Analysis of Blockbuster Inc.: Introduction
The Blockbuster Company, once a predominant force in the leisure industry, faced significant competition issues that led to its decline and eventual bankruptcy. In the era of VHS and DVD rentals, Blockbuster enjoyed unrivaled success with its vast network of physical rental stores. Nevertheless, the industry’s landscape dramatically transformed with the advent of online streaming services and digital distribution. This paper explores the challenges Blockbuster faces, examining the rise of new major competitors like Netflix and the strategies Blockbuster employs to adapt and compete in the fast-changing market. By analyzing Blockbuster’s response to these challenges, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamic nature of this industry and the meaningfulness of agility and digital transformation in remaining competitive.
Overview of Blockbuster Organizational Structure
According to the annual report of Blockbuster (2004, p.3), this company established in 1985 by David Cook in the US to provide in-home rental along with retail movie and game entertainment services through multiple distribution channels, for instance, stores, by-mail, vending kiosks, and digital devices. In 2004, this company had expanded very quickly because it had strong supply chain and efficient employees, for example, it had more or less 9,100 stores in the local and international market (it operated in twenty-four countries), and it had more than 84,300 employees (approximately 58,500 staff within the local market and 21,500 full-time staff) in order to carry on business. In addition, Ricky (2007, p.5) stated that Blockbuster became a very successful and market-leading company because the leaders of this company had initiated some effective strategies, such as product diversification strategy and market expansion all over the world. However, this successful company collapsed in 2010 because of mismanagement, leadership crisis, competitive disadvantage, high operating cost, some controversial issues, legal barriers, fall of share price in the stock exchange, and so on. However, the position of this company deteriorated from 2004, and competitors captured its market share significantly, for example, in 2010, Blockbuster had about 4,018 stores in the US to provide movie and game rental service and sale consumer electronics to the target customers (Blockbuster, 2010, p.2).
The Central Issue of Blockbuster Competitors
Throughout the global operation, Blockbuster Inc. has experienced huge crisis from the direct and indirect competitors like Netflix, which disturbed its operation and decreased profit margin in the US market; most importantly, the strategic plans of Netflix had severely affected the business of Blockbuster, for instance, Netflix provided the membership with minimal costs. At the initial stage, Netflix offered its members unlimited DVD rental facilities throughout the month with US$17.99 and developed an online market with no extra payment; therefore, the number of customers increased dramatically within a very short period in the US market (Lam, 2010 p. 2 and (Blockbuster, 2011, p.4). According to the annual report 2010 of Blockbuster, it had faced intense competition from retailers those rent, sell, or trade movies along with games, for example, Wal-Mart, Best Buy, and Target, Apple, Amazon, Gamefly, GameStop, and Movie Gallery, etc.; in addition, it faced stiff competition from Video-On-Demand (VOD) systems (Lam, 2010 p. 2). At the same time, these VOD systems had captured a market share of the home entertainment, which gave the opportunity to the cable operator and other television providers to provide VOD streaming with instant service facilities such as pay/view along with free content to play at once; therefore, more than 80% of the US customers had access to these systems. On the other hand, the following figure compares the operating profit of Netflix and blockbuster more elaborately –
