change the aircraft model to fit the requirements of the Federal Aviation Administration. The grounding cost the firm $828 million as additional costs in 2019, and more losses are expected as the grounding moves to 2020 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021).
The no-layoff policy is a weakness for the company because it does not account for unplanned or unpredictable events such as COVID-19, which could stop operations for months or years. Southwest management has failed to plan for prolonged natural disasters, which could stop flight movement, yet employees would be paid. If the company goes for more than six months without operations, it will face the possibility of bankruptcy due to salary expenses.
Opportunities
The airline can fix the grounding issue and introduce a layoff policy. The management should work towards making Boeing design changes that make it airworthy based on FAD requirements. Furthermore, the company could invest in a different aircraft model, especially the large ones. Introducing layoffs only for disastrous economic moments could keep the firm safe from possible bankruptcy in the future. However, since the policy has positively impacted employee relations, the layoffs should only apply in severe circumstances.
Threats
Like all other world airlines, Southwest is affected by the ongoing health crisis. The COVID-19 outbreak saw the airline industry incur billions of losses. Indeed, between March and April 2020, the industry employment dropped to 31,000 workers from 428,000 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Such an incident implies that natural disasters and bad weather threaten the Southwest. Therefore, the company should have a contingency plan to overcome such moments in the future.
Importance of SWOT
The strengths and weaknesses of a company are essential in assessing the internal factors that impact the business in the long and short terms. Opportunities and threats are critical because they highlight external factors influencing business operations. SWOT analysis is a planning tool that helps the management evaluate its framework concerning strategic goals.
Strengths show areas where the applied strategies work towards the set goals, while weaknesses highlight inconsistencies in strategic operations. Therefore, the weaknesses of an organization highlight areas that need improvement for the overall performance to meet the objectives. Opportunities highlight areas a firm could exploit to maximize profits within its strategy. Threats show a company’s possible challenges while working with a particular approach. Threats help the management plan for future contingencies to overcome foreseen challenges.
Current Financial Analysis
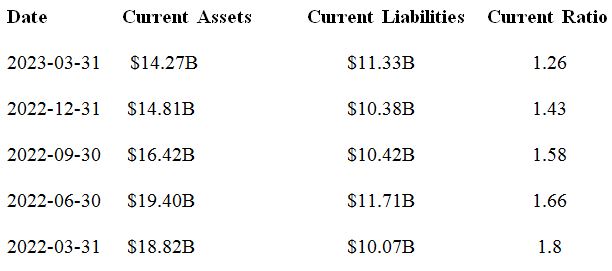
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that reveals an organization’s stability in terms of bankruptcy. The ratio shows the relationship between existing assets and liabilities by dividing the assets by liabilities (Borosky, 2022). As shown in Figure 1, the Southwest current ratio between the first quarters of 2022 and 2023 ranged between 1.2 and 1.8.
According to Borosky (2022), a ratio of 1 plus means that the current assets are twice the liabilities. However, if the ratio is less than 2, repayment of current liabilities may be challenging and affect the business’s operations (Borosky, 2022). As seen in Figure 1, Southwest’s current ratio continues from 2022 and is headed towards a worse direction of less than 1.
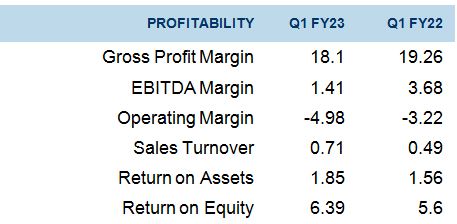
The second financial ratio is profit margin, which reveals the portion a firm keeps as profit from its overall sales. Gross profit margin is attained after subtracting operational costs and tax from revenues and dividing them by total revenues (Borosky, 2022). Figure 2 shows Southwest’s gross profit margin for the first quarter of 2022 and 2023 as 19.26 and 18.1, respectively. It reveals that the company has made less profit in 2023 than in 2022.
According to Borosky (2022), a profit margin of 5% is considered low, 10% average, and 20% high. Therefore, Southwest’s profit margin is average and far from high. Operating margin shows how much a firm makes on a single dollar sale after deducting operational costs before taxes or interests (Borosky, 2022). It is attained by dividing operating income by net sales. Figure 2 shows Southwest’s operating margins for the first quarter of 2022 and 2023 are -3.22 and -4.98, respectively. The company’s operating margin deteriorates and could worsen if the same performance is maintained.
Southwest Airlines Current Ratio Historical Data
Factors Related to Financial Health and Returns
Some factors related to financial health and returns are liquidity, solvency, and profitability. Liquidity is crucial in assessing financial health and returns because it shows the amount of cash and is easily converted to cash assets a company owns (Borosky, 2022). It indicates whether a firm can prosper in the long and short term, whereas if the company has fewer assets and more liabilities, it may not survive in the long term.
Solvency is a firm’s ability to meet its debt obligations continuously. Solvency weighs corporate debt against equity to determine whether the business can meet its debts and keep operating for a long time (Borosky, 2022). If the debts exceed equity, the firm has a higher possibility of closing down.
Profitability is the most accurate factor determining the business’s success or failure. A company cannot survive long without making profits (Borosky, 2022). Therefore, depending on the profit percentage made in a financial year, one can tell whether the business can survive in the short or long term.
