Introduction
Operations management (OM) is defined as the design, operation, and improvement of the systems that create and deliver the firm’s primary products. Operations Management is concerned with the management of entire system that produces or delivers a product. Operations Management includes certain decision making that has three aspects to it; Strategic or Long Term Decisions, Tactical or Intermediate Term Decisions and Operational Planning & Control or Short Term Decisions.
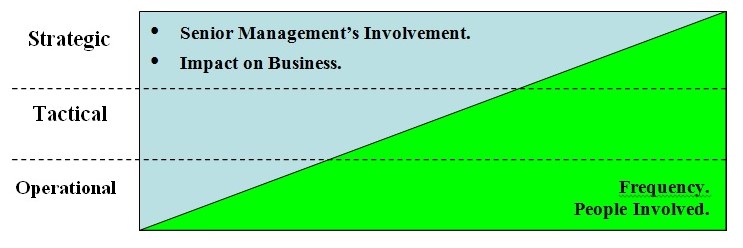
Operations Management in organizations has its own place just like any other department but companies like the one I have chosen to base my study on that is Pearl Oriental Innovation Limited, such companies are logistics based and operations management is the key to the efficient running of the organization. In order to get a deeper grasp of this subject it is important to consider the current issues related to operations management because these will form the groundwork for understanding the further study as related to the chosen organization. The current issues related to operations management are pivotal to all organizations where this department is essential and the issues are as follows:
Effectively consolidating the operations resulting from mergers:
- Mergers & Acquisitions.
- Economies of Scale & Economies of Scope.
Developing flexible Supply-Chains to enable mass customization of products and services; and also to be able to mass-distribute.
Managing global supplier, production and distribution networks:
- Outsourcing.
- Control versus Autonomy.
Increased “commoditization” of suppliers:
- Plug Compatibility.
Achieving the “Service Factory”:
- Personalized Services.
Enhancing Value Added Services:
- Production Progress.
- Advance Warnings.
- On-Site helps.
- Competent Helpline.
Making efficient use of Internet Technology:
- Seamless Integration of Internet with Physical Operations.
Achieving good service from Service Firms:
- Customer Experience.
- Striking a Balance between Service Focus & Manufacturing Focus.
Background to the Company
Pearl Oriental Corporation group of companies is the major and controlling shareholder in Pearl Oriental Innovation. The company’s core business is in logistics only but they have been diversifying into energy and resources in order to expand business and make more money. The company has been into coal mining and other energy resources lately. The major purpose for this diversification is long-term and sustainable profits to the company in a tangible and an intangible form. The company has been acquiring certain other companies in order to widen their base for production and profits. The company has also been involved in strategic partnerships, all for the same reason of increasing production capacity and profits.
The Pearl Oriental Logistics is their core business and this was established recently in 2001 and it deals with domestic logistics whereas the company has international logistics as well so it has complex operations. This company provides warehouse management, distribution within provinces, haulage transportation and since it’s established in Hong Kong the company has established nation-wide logistics in mainstream cities like China, Beijing etc. The company has 100,000 square yards warehouses in China that are rated high for national safety and they have advanced logistics including machine run or manual fork lifts, product safety, loading, transportation, bar-coding, tracking devices, palletization etc.
Operations strategy and Competitiveness as applied to Pearl
The topic according that will be applied to the chosen organization and then will form the basis for the analysis of the aspects of the theory chosen is operations strategy and competitiveness which will automatically include product design, process selection and manufacturing, total quality management, strategic capacity planning and aggregate planning.
Obviously the company has its operation strategies that enable it to satisfy their customers and also the final consumer in the market. The efficient execution of all operation and processes has made the company huge and successful and that shows the company is operating within the competitive dimensions that form the base point for a successful operations strategy. Competitive dimensions of a successful operations strategy are more than visible in this organization which confirms the reason to the success of this organization. These dimensions include cost, product quality and reliability, delivery speed & reliability, coping with changes in demand, flexibility in supply chain, ‘Design-to-Market’ Speed and other product-specific criteria like the following:
- Technical Liaison & Support.
- Meeting a Launch Date.
- Supplier After-Sales Support.
- Other Dimensions.
