Project Summary
This project aims to enter the American market with the Australian catering company Luus. The project has various quantitative and qualitative objectives. First, it is necessary to go to the California region, impose competition on American Range, build a warehouse and service center, and achieve $500,000 in sales in six months. After that, it is necessary to conclude contracts with 2-3 distributors. California was chosen because of its demographics. Cost and time are essential priorities for any project; however, entering a new market, including international, should first of all gain positive reputational points. In this regard, the most important priority will be the company’s performance, which will gain the first customers’ trust and gain a positive image in the market. As a result, one of the main criteria for success is the recognition of the Luus brand in California and the creation of networking. The brand’s strength will allow more and more new customers that provide revenue. Finally, the revenue itself is also a criterion for success and implies reaching a specific limit of 500 thousand dollars six months after the start of the project.
Work Breakdown Structure
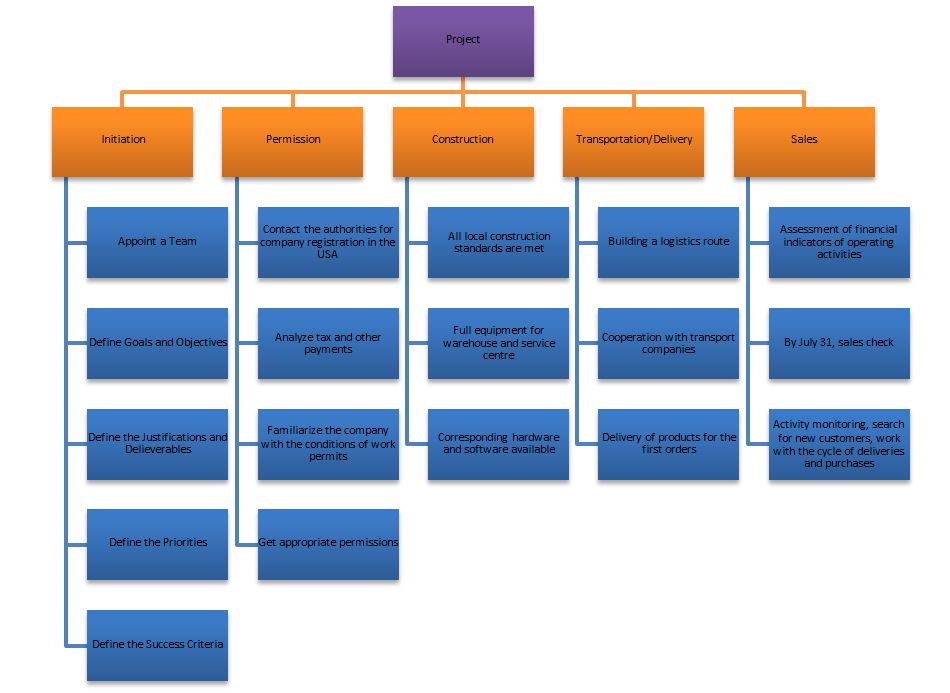
Since the scope of work, main tasks, and objectives, as well as success criteria and results, have been defined for this project, it is possible to divide the project structure into more minor elements. For this, a unique tool is used that reflects the hierarchical structure of the project, called the work breakdown structure (WBS). In this situation, it is necessary to identify the work items and products of the project process for integration into the usual work processes of the company. The project will last in several stages, reflecting the work breakdown structure, describing the project as a finished result, and gradually disassembling them into more minor results to improve monitoring and control (Larson, 2020). First of all, it is necessary to determine the main approaches used when creating a WBS, taking into account the specifics of the project.
Luus needs to enter the international market; California was chosen as the first possible location due to demographics. As a result, the company’s primary activity under the project, not related to its theoretical basis, will be aimed at obtaining appropriate permits to register a company in the country. Legal and political external factors, notably different US tax rates for multinational companies, play a role in this case. This type of taxation is constantly undergoing various changes, most often due to the problems of lost profits that these companies bring to the government. As a rule, the changes concern an increase in the corporate tax rate to a single level, exemption from tax on dividends, but at the same time taxing the entire world income of the company (Clausing, 2020). This information will be critical for the company concerning predicting the quantitative indicators of financial performance, one of which is the criterion for success.
After receiving the appropriate permits, the company must begin building a service center and warehouse to help conduct operations in California. As with the previous point, most of the questions here are related to the legal aspects of building compliance with safety conditions, sanitary standards, and much more. In addition, the purchase of complete equipment and software will be required, which implies high costs at this stage of the project. When purchasing the appropriate equipment from the company, the management should also consider the costs of transportation and logistics, the knowledge of which will allow further establishment of a route from Australia to America. Here, the transition to the next stage of the hierarchical structure in Figure 1, transportation and delivery, is just smoothed out. This stage involves analytical work to build the best delivery route from the point of production in Australia to warehouses in America, which requires cooperation with certain international transport companies. This cooperation can also be helpful in terms of delivery from warehouses to customers already in California.