Firm’s Financial Strength
As of 2019, Southwest was financially strong, but as reports of 2022 and 2023 show, it has drastically weakened. As shown in Figures 1 and 2, the company’s financial ratios continue to weaken, exposing the firm to more losses. Regarding margin, Figure 2 shows that Southwest is on average, but it could worsen following the drop from 2022. However, the return on assets has improved from the first quarter of the financial year 2022 to 2023, as shown in Figure 2. The capital structure of Southwest also seems strong because, as shown in Figure 2, the return on equity increased from 5.6 to 6.39, respectively, in the quarters of 2022 and 2023. After examining these factors, Southwest is still financially strong but could grow weaker if immediate action is not taken.
Factors Influencing a Company’s Success and Failure
The case study shows that Southwest’s efficient marketing and production have contributed to its current success. Exhibit 4 of the case study shows that Southwest spends more on advertising than other top airlines. Southwest spent 0.16 cents per revenue passenger mile in 2019, while American Airlines spent 0.06 and Delta Air Lines 0.12 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). The higher level of marketing could explain Southwest’s increased number of passengers in 2019.
Managerial competence has also been a significant factor in success, especially the leadership of Kelleher, who saw the firm increase from 27 planes and 2100 employees in 1981 to 350 aircraft and over 30,000 employees in 2001 (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). Other executives who succeeded Kelleher were critical pivots to the company’s growth. However, some strategies adopted by the management have contributed to Southwest’s failure. For example, the use of Boeing Max and the no-layoff policy resulted in critical losses for the firm in the past years.
Recommended Strategic Changes
Southwest could change three strategies to enhance its operations and minimize potential losses. One strategy is to improve the competencies of its employees, especially the mechanical team. The organization relies on a team that cannot detect mechanical problems in the grounded planes. Southwest should also change the policy of no layoff because even though it positively impacts employee relations, it could lead the firm to critical losses in the future. Lastly, Southwest could change its strategy of operating on more local destinations by adding more international flights.
Strategic Challenges and Opportunities
- Relying on incompetent mechanics
- No layoff policy
- Minimal international flights
Action Plan to Implement Strategic Changes
Southwest is experiencing the challenges of relying on incompetent mechanics for Boeing Max aircraft and having a no-layoff policy. The aircraft were grounded because they contained mechanical problems that went unnoticed by the company’s mechanical team, leading to the loss of over 300 lives within one year (Thompson & Gamble, 2021). The company could resolve this problem by outsourcing mechanical experts to identify the issues.
Southwest’s mechanical team should have the training to refresh their skills and operate better in the future. For the no-layoff policy, Southwest must introduce a layoff approach that is only to be exercised during a specific time. The procedure should only target a more significant percentage of employees when the airline goes out of operation for more than three months.
Strategic Plan to Fix Challenges and Recommendations
Specifically, Southwest should use different mechanical teams from Boeing to determine the mechanical problems with the grounded planes. The current mechanical team working on Southwest Airlines needs competence training from training institution services, such as Aviation One Services, to refresh their skills.
Southwest will then introduce a layoff policy, which will only apply if the firm goes out of operation for over three months. Specifically, the policy should only apply if more than half of the firm’s aircraft are out of operation or if more than half of the workers cannot attend to their duties following unavoidable disasters or conditions. Lastly, after identifying the mechanical problems with Boeing Max, Southwest management should plan to have more international flights to increase sales and profits. This implementation strategy is based on the current opportunity of adding more international and local flights to increase profits and sales.
Strategy Implementation
Implementing the strategies will have three specific agendas to address the changes. One of the agendas will be identifying and resolving mechanical issues with Boeing Max. This agenda should be a top priority requiring immediate action.
The first action will be for the management to consult with Boeing engineers to find the best mechanical team and identify and resolve issues with Boeing Max. This agenda should be implemented within the first three months because Southwest is already experiencing a setback due to the grounding of these planes. The people to implement this change should be operations managers for Southwest and Boeing, alongside various top mechanical engineers.
The introduction of a layoff policy should be the second priority and stipulated within the first three months. The human resource manager and recruiting manager should implement the layoff agenda because it involves employee welfare and job security. The two managers should develop a policy stating when and why employees will receive a layoff. They should then announce it to the employees while explaining the potential losses the firm could incur following a natural disaster that could stop normal operations for over three months.
Lastly, the agenda of adding more international flights to the Southwest system should be implemented. Since this is not urgent, it could be stipulated within the first two years. Following the urgent need to fix issues of grounded planes and recent losses resulting from COVID-19, the company should take it easy before burdening the management with new roles. Therefore, within those two years, the operational and coordinating managers should work towards introducing new flights and destinations around the World.
The next step would be allocating aircraft to new international roles. The two managers should also work with a marketing manager who will develop a commercial to advertise new flights and destinations to the public. Introducing more flights will be a critical financial change; hence, the team should also involve the accountants to work on the specific budgets to initiate such flights. Some expenses to be introduced will be fuel costs, the cost of servicing more international planes, and salaries for additional flight attendants.
References
Borosky, P. (2022). Beginner’s handbook and guide to financial statements and financial ratios. Independently Published.
Southwest Airlines Co. Financial statements. (2023). The Wall Street Journal. Web.
Southwest Airlines current ratio 2010-2022. (2023). Macrotrends. Web.
Thompson, A. A. & Gamble, J. E. (2021). Southwest Airlines in 2020: Culture, Values, and Operational Practices. 1-15.