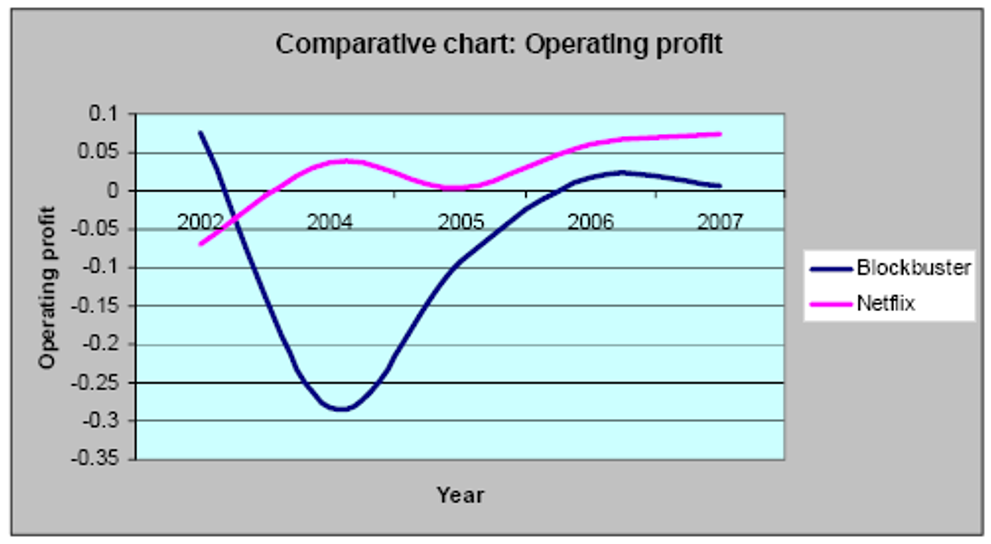
However, there are many other factors accelerated market competition, lost market share, and became bankrupt within seven years, such as conflicts among the leaders, failure to manage human resources, particularly expatriates (Lam, 2010 p. 2). As a result, this company had a need to concentrate on many internal and external factors to save the company from the bankrupt situation, but it failed to meet up these issues, for example, the top management had taken vertical integration and diversification strategy without justifying calculated balancing of costs and benefits (Ricky, 2007, p.7). At the same time, Ricky (2007, p.7) pointed out that Blockbuster bought recently released videotapes through a distributor for more than $70.0 a copy, which was high price considering the concurrent market and increased operating costs, so, it had not financial capabilities to stock enough copies of popular titles.
Most importantly, Ricky (2007, p.7) addressed that target customers and loyal customers were highly dissatisfied with the service of this company due to high price of the services and not to getting products according to their choice; moreover, most of customers interested about substitute less popular titles leave the store without renting anything at all. In addition, near 20% of customers was unable to rent their preferred video and this scenario influenced the top management of this company to form a strategic alliance with the movie studios; however, this strategy was not appropriate while movie studios purchased products from Blockbuster at lower rate and shared profits to boost its inventories of recent releases seven fold. According to the report of Ricky (2007, p.8), alliance with the movie studios permitted Blockbuster to start a triumphant “Go HomeHappy” marketing campaign to help the customer to select right videos from stock, which increased market share for a short time, but the integrate position of this company deteriorated for such steps.
On the other hand, it became hard for this company to carry out business outside the US market because it failed to control movie piracy (illegal copying and sale of movies) in the Southeast Asia zone, which adversely influenced the business, for instance, Pirated DVDs went on sale in Chinese market for a cheap price of $1.0 each (Ricky, 2007). However, piracy had a smaller effect on the video game industry in the US, but it created hindrance and completely damaged other related businesses including the home video game industry; in addition, between 2005 and 2009, it had only one profitable year is 2006 and other years’ profit fell steadily from $5.90 billion to $4.10 billion, and total lost was about 0.5 billion in 2009. Consequently, Blockbuster had reduced business operation in the international market from 2005 as profit margin of this company from foreign market decreased significantly, for example, it had stopped 24 stores in Hong Kong in 2005, and closed unprofitable stores in Germany and Portugal (Lam, 2010 p. 2).
