Introduction
In the corporate world, logistics performance can represent enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, higher production volumes, improved stock control, wiser warehouse space utilization, and more customer and supplier engagement. Standardizing supply chain processes also lead to greater manufacturing, which helps firms compete more effectively and, consequently, provide more benefits to clients. Supplier relationship management and collaboration are essential aspects of increasing the supply chain’s output.
Theories
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Considering an overview of the key concepts and theories relevant and applicable to the case, it is feasible to emphasize the major notions related to the features of logistics and supply chain management. The Council of Logistics Management, a professional association of logistics professionals dedicated to the advancement of logistics science, identifies logistics as the planning component of supply chain operations (Nunes et al., 2020). It also includes the execution and supervision of efficient and effective program management, flow, and warehousing, and all related information, from the original location to the point of consumption, in order to meet customer quality standards (Nunes et al., 2020). Sustainable supply chain management, which focuses on implementing environmental, managerial, and economic needs across a target company’s supply chain activities, has evolved as a method for companies to enhance long-term supply chain sustainability (Koberg & Longoni, 2019). According to the definitions, the sphere of supply chain management and logistics encompasses a set of notions related to asserting the correctness of elaborating product streams.
Supplier Development and Connections
In addition, it is possible to examine other theoretical aspects of logistics connected to the case study’s idea, which includes supply chains of a bottle of water. Supplier development is a metric that assists in improving a supply chain’s financial and social productivity, and it can be considered a new theoretical concept that needs further hypothesis testing (Yawar & Seuring, 2018). People may assist in developing their networks and sources by supporting the success of different suppliers and providing them with opportunities to cooperate. More supplier connections imply more firms competing for revenue and more alternatives to select from.
Commonality of Purpose and Collaboration
Furthermore, discussing the concepts of commonality and collaboration is obligatory in terms of the importance of building positive relationships with suppliers. Due to the improved communication mechanism, supplier collaboration has been proven to affect market growth via company sustainability (Ukko et al., 2022). Collaboration that is dependent on shared knowledge diminishes costs, enhances the delivery of services, and promotes mutual progress. The development of collaborative partnerships at various levels, both corporate and operational, is an established recommended approach that ensures total visibility. A characteristic or objective recognized by two or more individuals or objects is referred to as a commonality of purpose. In logistics and supply chain management, the commonality of purpose is essential since it ensures establishing effective contact between the supplier, customer, and other intermediaries. The role of leadership at each company in establishing and supporting initiatives related to the commonality of purpose and establishing supplier collaboration is described by the desire of companies to enhance cooperation.
Inventory Planning and Control
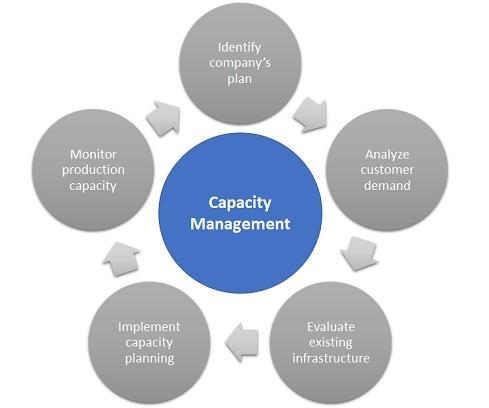
All processes and procedures connected to inventory should be emphasized at all stages of implementing business decisions in logistics. Inventory planning and management is a vital activity in every business, and various companies should concentrate on inventory control modeling using an optimization and simulation method (Vidal et al., 2019). According to the case, planning and controlling enable the customers to drill into demand information to recognize how to support production (Group B, 2022). A transport network, also known as a transportation network, is a system or graph in a geographical location that describes the infrastructure that allows and restricts mobility (Jia et al., 2019). Transportation in a distribution network corresponds to the transfer of items from one site to another, which starts with the arrival of resources at the warehouse at the beginning of the chain (Speranza, 2018). Moreover, highlighting capacity management, which was mentioned in the case, an established capacity management system’s purpose is to be able to respond to all possible demand situations (Gallego-García et al., 2019). It does so by making the appropriate inputs at the right time based on the available data.