Operations cannot (generally) excel simultaneously on all competitive dimensions. Management has to decide which Performance Parameter is critical to organization’s long-term success & competitiveness, and thus has preference over other relatively less-critical aspects of the strategy. Straddling occurs when a firm tries to match the benefits of a successful position taken by another firm, while maintaining its own existing position. Pearl Corp. has its operations multinationally distributed and it requires efficient communication and operations management. The company will have delivery speed & reliability, coping with changes in demand, flexibility in supply chain and ‘Design-to-Market’ Speed as its performance parameters since it is operating in major cities and for major companies it has to make sure delivery is on time in order to generate goodwill and increase reliability in the market to get more business. Obviously cost is essential so that the customers get lower prices with good quality business but that can be compromised to a certain extend since other parameters like delivery on time, reliability, quality management, flexibility in the supply chain and design to market speed are essential for the customers to enable good business for the industrial customers and these are the performance parameters for Pearl itself since its these parameters the company is capitalizing on and these have led the organization to the success it has achieved today.
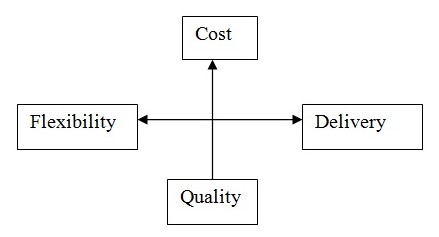
Quality rganizations need to deal with trade-offs in performance parameters and competitive dimensions for having a successful business. For example, if we reduce costs by reducing product quality inspections, we might reduce product quality.
For example, if we improve customer service problem solving by cross-training personnel to deal with a wider-range of problems, they may become less efficient at dealing with commonly occurring problems.
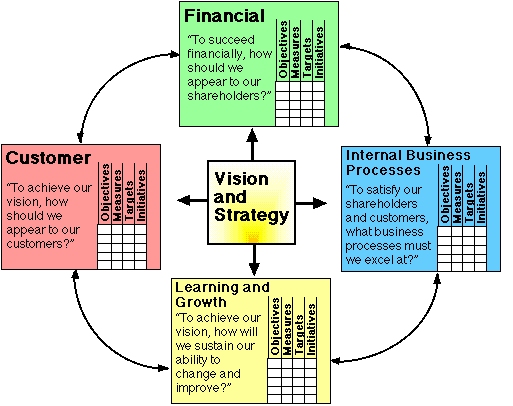
Organizations like Pearl can use Generic Strategy Map Template- Balanced Scoreboard to make sure the business is performing within the competitive dimensions and the performance parameters are being met carefully. It enables high degree of accuracy in explaining Customer Value Proposition, and creates awareness regarding internal processes, proficiencies and know-how—— that must be linked to that Value Proposition.
The scorecard essentially lines up your goals and helps the members of your organization go in the same direction to meet those goals. The Balanced Scorecard has four perspectives:
- Financial (This is to succeed financially and shareholders play an important part here since their holdings will be affected)
- Customer (Customer is the king!)
- Internal (The operations and process to specialize in and satisfy stakeholders)
- Learning & Growth (Change is an essential component to success)
Mission he Balanced Scoreboard
Logistics is all about handling the products of the customer and then delivering it on time in order to ensure efficient running of the customers business at the end of the day. Keeping a balance between these four perspectives enables a business to grow with time and achieve more in the market than expected. Pearl is a huge company and with nationwide operations and logistics management so a balance between finance, internal processes, customer and change are required and evident in the processes of the business. The company has been acquiring and forming strategic partnerships to learn and then grow plus expand its operations in more countries. Acquisitions provide production capacity, human resources and most importantly financial resources to the company so that they can handle finances in a better way and also grow. When finances are good and the company is growing the actions are undertaken to satisfy the customers only and internal sources are taken care of by the expansions only. Thus, all four perspectives set in a balance and enable the company to grow and expand successfully.7
Another strategy that is the Kaplan and Norton’s generic strategy Map that has suggested two theories under the financial perspective of the balanced map as explained above. The two theories as suggested under the financial perspective are as follows:
the Productivity Strategy is generally made up from two components:
- Improve cost structure: Lower direct and indirect costs.
- Increase asset utilization: Reduce working and fixed capital.
Pearl has already been doing that by acquiring and forming strategic partnerships with companies since that has helped them improve their cost structure and increase asset utilization and that has enabled them to expand further and increase their reliability. Since they have advanced logistics and operations to manage their logistics systems and enable better service to customers.
the Revenue Growth Strategy is generally made up from two components:
- Build the franchise: Develop new sources of revenue.