From the above discussion, it can be said that there were too many external and internal factors those affected the business of Blockbuster, but competitors (particularly Netflix) were the main problems of this company to sustain for a long time Netflix had a strong balance sheet with considerable capacity to borrow additional funds if necessary while its debt-to-equity ratio was 0.5%. However, Holguin (2009, p.11-18) compared the financial ratios of Blockbuster and Netflix –
Three Possible Solutions for Blockbuster Organizational Structure
The case analysis of the Blockbuster Inc. collapse has presented the further evidence that the leadership of the company has failed to assess the opportunities and threats of the market, essentials, their perception and opinion to response to the changing dynamics are not enough sharper to take appropriate strategic step in due course. To adopt suitable strategic alignment just in time is the major success factor while quick decision making another unavoidable criterion to coup with the dynamic environments that the Blockbuster Inc. has failed to comply with the degree of market orientation. At the same, time the Blockbuster Inc. case analysis bring in to view that resource based changes take place repeatedly in different manner with rapid shifting environments while technology is taking new shape in everyday that significantly stresses the management to properly address the changes with dynamic capabilities, failure to respond would collapse the company. To overcome the situation, the Blockbuster Inc. possible solution has presented as follows-
Blockbuster vs Netflix: One-Change in Leadership
D’Alessio (2006) defined that in an organization leadership is a reciprocal affiliation among the members of the organization where someone who has capabilities to transform vision of the organization into reality prefer to lead and the others fix on to follow him with mutual interdisciplinary, it is an art to influencing people to provide highest performance at any level. Vugt, Jepson & Cremer (2002, p.3) pointed out that the autocratic style of leadership has enough practical dilemmas to ensure public good, this type of leadership would engage to execute his personal decision that he considers very essential to bring the common good of the organization, for his decision he is not accountable to the team members. At the same time, the group members are directed to ensure their performance as the autocratic leader instructs, there is no option for the group members to make any question regarding the decision of the autocratic leadership. On the other hand, democratic leadership always ask for group member’s opinion for making any further decision to bring collective welfare with joint decision making process and this type of practice to integrate group members would contribute to accelerate overall group performance by enhancing information and experience sharing. Although there are both problem and prospect for all types of leaderships, in the reality of Blockbuster Inc., the company would be capable to overcome most of its crisis by replacing its autocratic leadership with democratic practice,
Haryanto et al. (2008, p.5) pointed out that under the leadership of Huizenga the company has gained a stable growth, John Antioco joined Blockbuster Inc. as its CEO in 1997, under his leadership the company reached at it top performance and he occupied his position more than a decade as an autocratic leader without emphasizing board’s direction to cost cutting. He put more emphasis on non-strategic assets and led an aggressive investment drive on the online version to compete with Netflix, in the time of Blockbuster’s revenue reducing, Antioco continued to raising his compensation package. John Antioco received a salary of US$ 7 million, 5 million stock options, and US$ 27 million from the restricted stock in 2004 while Blockbuster Inc. recorded a loss of US$ 1.25 billion, the annoying situation generated panic among the large shareholders like Carl Icahn, who claimed Antioco to pay large dispute following the failure to merger with Hollywood Entertainment. As a result, the relation between Antioco and Icahn turned into hustle and opponent to each other, without caring the organizational greater interest and struggle with competitors; they started to fight against each other in the internal environment rather than external. Although the boards of directors were not happy with Antioco’s performance, but they had not taken any step to dismiss him or any other organizational step.
The internal battle of leadership in the Blockbuster Inc. supersedes the company’s attention to spotlight on the external combat with the competitors, rising conflicts seriously hampered normal performance of Blockbuster, and distorted noteworthy physical and financial resources and the company lost most of its potentials to prevent crisis caused by CEO. Replacing the autocratic leadership of Mr. John Antioco with democratic leadership and integrating group options could be an alternative from Blockbuster Inc. to overcome the stagnant situation.
Blockbuster vs Netflix: Two-Change in Organizational Environment
Lam (2004, p.1) argued that there are three dimensional relationship between the organization and its innovation that strongly bring organizational changes from different perspectives, firstly innovation influence to bring organizational structural change, secondly innovation is the course of action to develop organizational skills and knowledge and finally by adoption of innovation the organization reaches at its capacity building. The vast area of existing literature of organizational behavior has aimed to address the question whether the organization could demonstrate its ability to change and adapt to foremost alternating technological change as well as enabled itself to covey environmental shifts, as a result, has the organization faced radical renovation in the organizational structure and human resource selection process. This is a vital consideration for an organization to assess its strength of strategic adaptation with the continuous changes in the business environment, failure to do so would significantly destroy the organizational capacities for learning, value creation, timely response to the market demands, and potentials to shaping organizational alteration related to the technological changes.
Lam (2004, p.3) also added that the capabilities to integrate with the innovation with right use of creative resources along with new technologies is the precondition for an organization to bring its business success, on the contrary, the opening of any new technology always comes with complex opportunities and big challenges for the organizations. It is emergence for the managerial employees to learn the practice of new technology and bring new form within the organizational structure that would capable to generate new product and services adopting new technology within the changed environment. The contingency theoreticians urged that it is essential for modern business to aware about the structural diversity of the organization to coup with new technology and environmental tasks, such to compliance necessitate for complex dynamics of the technology and product market with rising uncertainty and unpredictability; flexible organizational structures with less bureaucratic than more organic could resolve this problem.
