Introduction
“The time is always right to do what is right,” said Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., one of the most famous civil rights leaders. His words expressed the hopes of many people for justice, fairness, and equal opportunity for African Americans. The civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s changed the face of American culture forever, and we all live with the consequences of it. It has influenced all spheres of life – educational and law enforcement systems, public space, and cultural beliefs and ideals.
Main body
There is nothing more important than equal opportunities in education because a good education provides opportunities for social growth. However, in the 1950s, schools in the south were segregated; Black families often paid a “black tax” to support their underfunded schools; Black teachers had lower salaries than white teachers (Ramsey, 2017). In 1954, the court case of Brown versus The Board of Education blocked segregated schools as unconstitutional. Not everyone was happy with this decision; in Arkansas, the National Guard, on Governor Orval Faubus’s orders, blocked the school entrance for 12 black teenagers. They were known as The Little Rock Nine, and they had to fight to attend school for 23 days (“The Little Rock Nine”). This incident inspired other African Americans to stand up for themselves and oppose segregation in other public areas.
A striking historical example of the division of public space was the Montgomery city code that required all public transportation to be segregated. Black people had to sit in the colored section and give up their seats for White people if needed. That is what happened to Rosa Parks on December 1st, 1955, but she refused to give up her seat to a White man, which led to her arrest and conviction (“Rosa Parks”). It sparked a huge backlash against the Montgomery Bus Company and inspired the Montgomery Bus boycott. It was a peaceful protest headed by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. when Black people refused to use buses and traveled on foot (“Montgomery Bus Boycott”). The bus boycott showed the ability of nonviolent mass protest to challenge racial segregation successfully and was used as an example for other southern demonstrations that followed.
After the Montgomery boycotts, Martin Luther King became a significant figure in the black community who changed the American culture and made many people believe in themselves and the possibility of equality. His legendary speech, I Have A Dream, inspired generations of Black and White people to fight for equal treatment for everybody (“Martin Luther King, Jr.”). Dr. King organized many protests around the country, and because of him, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the 1965 Voting Rights Act were successfully passed into law (Nationa Geographic, 2020). Maybe most importantly, he influenced the minds of generations and laid the seeds of mutual understanding and mutual respect.
Conclusion
The civil rights movement caused a wave of repercussions in American culture and changed our world. Neither education nor the public sphere and culture will be the same as before this movement. Fortunately, regardless of race, most Americans view the impact of the fight for equal rights as positive.
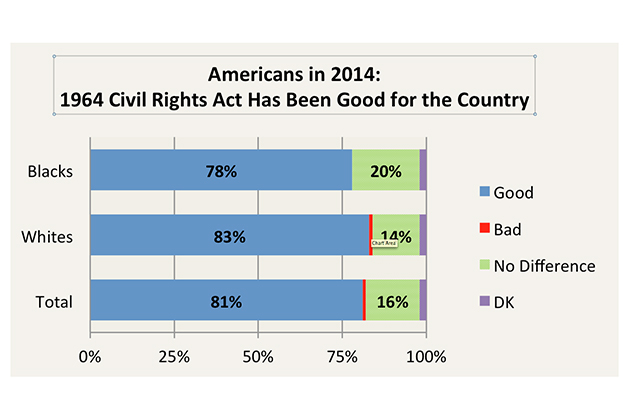
This speaks of the most crucial change that has happened and is happening in the souls and heads of people. It’s never too late to do the right thing and continue the changes stated for our future.
Works Cited
“Martin Luther King, Jr.-Facts and Information.” Culture, National Geographic, Web.
“Montgomery Bus Boycott.” History.com, A&E Television Networks.
“Montgomery Bus Boycott.” Martin Luther King, Jr. Encyclopedia, Stanford University: The Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute.
“Rosa Parks.” Biography.com, A&E Networks Television, Web.
“The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.” Archives.gov, Web.
“The Little Rock Nine.” National Museum of African American History and Culture.
Ramsey, Sonya. “The Troubled History of American Education after the Brown Decision.” The American Historian, 2017, Web.