- Increase customer value: Work with existing customers to expand relationships with company.
Pearl through its acquisitions has now started to diversify its business into energy and resources since it has a higher return in business. Diversification backs up the core business as well. This has not only improved goodwill in the market but through their partners and acquisitions they are now able to provide nationwide services of warehouses and logistics in all the mainstream cities like China, Beijing etc.
Kaplan and Norton have suggested theories under the internal perspective of the balanced map as well. The Internal Perspective explains business procedures and the particular activities that the organization have to accomplish to sustain the customer value proposition:
Product Leadership Strategy: Leading Edge Innovation Process.
Pearl is an innovation company and they are quick to accept to changes and also set the trends of the market since as the name suggests Pearl Oriental Innovation Limited is all about innovation in logistics and warehouse management. They are leading their way to the top and they are a huge enterprise operation nationwide in all mainstream cities.
Customer Intimacy Strategy: Excellent Customer Management Process.
Pearl has believed in providing the customers what the want and due to that they have on-time delivery and flexibility of supply chain as their most important performance parameters. Customer relationship management systems have also helped enhance customer intimacy.
Operational Excellence Strategy: Excellent Distribution, Efficient Operations etc.
Pearl is all about operational excellence since they haven’t compromised on this perspective at all and they have advanced logistics to support their business including efficient operations and strategies to complement their business.
Regulatory & Environmental Excellence: Compliance with Govt. Regulations & Community Expectations.
Since Pearl is operating in different cities and areas so every area has its own set of rules and community expectations but Pearl integrates into the culture and traditions of these cities thus following all legalities and meeting all community expectations has made Pearl a popular organization. It is essential to meet all legalities and community expectations in order to generate goodwill and attract good business.
Kaplan and Norton have suggested theories under the learning and growth perspective of the balanced map as well and there are three principle categories of intangible assets needed for learning & growth:
- Strategic competencies, skills & knowledge. Pearl through its acquisitions has given its existing employees to learn and grasp the changes of the new environments in each acquired organizations thus ensuring enormous strategic competencies in the employees.
- Strategic technologies, information system, toolbox, networks. Pearl is all about innovation and technology is the lynchpin to all operations of the company.
- Climate for action, is required to encourage, give power to and support the workers for successful plan achievement. Pearl is doing this by bringing in more human resources, financial resources and opportunities to learn and change therefore increasing the opportunities of existing employees to grow personally, professionally and financially thus creating a climate for action.
Total Quality Management
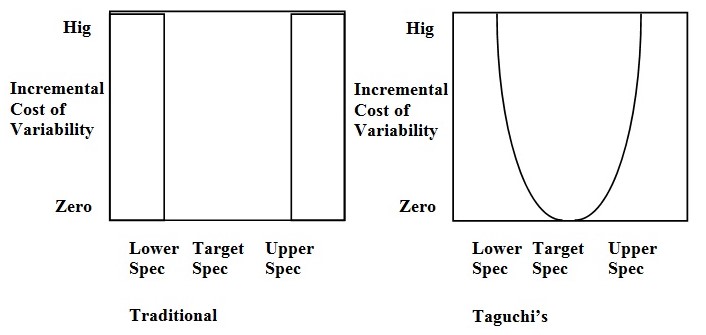
TQM is managing the entire organization in such a way that it excels in all dimensions. Taguchi’s View of Variation explains better the quality management within a company and also that its essential especially for Pearl since TQM will help them achieve zero defects in their logistics and the warehousing services they provide and that will further help them achieve operational excellence. Although the company already has advanced logistics and quality management since it is evident in their efficient systems and successful integration in different cities and establish nationwide logistics and warehouse services. Traditional view is that quality within the LS and US is good and that the cost of quality outside this range is constant, where Taguchi views costs as increasing as variability increases, so seek to achieve zero defects and that will truly minimize quality costs. Zero defects is a very opular theory but its important that organizations implement it in manufacturing and companies like Pearl that deal in warehousing services and logistics need it to since any error or defect in storing the customers product can cause discrepancies and problems or losses for the customer’s business.
