Introduction
Tesla Motors is an American-based company that manufactures electric trains and cars at affordable prices in the American, European and Asian markets. Its name was adopted from an electrical engineer and physicist Nikola Tesla. This paper will discuss the competitive and financial analysis of Tesla Motors.
Financial analysis
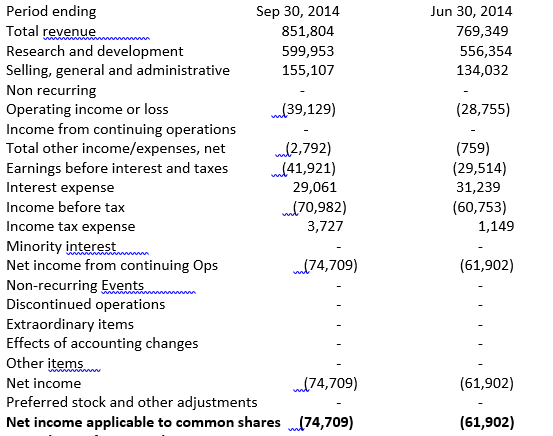
In September 2014, the company had a total net income of US$ 74,709. The company’s records show that this income originated from a 464% profit increase (Tesla, 2013). The company has experienced a rapid increase in its assets. For instance, within five years, the value of the assets increased from 330.78 Million to 2.42 billion. From data taken from the cash flow statement in the year 2013, the company has undergone a general increase in profitability, as shown by the increase in revenue in 2010.
The income statement of tesla motors presented in quarterly data into thousands
Porter’s Five forces analysis
The threat from new entrants
New electric car companies are emerging every day to compete for the share of the market. The company joined the electric company in 2003 and encountered several financial challenges that nearly led to its closure. Tesla faces threats, especially from well-established automobile companies that decide to expand their products to cover the electric car market (Marcovici, 2013). As the electric car market grows and becomes appealing to more consumers, new entrants are expected to increase and offer threats to Tesla (Mangram, 2013).
The bargaining power of buyers
The overall bargaining power of buyers is low significantly low because of the high costs of their products. Electric cars are very expensive, and therefore very few people buy them. However, government incentives and reduced costs of production are expected to increase purchases because they will lower the costs of electric cars.
Threat of substitution
Tesla’s heart of substitution is relatively low because its products are unique, and its innovations give it a competitive advantage over other companies. Possible threats to substitution include public transportation means such as trains and buses. However, many people prefer private means of transportation for their convenience. The increasing demand for electric cars is eradicating the threat of Tesla’s substitution (Marcovici, 2013).
The bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is low because of high competition among suppliers for Tesla supply contracts (Marcovici, 2013). The company purchases various components from more than 200 suppliers. Examples of Tesla’s main suppliers include Panasonic Corp, TI Automotive, Hope Global, Argent, ABC Group, and AGC Automotive (Mangram, 2013). Tesla’s diverse distribution channels also lower the bargaining power of suppliers.
The intensity of existing rivalry
Currently, there is intense rivalry in the automotive industry because of the numerous players who offer different products to meet the needs of customers. However, the electric car industry has modest rivalry because Tesla has positioned itself as an authority through its unique and innovative products. The main Tesla’s competitors in the electric car industry include Nissan, BMW, Audi, Toyota, Ford, Opel, and Chevrolet (Marcovici, 2013).
References
Mangram, M. (2013). The Globalization of Tesla Motors: A Strategic Marketing Plan Analysis. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 4(10), 289-312.
Marcovici, M. (2013). The Tesla Motors way How to Build a Car Manufacturer from Scratch (1. Aufl., Neue Ausg. Ed.). Norderstedt: Books on Demand.
Tesla, N. (2013). A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other Essays. Lanham: Start Publishing LLC.