Barnard (2008) added that the Blockbuster Inc. has been overloaded with extra burden of excessive employees both in home and abroad while digital distribution process could enable to reduce its workforce in a significant lower level that ultimately contribute the company with tremendous cost cut. At the same time, the company has the potentials to restructure its human resource putting more emphasis on the technically fit employees that aimed to change the environmental change at its workplace. An a part of alternative strategy to overcome current crisis, Blockbuster Inc. could adopt enhanced emphasis on research and development that would aim to develop new product and services, specially digital product; rather than copying the product and services of Netflix, it is essential to introduce to engage own creativity of the own. As the pioneer of movie rental service Blockbuster Inc. has greater experience with the test and choice of the customers as well as market needs, where Netflix is the newcomer in relation of Blockbuster Inc. Thus, digitalizing of the overall organizational environment of Blockbuster Inc. would remove the structural faults and deliver the appropriate solution for the company to sustain in the market with suitable growth that would provide further potential to maximize its revenue
Blockbuster vs Netflix: Three-Change in Merger and Acquisition Strategy
Akgöbek (2012, p.3) pointed out that in the modern globalization era merger and acquisition is a sustainable growth strategy that produce better solution to encounter with worse situation among the competitors to ensure pace within the competitive environment along with changing market dynamics. The conceptual framework of corporate mergers and acquisition have engaged to explore the real life scenario on which the companies are forced to formulate strategic alliances, in the era of ICT with the changing nature of information flow has influenced corporate world to evaluate any amalgamation with more accuracy that may not bring any negative outcomes. Thus, both the companies are most likely to be better informed regarding the strength and weakness of the company for which they are going to form strategic alliance, there should be at least one rational logic for a successful merger and acquisition that would contribute the company to overcome concurrent dilemmas and assist to gain both organic and inorganic growth.
In the journey to the movie and game rental market Blockbuster Inc. has vast experience of merger and acquisition, although all of the M&A (Merger and Acquisition) efforts are not enriched it with very good experiences, but at the present crisis, merger and acquisition could be a right solution to overcome the crisis. Almeida (2011) explored that the history of the Blockbuster Inc. evidenced the company leads its first acquisition in 1994 by purchasing Viacom Inc. media company with US$ 8.4 billion with the aim to strengthen its performance as a giant in this sector, in 2003, it acquired the mainstream stake of the Cinemanow.com to address customer’s needs to downloading opportunity. In 2007, the company resolute to acquire MovieLink, to address the market demand for pay-per-view downloads of movies; in 2008, it attempted to purchase Circuit City with about $1 billion and raised question how the company would be benefited from such a deal. The company also attempted to acquire Hollywood Entertainment Corporation with big deal, but was rejected due to lack of regulatory matters, at this point Blockbuster Inc. needed to have aggressive drive to commence merger with Hollywood Entertainment Corporation or any other competitor to protect big collapse.
Best Solution for Blockbuster Inc.
After long analysis of the concurrent position of Blockbuster Inc., it is essential to identify the best solution that would positively contribute the company to ensure exact direction to overcome the crisis, the company already filled for Chapter 11 and the liquidation is not so far. Thus, under such crucial condition a strong strategic association through merger and acquisition could protect the company from bankrupt and could provide enhanced opportunity to sustain, as the company has lack of present resources for innovation and new product development, it is essential to manage and administer present situation at a form of strategic alliance of merger and acquisition. This study has presented three different solutions for Blockbuster Inc. to overcome concurrent crisis, the implication of first two solution is unavoidably linked with enough financial resources which are not available to the company, but the third solution is the way out that would generate cash inflow for further improvement. Thus, third solution ‘changing the merger and acquisition’ direction for strategic choice is the best solution for Blockbuster Inc.
Blockbuster Organizational Structure & Implementation of Solutions
The leaders of this company should implement the strategic solution in order to solve the main problem of this company; however, this report suggests that merger and acquisition strategy would be effective strategy for Blockbuster because it has not enough financial capabilities to carry on business with its own resources and it needs help to introduce new technology. However, it should change organizational structure to meet the criteria of the new firms and increase accountability of the current leaders because they have to manage the company with limited resources.