Quality management is essential because if the operations falter and fail to perform as expected then it is obvious that Pearl might loose its customers and also its goodwill that has generated with time. The efforts the company has been making continuously to grow and expand through acquisitions and partnerships can all go to waste if there is any failure of performance in the operations and logistics of the warehouse such as delivering on the wrong time or in the wrong packing etc. These failures can cause problems for Pearl but it is evident that they have taken care of all these matters and due to this they have been performing exceptionally well in all the areas. They have also considered all costs of quality so that quality remains exceptional and these costs are as follows:
- Appraisal Cost: Inspection, Testing, Audit, etc.
- Prevention Cost: Sum of all costs to prevent defects – cost to identify defects, cost to implement corrective actions, cost to redesign the product, etc.
- Internal Failure Cost: Costs for defects incurred within the system – Scrap, Rework, Repair, etc.
- External Failure Cost: Costs for defects that pass through the system – Customer Warranty Replacement, Loss of Customer or Goodwill, Complaint handling, Product Repair, etc.
Service quality management applies to Pearl since they are providing a service of warehousing and logistics to their customers. Service quality management covers the following aspects:
- A perceived service quality questionnaire survey methodology. This can help to understand the competitive dimensions and failure of the company since
- Examines “Dimensions of Service Quality” including: Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, Empathy, and Tangibles (e.g., appearance of physical facilities, equipment, etc.)
- New version of this methodology is called “e-Service Quality” dealing service on the Internet.
- Dimensions of Service Quality on the e-Service methodology include: Reliability, Responsiveness, Access, Flexibility, Ease of Navigation, Efficiency, Assurance/Trust, Security/Privacy, Price Knowledge, Site Aesthetics, and Customization/Personalization.
Supply Chain Flexibility
Supply Chain is all activities, functions, entities and stages associated, directly or indirectly, with the flow (and transformation) of goods, funds and information, are collectively called Supply Chain. Pearl considers flexibility of its supply chain as a competitive dimension. Supply Chain has a set flow and includes movement of Products, Information, and Funds. Customer is an integral part of the supply chain. It is more accurately termed as “supply network” or “supply web”. The typical stages of a supply chain include: customers, retailers, distributors, manufacturers, suppliers. All stages may not be present; number of intermediaries may vary from channel to channel. For e.g. direct selling and online presence – Dell. There are specifically three kinds of flows in a supply chain and they are as follows:
Upstream:
- Material: Products, Parts.
- Information: Capacity, Delivery Schedules.
- Finance: Invoices, Pricing, Credit Terms.
Internal:
- Material: Raw Material to Finished Goods.
- Information: Production Plans, Labor Scheduling, etc.
Downstream:
- Material: Returns; Repairs; After-Sales Services.
- Information: Customer Orders, Point-of-Sale Data.
- Finance: Payments.
Pearl pays special attention to its supply chain since its complex and critical to the success of their business. On time delivery is one of their competitive dimensions and performance parameters so supply chain plays an essential part in their business and most importantly its warehousing services and advanced logistics which are backed by an effective supply chain.
An effective supply chain implements all of its horizons for confirmation of the effective inculcation of the supply chain into the operations of the business. There are three segmentations and they are as follows but each one is important to be implemented for having a successful supply chain:
Internal Supply Chain:
- Includes internal functions like: Product development, Manufacturing, Marketing, Operations, Distribution, Finance, Customer service, etc.
Organizational Supply Chain:
- Includes Internal Supply Chain, and
- Immediate Suppliers and Immediate Customers.
Extended Supply Chain:
- Supply Chains of the entire network of companies that work together to design, produce, deliver, and service products.
- Suppliers’ suppliers, Suppliers, Manufacturers, Transporters, Warehouses, Retailers, Customers, Customers’ customers.
Pearl has a very efficient supply chain that encompasses the internal operations and organizational supply chains that is connection with the customers and also suppliers so that the customer’s products can be stored the right way and delivered on time. The company also has an extended supply chain to network with all the elements in their supply chain which includes connections between all the operations of the company in different cities so that customer gets quality service and the company enjoys operational excellence.
Supply Chain has to be flexible and efficient thus it has certain objectives to be met in order to ensure efficient and effective implementation of the supply chain in all the operations of the business. The objectives of the supply chain are as follows:
- Maximize overall value or the surplus created.