Finally, the last stage of the project is responsible for direct sales, in other words, for the launch of Luus’ operations in the US market. This stage involves evaluating activities, checking the company’s financial performance, and taking into account all taxes, deductions, and production costs, up to the calculation of net profit. Sales must reach the $500,000 mark by a specific date, which will also be subject to an assessment of the project’s success. Otherwise, at this stage, the project will be evaluated, and the functional activities of the company abroad will be monitored. Further actions that will be taken within the framework of the results obtained will already be submitted to the local management as improvement tasks and will not be considered part of the project activity, which comes to its logical conclusion after this stage. The hierarchical structure of the WBS has three levels, on the third of which tasks were identified that could be delegated to an employee or the appropriate department for a solution.
Project Scheduling
Resource management and project scheduling are essential tools to demonstrate to some extent the adaptability and flexibility of project activities. The tasks listed above in the hierarchical structure in Figure 1 and milestones with specific dates imply stable completion on schedule. However, such projects do not always go smoothly, and due to the high costs at different stages, the company may find itself in conditions of limited resources (Larson, 2020). Because the focus is on building a reputation in a new market, Luus is sacrificing some of its time to profit and scale costs. The primary resources that the company has are people, equipment, and materials, which in this case are both materials for the production of equipment, and directly Luus products, which is also equipment.
This project has no strict time limits; all preliminary milestones are more indicative than defining success criteria. Only in the case of contracts, where the terms are already documented and supported by possible benefits, will the project receive a strict time frame. In this regard, obtaining permits for preliminary market analysis is not limited in time, and therefore the company can economically allocate the resources necessary for these tasks. At this stage, Luus can focus on the necessary internal improvements of the company, in particular related to e-commerce, which is used as a good lever for entering the international market in any business industry (Qi et al., 2020). Therefore, this project, among other things, can draw attention to the strengths and weaknesses of the company before selling products to the US market.
The project stages are highly dependent on each other: without permits, construction cannot begin; without construction, there is nowhere to transport products; without products, it is impossible to move on to sales. In this regard, this project will require many time and resources. However, as already mentioned above, much more costs or materials will be required at the initial stage and the involvement of human resources. In case of rejection and creation of a resource shortage condition, it is required to apply heuristic approaches. These approaches reduce project delay by postponing third-level tasks within one project stage where resources are scarce and moving on to other tasks that can be completed. This approach leads to the optimization of time frames and usefulness of resource use and is widely used in technology as well (Gawali and Shinde, 2018). At the same time, actions that have not begun are postponed and only within the framework of the project stage since, without permits, it is impossible to proceed to construction.
At the same time, the tasks of the third level in the WBS hierarchy can, for the most part, be executed in parallel. Figure 2, based on Table 1, shows that when sufficient resources are located, in other words, in a normal situation, in parallel, the department can analyze future financial activities, taking into account the specifics of taxation in California, other employees receive appropriate permissions, while in parallel based on the experience of these two departments, future employees in America will be informed about the specifics of the working conditions. In the same way, as in the case of transportation, heuristic methods will optimize the work of creating a route and concluding agreements with transport companies. Finally, only monitoring the company’s operations is necessary at the last stage, which does not imply work in conditions of a lack of resources. However, using heuristic methods for reducing the duration is possible in the future when planning or other Luus project activities. Figure 2 shows the project schedule under conditions of a possible shortage of resources. We will assume that four conditional units of resources are available weekly. ES is chosen precisely in which parallel actions of only the same stages defined in WBS are allowed. A reserve fund for specific actions is allocated in the amount of two weeks where the delay is not under the company’s control.
Table 1. Resource Allocation.
Risks and Reaction Planning
Several risks accompany any entry into the international market of the company. The first risk management stage involves risk identification (Larson, 2020). First of all, these are risks associated with economic factors: inflation, exchange rates, and much more. As an option to combat these risks, it is proposed to use various derivative instruments, including options and futures, but this is a topic for a separate work (Roncalli, 2020). A more realistic option is to create a reserve fund after the costs of the first investments in the project, such as the purchase of equipment and the construction of premises.
In addition to external factors and economic risks, political, social, technological, and environmental factors play a lesser role. First, the policies of a US country can influence the activities of multinational companies through the regulation of taxes (Clausing, 2020). Secondly, the competitiveness of a company that manufactures appliances directly depends on technological progress and the corresponding performance of competitors (Narayanan, 2020). Finally, the extent to which a company will comply with social and environmental responsibility requirements will determine its reputational image. The risks of external factors are manageable to varying degrees.