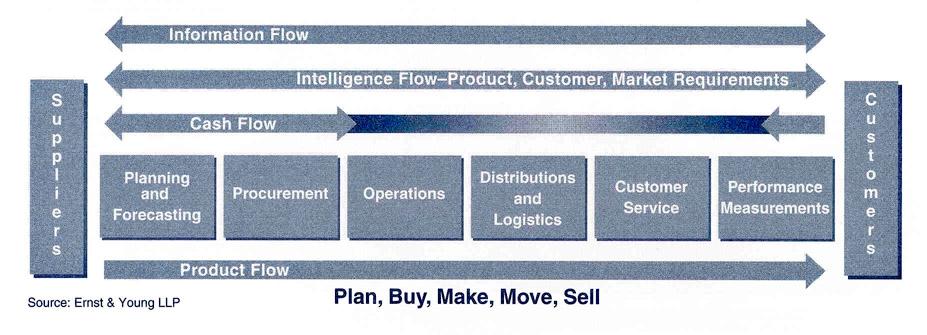
Theory and Practice
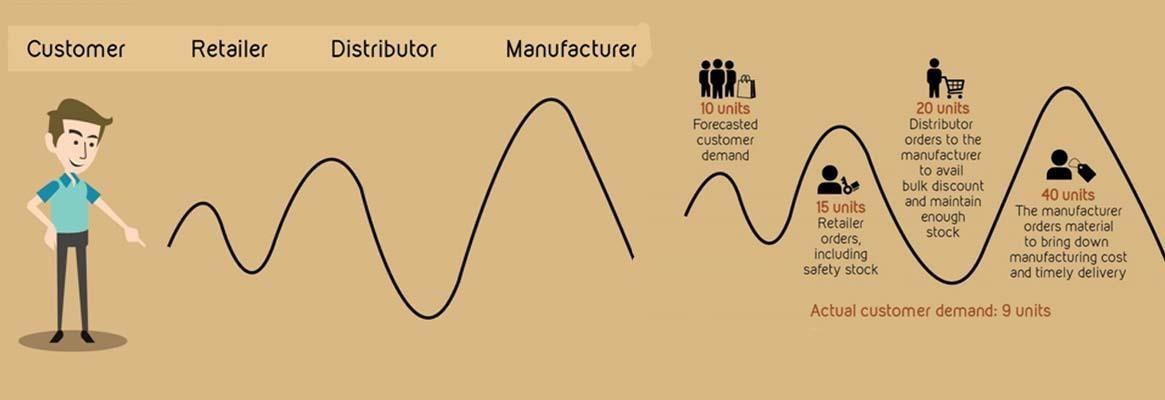
The Bullwhip Effect
In terms of linking theory to practice, it is compulsory to emphasize the theoretical aspects of the bullwhip effect. One of the major impediments in supply chains is the bullwhip phenomenon, also referred to as demand information augmentation (Yang et al., 2021). The bullwhip effect is a supply chain management phenomenon in which supply chain inadequacies are caused by demand projections. Counteracting the bullwhip effect, avoiding multiple demand forecasts and eliminating games in shortage is obligatory (Group B, 2022). Considering the case with a bottle of water production and distribution, a practical example would be the fact that there is a seasonal trend in this product. Moreover, if not controlled well, the level of demand can exceed the ability to supply the item.
Capacity Management
In addition, it is feasible to highlight the concept of capacity management and its practical implication in the case related to the production and shipping of a bottle of water. The objectives of capacity management include quality, costs, flexibility, working capital, and speed (Group B, 2022). Considering the figures, a short-term capacity has time span up to 3 months, whereas a long-term capacity is referred to a period of 12-18 months (Group B, 2022). For instance, using calculations, it is possible to estimate the capacity of the water bottle plant. For this type of enterprise, capacity can be determined in relation to the maximum number of water bottles manufactured in a period of time.
Practical Issues
Concerning the identification of real-world practical issues and problems arising from the case, it can be stated that specific concerns are connected to supplier relationship management. The methodical strategy to analyzing suppliers that deliver goods, resources, and services to a business, as well as each supplier’s commitment to success, is known as supplier relationship management (Amoako-Gyampah et al., 2019). Considering the ideas of how a low level of supplier relationship management can be avoided, instead of reacting, businesses should develop a supplier relationship management plan since a lack of vision can lead to inconsistency. In addition, analyzing customer relationship management statistics might be the solution to answering concerns about strategic suppliers and permissible risks for a firm. In terms of the case, it can be noted that push and pull inventory strategies can suffer due to the lack of proper communication. In fact, without an established system of relationships between customers, suppliers, and other parties, the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chains can be questioned.