- Supply Chain Value or Surplus: is approximately the final product worth to the customer (total revenue) minus the total cost the supply chain expends in filling the customer’s request.
- Sources of Revenue: the end customer sales; rest everything is capital exchange.
- Sources of Cost: flows of information, products, or funds between stages of the supply chain.
- Supply chain success should be measured by total supply chain profitability, not by the profits at any individual stage.
- Supply chain management is the management of flows between, and among supply chain stages to maximize total supply chain profitability.
Supply chain is important and essential. The design and management of SC flows (product, information, and funds) affects the success of a Supply Chain. For e.g. Dell: success. Quaker Oats (Snapple): failure to integrate the Downstream. SC decisions can play a significant role in the success or failure of a firm. For e.g. Walmart vs K-Mart.
Montgomery Ward vs SEARS
Supply chain requires efficient decisions to be made at the right time for the desired outcome and it has four phases:
- Strategy or design phase.
- Planning Phase.
- Operations Phase.
- Monitoring, Measurement, and Control Phase.
Pearl as a logistics and warehousing company does devise a strategy and plan in order to ensure the right implementation from the beginning only but it pays most attention to the operations phase. This is the phase where the rubber hits the road. SC structure & operating policies are determined; the goal is to implement the operating policies as effectively as possible. The time horizon is weekly or daily or even shift. Middle & Lower Management takes charge mostly. There is much less uncertainty due to short time horizon and decisions regarding individual customer orders; regarding production is a priority. It allocates orders to inventory or production, sets order due dates, generates pick lists at a warehouse, allocates an order to a particular shipment, sets delivery schedules, places replenishment orders, etc. Storage; Distribution; Quality Checking; etc are also included.
Hau Lee’s concept of Supply Chain Management is also important and essential for having an efficient supply chain. Hau Lee’s approach to supply chain (SC) is one of aligning SC’s with the uncertainties revolving around the supply process side of the SC.
A stable supply process has mature technologies, and an evolving supply process has rapidly changing technologies. The types of SC are as follows:
- Efficient SC.
- Risk-Hedging SC.
- Responsive SC.
- Agile SC.
Conclusion
Pearl has been a successful logistics company that deals in warehousing services and it has been diversifying into energy and resources as well but the basis for the company’s success has always been operational excellence and successfully implemented operations strategies and competitive dimensions. The topic that was chosen has been explained in relation to the chosen company and the culmination point would be that Pearl is a successful company that is operational excellence personified.
Works Cited
Chase, R.B and D.A. Garvin. “The Service Factory.” Harvard Business Review, 1989, pp. 61-69.
Hayes, R.H and G.P. Pisano. “Beyond World Class: The New Manufacturing Strategy.” Harvard Business Review, 1994, pp. 77-86.
Hayes, Robert; Gary Pisano; David Upton and Steven Wheelwright, Operations, Strategy and Technology: Pursuing the Competitive Edge. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
Hill, T.J. Manufacturing Strategy-Text and Cases. Burr Ridge; IL: Irwin/McGraw Hill, 2000.
Hopp, W, and Spearman, Factory Physics: A New Approach to Manufacturing Management. Burr Ridge IL: Irwin/McGraw Hill, 2000.
Johnson, G. and Scholes, K. Exploring Corporate Strategy, 5th Edn, Hemel Hempstead: Prentice Hall International, 1999.
Journal of Operations Management. Washington D.C: American Production and Inventory Control Society, 1980-current.
Kaplan, Robert S; and David P. Norton. The Strategy Focused Organization. Cambridge, M.A: Harvard Business School Press, 2001.
McGahan, A. “How Industries Evolve – Principles for Achieving and Sustaining Superior Performance”. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, 2004.
Skinner, W. (ed.) “Special Issue on Manufacturing Strategy.” Production and Operations Management 5, no. 1 (1996).
Slack, N. and M. Lewis, Operations Strategy. Harlow, England and New York: Prentice Hall, 2002.
Winter, S.G. “Knowledge and competence as strategic assets”, in Teece, D.J. (Eds),The Competitive Challenge: Strategy for Industrial Innovation and Renewal, Harper & Row, New York, NY, 1987, pp.159-84.
Zander, U., Kogut, B. “Knowledge and the speed of transfer and imitation of organizational capabilities: an empirical test”, Organization Science, Vol. 6 No.1, 1995, pp.76-92.