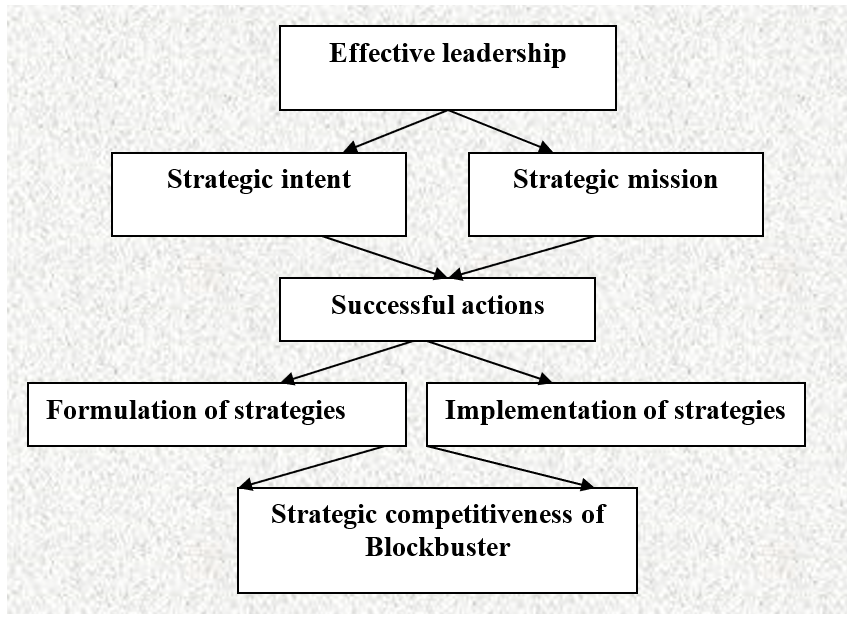
Blockbuster Inc.: Strategic Leadership
Subsequent figure shows strategic leadership and management process of Blockbuster, which concentrates on the mission of this company –
Blockbuster Inc.: Evaluation and Control
The leaders of Blockbuster should evaluate the performance of the stores in the US and foreign market and assess the improvement in profits margin (monthly basis) to avoid any further crisis and to initiate prompt corrective measures; therefore, unit managers would organize periodical meeting with the workers of retail stores to monitor their activities and find gradual development of them. Moreover, the leaders of Blockbuster should recognize the uncertainty in terms of return on investment capital and it should categorize profitable and non-profitable stores after surveying market; additionally, the managers can review the market survey reports to assess the impact of mergers and acquisition on the company and to broaden its service range with innovative and diversified product line.
Analysis of Blockbuster Organizational Structure: Conclusion
To re-establish the company, it should ask rescue package from the government of the US because it has many retail outlets those could run with this fund and could become profitable company by implementing new alternative strategy. In addition, it should change promotional activities, take the brand development program and should consider the feedback of the consumers to change organizational policies and behaviors accordingly. On the other hand, new leaders must have to work with integrity and they must not take large remuneration because Antioco received $51.6 million in compensation for 2004 without considering the ethical codes. Furthermore, it is essential for the company to build a sustainable business model to face the challenges of competitors without eroding value, for instance, it should introduce new technologies to decrease operating expenses and to develop customer services.
5 Key Reasons Why Blockbuster Failed
This table summarizes the reasons for Blockbuster’s failure with an explanation for each cause:
References
Akgöbek, I. (2012). Mergers and Acquisitions as a Growth Strategy. Web.
Almeida, J. C. D. (2011). Blockbuster: The Fall of a Giant.
Barnard, A. (2008). IST 301 – Section 003 – Final Project. Web.
Blockbuster. (2004). Annual report 2004 of Blockbuster. Web.
Blockbuster. (2010). Annual report 2010 of Blockbuster. Web.
Blockbuster. (2011). Annual report 2011 of Blockbuster.
D’Alessio, F. A. (2006). Business Leadership Review III:. Web.
Haryanto, A. Song, H. Lu, Y. Aybar, Y. (2008). Business leadership in changing time Blockbuster Inc.
Holguin, E. (2009). Competition in the Movie Rental Industry in 2008: Netflix and Blockbuster. Web.
Lam, A. (2004). Organizational Innovation.
Ricky, R. (2007). Brief Marketing Strategy of Blockbuster.
Vugt, M. V. Jepson, S. F. & Cremer, D. D. (2002). Autocratic leadership in social dilemmas: A threat to group stability, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 40 (1). Web.