Social risks can be managed by demonstrating inclusiveness, diversity, and ethics in the approach to human resource management. Environmental responsibility implies the desire to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, waste-free production, and preserve the environment. One can focus on specific issues in California and allocate a portion of the budget to follow up on them. Supporting certain charitable foundations also reduces the company’s reputational risks.
Political factors are usually beyond the control of companies: organizations are forced to play by the rules of the country in which they trade. In this situation and in the case of economic risks, the company must keep a reserve fund to adapt to various external conditions. In favorable development of events, the reserve fund can be used for further expansion of the company within the United States or to other countries. On the other hand, the management of this type of risk largely depends on fulfilling the success criteria in the financial performance of Luus after entering the American market.
The second stage of risk management is risk assessment. After entering the California market, at the sales stage of the project, the stage of monitoring the company’s performance begins. This monitoring can be used for market analytics and assessing the potential risks listed above. This assessment will make it possible to translate the qualitative designation of risks into quantitative indicators of the reserve fund, possible losses due to tax increases, already depending on sales results. The project’s risk assessment is connected to a greater extent with economic reasons: a possible lack of demand and the instability of the manufacturer’s exchange rate. It also requires an approach with a reserve fund in the amount depending on the allowable minimum cash flow of the company.
Finally, the development of risk response prevents possible consequences or at least reduces them. From a reputational standpoint, a company can mitigate the impact of poor performance or production errors by operating in a socially or environmentally responsible manner. It includes client-oriented service, individual consideration of each case, and compensation for damage to clients. Cost risks include low sales and currency issues. In case of low sales, the company should better cooperate with domestic transport companies and look for customers outside the allocated region. The currency issue can be solved with the help of hedging or other derivative instruments.
Recommendations
Most of the identified recommendations aim to prevent specific risks or optimize project activities. First, it is recommended to conduct in parallel those tasks that are weakly dependent on each other within the same stage of the project. Thus, due to heuristics, the duration of the plan execution will be reduced. Second, creating a reserve fund and using hedging instruments can protect the company from the economic risks of low sales or volatile exchange rates. Otherwise, the adopted plan is entirely consistent with the intended milestones and goals, which, in the event of a favorable environment for interaction with uncontrollable external factors, will give the declared or even better result.
Project Progress and Performance Evaluation
The best quantitative assessment of the effectiveness of the project is specific financial indicators. First, the company’s sales should increase, although the debt may be increased at first. Secondly, a significant increase in sales is required to balance or even increase the gross profit ratio, which will initially be lowered as transportation costs and additional taxation increase. The project’s preliminary estimate likely set the number at $500,000 to return to previous net income figures, which fell due to expansion expenses. It is also worth noting at what pace the short and long-term assets of Luus will grow, increasing due to new buildings and equipment. Here, it is essential to keep the current ratio close to one to reduce the company’s liquidity and relevance.
Potential reasons for success lie in the reputational foundation and positioning of the company in the market, which can fill the desired niche with the right marketing advertising channel. In addition, if the company’s technological process is environmentally friendly, like the action of Luus products, then the company can also win many customers. The reasons for failure lie in low sales due to incorrect positioning of products in a new market or, as indicated above, in adverse political external factors that can increase the company’s taxation. In this situation, the best recommendation during the project would be to devote extra effort to studying US tax activity’s current environment, including plans and bills in this area. Strengthening the reasons for success can be achieved through the organization of R&D to create an ecological product line; due to customer-oriented service, which will distinguish the company from competitors in the market. Finally, such diversification could enable further development in the American market by meeting the current requirements for environmental responsibility already adopted at the federal level.
Reference List
Clausing, K. (2020) ‘Taxing multinational companies in the 21st Century’, Tackling the Tax Code: Efficient and Equitable Ways to Raise Revenue, pp. 237-283. Web.
Gawali, M. B., and Shinde, S. K. (2018) ‘Task scheduling and resource allocation in cloud computing using a heuristic approach’, Journal of Cloud Computing, 7(1), pp. 1-16. Web.
Larson, E. (2020). ISE eBook Online Access for Project Management: The Managerial Process. 8th eds. New York City, NY: McGraw-Hill Higher Education (International).
Narayanan, K. (2020) ‘Technology Acquisition and Competitiveness: Evidence from the Indian IT Industry’ in High-Tech industries, employment and global competitiveness (pp. 70-96). Delhi: Routledge India.
Qi, X., et al. (2020) ‘Motivations for selecting cross-border e-commerce as a foreign market entry mode’, Industrial Marketing Management, 89, pp. 50-60. Web.
Roncalli, T. (2020). Handbook of Financial Risk Management. London: Chapman and Hall/CRC.