Future Recommendations
The supply chain distribution network starts with the providers; thus, evaluating supplier partnerships should be the first stage in optimizing the supply chain. Eliminating links with suppliers that have shown to be liabilities is a straightforward method to strengthen the supply chain. People that wish to optimize their supply chain should consider how quickly their suppliers can finish their requests. People must reorder things sooner to prevent stockouts if a provider needs weeks to finish manufacturing an order. It is critical to examine how soon suppliers can transport orders once they have been finished in order to enhance delivery performance. Furthermore, effective supply networks are compact, cost-effective, and trustworthy; therefore, re-evaluating the supply chain strategy is required if individuals attempt to keep their supply chain expenses down while the procedure stays dependable. Preparation around providers and other elements, such as location, is also a component of successful supply chain management. This guarantees that customers receive their goods on time and reduces supply chain expenses.
Key Learning Points
Referring to a provision of a short summary of the key learning points that the other students in the class should take away, it is feasible to emphasize the importance of building supplier relationships. Moreover, it is proven that establishing collaboration between the customers, end users, and suppliers can positively influence the level of productivity of the supply chain. Even though other essential notions related to supply chain management and logistics were described and discussed in the paper, communication, cooperation, and collaboration aspects should be especially highlighted. The figures, statistical data, analysis, and elaboration of sophisticated schemes, charts, and structures is substantial for a company. At the same time, it can be considered impossible to maintain an appropriate level of quality of a supply chain or logistics infrastructure due to the lack of understanding and a badly established contact channel.
Conclusion
To summarize, according to the definitions, the area of supply chain management and logistics covers a collection of conceptions connected to claiming the accuracy of developing product streams. The bullwhip effect is a supply chain management phenomenon in which demand predictions induce supply chain shortcomings. Supplier relationship management is a rigorous approach to examining suppliers that contribute goods, resources, and services to a business and each supplier’s commitment to success. Because the distribution network of the supply chain begins with the providers, assessing supplier partnerships should be the first step in supply chain optimization.
References
Amoako-Gyampah, K., Boakye, K. G., Adaku, E., & Famiyeh, S. (2019). Supplier relationship management and firm performance in developing economies: A moderated mediation analysis of flexibility capability and ownership structure. International Journal of Production Economics, 208, 160-170. Web.
Gallego-García, S., Reschke, J., & García-García, M. (2019). Design and simulation of a capacity management model using a digital twin approach based on the viable system model: Case study of an automotive plant. Applied Sciences, 9(24), 5567. Web.
Group B. (2022). Journey of a water bottle [PowerPoint slides].
Jia, G. L., Ma, R. G., & Hu, Z. H. (2019). Review of urban transportation network design problems based on citespace. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019. Web.
Koberg, E., & Longoni, A. (2019). A systematic review of sustainable supply chain management in global supply chains. Journal of Cleaner Production, 207, 1084-1098. Web.
Nunes, L. J. R., Causer, T. P., & Ciolkosz, D. (2020). Biomass for energy: A review on supply chain management models. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 120, 109658. Web.
Speranza, M. G. (2018). Trends in transportation and logistics. European Journal of Operational Research, 264(3), 830-836. Web.
Ukko, J., Saunila, M., Nasiri, M., & Rantala, T. (2022). The importance of sustainability engagement in small businesses supplier collaboration. Sustainable Development, 30(1), 1-9. Web.
Vidal, G. H., Villadiego, D. J., & Calle, M. M. (2019). Inventory planning and control with optimization and simulation considerations: A case study. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 12, 13. Web.
Yang, Y., Lin, J., Liu, G., & Zhou, L. (2021). The behavioural causes of bullwhip effect in supply chains: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Production Economics, 236, 108120. Web.
Yawar, S. A., & Seuring, S. (2018). The role of supplier development in managing social and societal issues in supply chains. Journal of Cleaner Production, 182, 227-237. Web.